Abstract
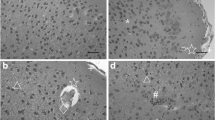
The aim of this study was to investigate microstructure and ultrastructure alterations in the pallium of immature mice exposed to cadmium. Forty immature mice were randomly divided into control, 1/100 LD50 (1.87 mg/kg, low), 1/50 LD50 (3.74 mg/kg, medium), and 1/25 LD50 (7.48 mg/kg, high) dose groups. After oral cadmium exposure for 40 days, the pallium of mice was obtained for microstructure and ultrastructure studies. The results showed that both microstructure and ultrastructure alterations of the pallium were observed in all treated mice and the most obvious alterations were in the high dose group. Microstructural analysis showed seriously congested capillary in the pia mater of the pallium in the high cadmium group. Meanwhile, vacuolar degenerate or karyopyknosis presented in some neurocytes, capillary quantity, and the number of apoptotic cells increased, some neurocytes became hypertrophy, the pia mater separated from the cortex, and local hemorrhage and accompanied inflammatory cell infiltration were also observed. Ultrastructural analysis showed that rough endoplasmic reticulum was expanded, heterochromatin marginalized, perinuclear space distinctly broadened, swelling and vacuolization mitochondria appeared, synapse was swelling, presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes presented fusion, and most of mitochondrial cristae were ambiguous. The results indicated that cadmium exposure for 40 days induced dose-dependent microstructure and ultrastructure alterations in pallium of immature mice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Järup L, Berglund M, Elinder CG, Nordberg G, Vahter M (1998) Health effects of cadmium exposure—a review of the literature and a risk estimate. Scand J Work Environ Health 24:1–51
Abdalla FH, Cardoso AM, Pereira LB, Schmatz R, Gonc alves JF, Stefanello N, Fiorenza AM, Gutierres JM, da Silva Serres JD, Zanini D, Pimentel VC, Vieira JM, Schetinger MRC, Morsch VM, Mazzanti CM (2013) Neuroprotective effect of quercetin in ectoenzymes and acetylcholinesterase activities in cerebral cortex synaptosomes of cadmium-exposed rats. Mol Cell Biochem 381:1–8. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1659-x
Du J, Cheng SY, Hou WX, Shi BM, Shan AS (2013) Effectiveness of maifanite in reducing the detrimental effects of cadmium on growth performance, cadmium residue, hematological parameters, serum biochemistry, and the activities of antioxidant enzymes in pigs. Biol Trace Elem Res 155:49–55. doi:10.1007/s12011-013-9769-6
Xu B, Chen S, Luo Y, Chen Z, Liu L, Zhou H, ChenW ST, Han X, Chen L, Huang S (2011) Calcium signaling is involved in cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis via induction of reactive oxygen species and activation of MAPK/mTOR network. PLoS One 6:e19052. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019052
Yuan Y, Jiang CY, Xu H, Sun Y, Hu FF, Bian JC, Liu XZ, Gu JH, Liu ZP (2013) Cadmium-induced apoptosis in primary rat cerebral cortical neurons culture is mediated by a calcium signaling pathway. PLoS One 8:e64330. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064330
López E, Figueroa S, Oset-Gasque MJ, González MP (2003) Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced by cadmium in cortical neurons in culture. Br J Pharmacol 138:901–911. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705111
Chen L, Liu L, Huang S (2008) Cadmium activates the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway via induction of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of protein phosphatases 2A and 5. Free Radic Biol Med 45:1035–1044. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.07.011
Wang B, Du YL (2013) Cadmium and its neurotoxic effects. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:898034. doi:10.1155/2013/898034
Carageorgiou H, Katramadou M (2012) Aspects of cadmium neurotoxicity. In: Li YV, Zhang JH (eds) Metal ion in stroke, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp. 703–749
Labudda M (2011) Biochemical mechanisms of neurotoxicity caused by cadmium. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig 62:357–363
Pal R, Nath R, Gill KD (1993) Influence of ethanol on cadmium accumulation and its impact on lipid peroxidation and membrane bound functional enzymes (Na+, K (+)-ATPase and acetylcholinesterase) in various regions of adult rat brain. Neurochem Int 23:451–458. doi:10.1016/0197-0186(93) 90129-s
Ohtani-Kaneko R, Tazawa H, Yokosuka M, Yoshida M, Satoh M, Watanabe C (2008) Suppressive effects of cadmium on neurons and affected proteins in cultured developing cortical cells. Toxicology 253:110–116. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2008.08.021
Rigon AP, Cordova FM, Oliveira CS, Posser T, Costa AP, Silva IG, Santos DA, Rossi FM, Rocha JB, Leal RB (2008) Neurotoxicity of cadmium on immature hippocampus and a neuroprotective role for p38 MAPK. Neurotoxicology 29:727–734. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2008.04.017
Rai A, Maurya SK, Khare P, Srivastava A, Bandyopadhyay S (2010) Characterization of developmental neurotoxicity of As, Cd and Pb mixture: synergistic action of metal mixture in glial and neuronal functions. Toxicol Sci 118:586–601. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfq266
Amara S, Douki T, Garrel C, Favier A, Ben Rhouma K, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H (2011) Effects of static magnetic field and cadmium on oxidative stress and DNA damage in rat cortex brain and hippocampus. Toxicol Ind Health 27:99–106. doi:10.1177/0748233710381887
Yang XF, Ge YM, Jiang JQ, Xu ZY, Cui YH, Wang ZL (2012) Acute toxic effect of cadmium chloride in mice. Chin J Vet Sci 32:467–471
Govil N, Chaudhary S, Waseem M, Parvez S (2012) Postnuclear supernatant: an in vitro model for assessing cadmium-induced neurotoxicity. Biol Trace Elem Res 146:402–409. doi:10.1007/s12011-011-9263-y
Nishimura Y, Yamaguchi JY, Kanada A, Horimoto K, Kanemaru K, Satoh M, Oyama Y (2006) Increase in intracellular Cd2+ concentration of rat cerebellar granule neurons incubated with cadmium chloride: cadmium cytotoxicity under external Ca2+-free condition. Toxicol in Vitro 20:211–216. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2005.06.006
Rose CS, Heywood PG, Costanzo RM (1992) Olfactory impairment after chronic occupational cadmium exposure. J Occup Med 34:600–605
Lukawski K, Nieradko B, Sieklucka-Dziuba M (2005) Effects of cadmium on memory processes in mice exposed to transient cerebral oligemia. Neurotoxicol Teratol 27:575–584. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2005.05.009
Leal RB, Rieger DK, Peres TV, Lopes MW, Gonçalves CAS (2012) Cadmium neurotoxicity and its role in brain disorders. In: Li YV, Zhang JH (eds) Metal ion in stroke, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp. 751–766
Choudhuria S, Liu WL, Berman NEJ, Klaassen CD (1996) Cadmium accumulation and metallothionein expression in brain of mice at different stages of development. Toxicol Lett 84:127–133. doi:10.1016/0378-4274(95)03444-7
Abib RT, Peres KC, Barbosa AM, Peres TV, Bernardes A, Zimmermann LM, Quincozes-Santos A, Fiedler HD, Leal RB, Farina M, Gottfried C (2011) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects rat brain mitochondria against cadmium-induced damage. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2618–2623. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.07.006
Wong KL, Klaassen CD (1982) Neurotoxic effects of cadmium in young rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 63:330–337. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(82)90261-7
Haider S, Anis L, Batool Z, Sajid I, Naqvi F, Khaliq S, Ahmed S (2015) Short term cadmium administration dose dependently elicits immediate biochemical, neurochemical and neurobehavioral dysfunction in male rats. Metab Brain Dis 30:83–92. doi:10.1007/s11011-014-9578-4
Yang XF, Fan GY, Liu DY, Zhang HT, Xu ZY, Ge YM, Wang ZL (2015) Effect of cadmium exposure on the histopathology of cerebral cortex in juvenile mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 165:167–172. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0246-2
Bar-Sela S, Reingold S, Richter ED (2001) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a battery-factory worker exposed to cadmium. Int J Occup Environ Health 7:109–112. doi:10.1179/107735201800339470
Shukla A, Shukla GS, Srimal RC (1996) Cadmium-induced alterations in blood-brain barrier permeability and its possible correlation with decreased microvessel antioxidant potential in rat. Hum Exp Toxicol 15:400–405. doi:10.1177/096032719601500507
Tobwala S, Wang HJ, Carey JW, Banks WA, Ercal N (2014) Effects of lead and cadmium on brain endothelial cell survival, monolayer permeability, and crucial oxidative stress markers in an in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier. Toxics 2:258–275. doi:10.3390/toxics2020258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the studies were conducted.
Funding
This study was supported by the Grant of Aid Project for Leading Young Teachers in Henan Provincial Institutions of Higher Education of China (Grant No.2010GGJS-136) and Science and Technology Research Important Project of Education Department Henan Province (Grant No.13A230142).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they no conflict of interest.
Additional information
X. F. Yang and Q. G. Han contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X.F., Han, Q.G., Liu, D.Y. et al. Microstructure and Ultrastructure Alterations in the Pallium of Immature Mice Exposed to Cadmium. Biol Trace Elem Res 174, 105–111 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0657-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0657-8