Abstract
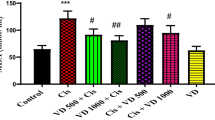
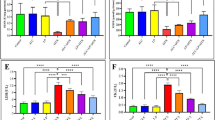
The objective of this study is to evaluate the possible protective effects of selenium (Se) against cyclophosphamide (CP)-induced acute cardiotoxicity in rats. A total of 42 male Spraque-Dawley rats were divided into six groups (n = 7). Rats in the first group were served as control. Rats in the second group received CP (150 mg/kg) at the sixth day of experiment. Animals in the third and fourth groups were treated with only 0.5 and 1 mg/kg Se respectively for six consecutive days. Rats in the fifth and sixth groups received respective Se doses (0.5 or 1 mg/kg) for 6 days and then a single dose of CP administered on the sixth day. On day 7, the animals were sacrificed; blood samples were collected to measure malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), and ischemia-modified albumin (IMA) levels. Heart tissues were processed routinely and tissue sections were stained with H + E for light microscopic examination. In the CP-treated rats MDA, LDH, CK-MB, and IMA serum levels increased, while GSH levels decreased. Microscopic evaluation showed that tissue damage was conspicuously lower in CP plus Se groups. Moreover, 1 mg/kg Se was more protective than 0.5 mg/kg Se as indicated by histopathological and biochemical values. In conclusion, Se is suggested to be a potential candidate to ameliorate CP-induced cardiotoxicity which may be related to its antioxidant activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drimal J, Zurova-Nedelcevova J, Knezl V, Sotnikova R, Navarova J (2006) Cardiovascular toxicity of the first line cancer chemotherapeutic agents: doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, streptozotocin and bevacizumab. Neuroendocrinol Lett 27(2):176–179
Song J, Liu L, Li L, Liu J, Song E, Song Y (2014) Protective effects of lipoic acid and mesna on cyclophosphamide induced haemorrhagic cystitis in mice. Cell Biochem Funct 32:125–132
Perini P, Calabrese M, Rinaldi L, Gallo P (2007) The safety profile of cyclophosphamide in multiple sclerosis therapy. Expert Opin Drug Saf 6:183–190
Ettaya A, Dhibi S, Samout N, Elfeki A, Hfaiedh N (2016) Hepatoprotective activity of white horehound (Marrubium vulgare) extract against cyclophosphamide toxicity in male rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94(4):441–447
De Jarnett N, Conklin DJ, Riggs DW et al (2014) Acrolein exposure is associated with increased cardiovascular disease risk. J Am Heart Assoc 6:3
Viswanatha SAH, Patel UM, Koti BC, Gadad PC, Patel NL, Thippeswamy AH (2013) Cardioprotective effect of saraca indica against cyclophosphamide induced cardiotoxicity in rats: a biochemical, electrocardiographic and histopathological study. Indian Journal of Pharmacology 45:1
Mythili Y, Sudharsan PT, Varalakshmi P (2005) dl-alpha-lipoic acid ameliorates cyclophosphamide induced cardiac mitochondrial injury. Toxicology 215:108–114
Nazıroglu M (2009) Role of selenium on calcium signaling and oxidative stress-induced molecular pathways in epilepsy. Neurochem Res 34(12):2181–2191
Gouaze V, Mirault ME, Carpenter S, Salvayre R, Levade T, Andrieu-Abadie N (2001) Glutathione peroxidase-1 over expression prevent ceramide production and partially inhibits apoptosis in doxorubicin treated human breast carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 60:488–496
Rodrigo-Moreno A, Andrés-Colas N, Poschenrieder C, Gunse B, Penarrubia L, Shabala S (2013) Calcium- and potassium-permeable plasma membrane transporters are activated by copper in Arabidopsis root tips: linking copper transport with cytosolic hydroxyl radical production. Plant Cell Environ 36(4):844–855
Benstoem C, Goetzenich A, Kraemer S et al (2015) Selenium and its supplementation in cardiovascular disease-what do we know? Nutrients 7:3094–3118
Oster O, Prellwitz W (1990) Selenium and cardiovascular disease. Biol Trace Elem Res 24(2):91–103
Gado AM, Adam ANI, Aldahmash BA (2013) Cardiotoxicity induced by cyclophosphamide in rats: protective effect of curcumin. Journal of Research in Environmental Science and Toxicology 2(4):87–95
Ayhanci A, Gunes S, Sahinturk V et al (2010) Seleno L-methionine acts on cyclophosphamide-induced kidney toxicity. Biol Trace Elem Res 136:171–179
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH (1990) Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzymol 186:407–421
Bar-Or D, Lau E, JV W (2000) A novel assay for cobalt-albumin binding and its potential as a marker for myocardial ischemia-a preliminary report. J Emerg Med 19:311–315
Xu X, Xuewu Z (2015) Effects of cyclophosphamide on immune system and gut microbiota in mice. Microbiol Res 171:97–106
Dhesi S, Chu MP, Blevins G et al (2013) Cyclophosphamide-induced cardiomyopathy: a case report, review, and recommendations for management. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep January–March 1–7
Alhumaidhaa KA, Salehb DO, Abd El Fattah MA, El-Erakyb WI, Moawada H (2015) Cardiorenal protective effect of taurine against cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in albino rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 18:1–9
Zver S, Zadnik V, Bunc M, Rogel P, Cernelc P, Kozeljc M (2007) Cardiac toxicity of high-dose cyclophosphamide in patients with multiple myeloma undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol 85(5):408–414
Gottdiener JS, Applebaum ER, Ferrans VJ, Deisseroth A, Ziegler J (1981) Cardiotoxicity associated with high-dose cyclophosphamide therapy. Arch Intern Med 141:75–63
Shrivastava M, Kar V, Shrivastava S (2011) Cyclophosphamide altered the myocardial marker enzymes: protection provoked by hesperidin in rats. J App Pharm 4(3):407–415
Christenson RH, Duh SH, Sanhai WR, AH W, Holtman V, Painter P (2001) Characteristics of an albumin cobalt binding test for assessment of acute coronary syndrome patients: a multicenter study. Clin Chem 47(3):464–470
Ertekin B, Kocak S, Dundar ZD et al (2013) Diagnostic value of ischemia-modified albumin in acute coronary syndrome and acute ischemic stroke. Pak J Med Sci 29(4):1003–1007
Thomas RA, Krishnakumari S (2015) Cardiac biomarkers: past, present and future. Int J cur Res Rev 7:21
Dawie J, Chawla R, Worku Y, Azazh A (2011) Diagnosis of ischemic heart disease using CK-MB, troponin-I and ischemia modified albumin. Ethiop Med J 49:25–33
Ma Y, Kang W, Bao Y, Jiao F, Ma Y (2013) Clinical significance of ıschemia-modified albumin in the diagnosis of doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in breast cancer patients. PLoS One 8(11):1–8
Sudharsan PT, Mythili Y, Selvakumar E, Varalakshmi P (2005) Cardioprotective effect of pentacyclic triterpene, lupeol and its ester on cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress. Human Exp Toxicol 24:313–318
Nagi MN, Al-Shabanah OA, Hafez MM, Sayed-Ahmed MM (2011) Thymoquinone supplementation attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. J Biochem mMolecular. J Biochem Molecular Toxicol 25(3):135–142
Tarek MK, Motawi NAH, Sadik AR (2010) Cytoprotective effects of dl-alpha-lipoic acid or squalene on cyclophosphamide induced oxidative injury: an experimental study on rat myocardium, testicles and urinary bladder. Food Chem Toxicol 48(8–9):2326–2336
Li W, Guo M, Liu Y et al (2016) Selenium induces an anti-tumor effect via inhibiting intratumoral angiogenesis in a mouse model of transplanted canine mammary tumor cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 171:371–379
Ostadalova I, Vobecky M, Chvojkova Z et al (2007) Selenium protects the immature rat heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem 300(1–2):259–267
Alissa EM, Bahijri SM, Ferns GA (2003) The controversy surrounding selenium and cardiovascular disease: a review of the evidence. Med Sci Monit 9:9–18
Miller TL, Neri D, Extein J, Somarriba G, Strickman-Stein N (2007) Nutrition in pediatric cardiomyopathy. Prog Pediatr Cardiol 24(1):59–71
Türker Y, Nazıroğlu M, Gümral N et al (2011) Selenium and L-carnitine reduce oxidative stress in the heart of rat induced by 2.45-GHz radiation from wireless devices. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:1640–1650
Toufektsian MC, Boucher F, Pucheu S (2000) Effect of selenium deficiency o the response of cardiac tissue to ischemia and reperfusion. Toxicol 148:125–132
Allan C, Lacourciere G, Stadtman T (1999) Responsiveness of seleno proteins to dietary selenium. Ann. Rev Nutr 19:1–16
Olayinka ET, Ore A, Ola OS, Adeyemo OA (2015) Ameliorative effect of gallic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative injury and hepatic dysfunction in rats. Med Sci 3:78–92
Asiri YA (2010) Probucol attenuates cyclophosphamide induced oxidative apoptosis, p53 and Bax signal expression in rat cardiac tissues. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 3(5):308–316
Mythili Y, Sudharsan PT, Selvakumar E, Varalakshmi P (2004) Protective effect of dl-lipoic acid on cyclophosphamide induced oxidative cardiac injury. Chem Biol Interact 151:13–19
Kumar S, Dhankhar N, Kar V, Shrivastava M, Shrivastava S (2011) Myocardial injury provoked by cyclophosphamide, protective aspect of hesperidin in rats. IJRPBS 2(3): 1288–1295
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by grants (P.N 2014-254) from the Eskisehir Osmangazi University Scientific Research Project, Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experiments were conducted in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals prepared by the National Academy of Sciences (1996) and approved by Eskisehir Osmangazi University Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (Protocol no 14.01.2014-254/2014).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunes, S., Sahinturk, V., Karasati, P. et al. Cardioprotective Effect of Selenium Against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 177, 107–114 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0858-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0858-1