Abstract
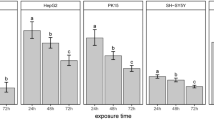
A high concentration of vanadium (V) has toxic effects on human and animals and is one of environmental pollutants. In the present study, we have conducted a fundamental study using cultured Vero cells from monkey kidney for the future environmental monitoring. Orthovanadate (VAN), one of V compounds, of 10−10 and 10−8 M did not affect the cell growth although the higher concentration of above 10−6 M VAN inhibited the cell growth accompanied with the decrease in cell numbers and morphological changes. Given that the washing method with ice-cold Li is also effective for determination of the cellular Na content, we used this method for the determination of the V content of the Vero cells. The V distributions in Vero cell; in the 10−3 M VAN solution, extracellular and intracellular were obtained as 1:0.564:0.036 and 1:0.662:0.098 at 60 and 120 min after the treatment of VAN. The intracellular V content was 10% of the applied concentration of VAN. Consequently, it was suggested that V concentration of 10−7 and 10−6 M in the tissue and environment, respectively, might become the threshold concentration; a criterion of the environmental contamination when we carry out environmental monitoring.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hopkins LL Jr, Tilton BE (1966) Metabolism of trace amounts of vanadium 48 in rat organs and liver subcellular particles. Am J Physiol 211:169–172
Hopkins LL Jr, Mohr HE (1974) Proceedings: vanadium as an essential nutrient. Fed Proc 33:1773–1775
Schwartz K, Mile DB (1971) Growth effects of vanadium in the rat. Sci 174:426–428
Nakai M, Watanabe H, Fujiwara C, Kakegawa H, Satoh T, Takada J, Matsushita R, Sakurai H (1995) Mechanism on insulin-like action of vanadyl sulfate: studies on interaction between rat adipocytes and vanadium compounds. Biol Pharm Bull 18:719–725
Sakurai H, Tsuchiya K, Nukatsuka M, Sofue M, Kawada J (1990) Insulin-like effect of vanadyl ion on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Endocrinol 126:451–459
Rehder D (2003) Biological and medicinal aspects of vanadium. I Inorg Chem Commun 6:604–617
Cantley LC, Josephson L, Warner R, Yanagisawa M, Lechene C, Guidotti G (1977) Vanadate is a potent (Na+ + K+)ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem 252:7421–7423
Cantley LC Jr, Cantley LG, Josephson L (1978) A characterization of vanadate interactions with the (Na+ + K+) ATPase. J Biochem 253:7361–7368
Cantley LC Jr, Resh MD, Guidotti G (1978) Vanadate inhibits the red cell (Na+ + K+) ATPase from the cytoplasmic side. Nature 272:552–554
DiPolo R, Rojas HR, Beauge L (1979) Vanadate inhibits uncoupled Ca efflux but not Na-Ca exchange in squid axons. Nature 281:229–230
Barrabin H, Grrahan PJ, Rega AF (1980) Vanadate inhibition of the Ca-ATPase from human red cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 600:796–804
Nayler RA, Sparrow MP (1983) Mechanism of vanadate-induced contraction of airway smooth muscle of the guinea-pit. Brit J Pharmacol 80:163–172
Ueda F, Kishimoto T, Ozaki H, Urakawa N (1982) Dual actions of vanadate on high K-induced contraction in guinea pig taenia coli. Jpn J Pharmacol 32:149–157
Ueda F, Kishimoto T, Ozaki H, Karaki H, Urakawa N (1984) Effects of vanadate on mechanical and electrical activities in guinea pig taenia coli. Nippon Heikatsukin Gakkai Zasshi 20:85–93
Ozaki H, Ueda F, Urakawa N (1982) Inhibitory effects of vanadate on the contractile responses in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 80:317–322
Ueda F, Karaki H, Urakawa N (1985) Contractile effects of vanadate on monkey and rabbit tracheal smooth muscle. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Thér 276:120–132
Ueda F, Urakawa N (1983) Influence of DIDS on the dual actions of vanadate on high K-induced contraction in the guinea pig taenia coli. Jpn J Pharmacol 33:894–896
Mochizuki M, Ueda F, Hondo R (1997) Relation between the high K induced tension and cellular vanadium contents in isolated tissues of guinea pig (in Japanese). The 124th Meeting of Japanese Society of Veterinary Science. Tokyo Press Co, Kagoshima, Japan
Mochizuki M, Ueda F, Sano T, Hondo R (2000) Relationship between vanadate induced relaxation and vanadium content in guinea pig taenia coli. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 78:339–342
NAS (1974) Medical and biologic effects of environmental pollutants, vanadium, National Academy of Sciences. National Research Council, Division of Chemistry and Chemical Technology, Environmental studies board, Washington. (translation in Japanese: Ono, T., Wada, K., Tokyo Kagaku Dojin)
Woodin MA, Liu Y, Neuberg D, Hauser R, Smith TJ, Christiani DC (2000) Acute respiratory symptoms in workers exposed to vanadium-rich fuel-oil ash. Am J Ind Med 37:353–363
Tosukhowong P, Tungsanga K, Eiam-Ong S, Sitprija V (1999) Environmental distal renal tubular acidosis in Thailand: an enigma. Am J Kidney Dis 33:1180–1186
Simonoff M, Conri C, Simonoff G (1986) Vanadium in depressive states. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 59:463–466
Kammerer M, Mastain O, Le Dréan-Quenech'du S, Pouliquen H, Larhantec M (2004) Liver and kidney concentrations of vanadium in oiled seabirds after the Erika wreck. Sci Total Environ 333:295–301
Mochizuki M, Ueda F, Hondo R (1998) Vanadium contents in organs of wild birds. J Trace Elem Exp Med 11:431
Mochizuki M, Ueda F, Sasaki S, Hondo R (1999) Vanadium contamination and the relation between vanadium and other elements in wild birds. Environ Pollut 106:249–251
Mackey EA, Becker PR, Demiralp R, Greenberg RR, Koster BJ, Wise SA (1996) Bioaccumulation of vanadium and other trace metals in livers of Alaskan cetaceans and pinnipeds. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 30:503–512
Mochizuki M, Mori M, Hondo R, Ueda F (2008) A new index for evaluation of cadmium pollution in birds and mammals. Environ Monit Assess 137:35–49
Mochizuki M, Mori M, Hondo R, Ueda F (2009) Biological monitoring using a new technique. In: Harris JD, Brown PL (eds) Wildlife: destruction, conservation and biodiversity. Nova Science Publishers, NY, pp 293–300
Mochizuki M, Mori M, Hondo R, Ueda F (2010) A cadmium standard regression line: a possible new index for biological monitoring. In: El Ahmed N (ed) Impact, monitoring and management of environmental pollution. Nova Science Publishers, NY, in printing
Mochizuki M, Mori M, Hondo R, Ueda F (2010) The biological monitoring of wild birds, Part2: the possibility of a new index for biological monitoring. In: Daniels JA (ed) Advances in environmental research, volume 4. Nova Science Publishers, NY, in printing
Ueda F, Mochizuki M, Mori M, Hondo R (2009) A new technique for biological monitoring. In Mastorakis N, Helmis C, Papageorgios C, Bulucea CA, Panagopoulos T (ed) Energy, environment, ecosystems, development and landscape architecture, energy and environmental engineering series. WSEAS press, pp 176–184
Mochizuki M, Mori M, Hondo R, Ueda F (2009) A new index for heavy metals in biological monitoring. In Mastorakis N, Helmis C, Papageorgios C, Bulucea CA, Panagopoulos T (ed) Energy, environment, ecosystems, development and landscape architecture, energy and environmental engineering series, WSEAS press, pp 185–191
Friedman SM (1974) Lithium substitution and the distribution of sodium in the rat tail artery. Circ Res 34:168–175
Kishimoto T, Ozaki H, Urakawa N (1980) A quantitative relationship between cellular Na accumulation and relaxation produced by ouabain in the depolarized smooth muscle of guinea pig taenia coli. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 312:199–207
Mochizuki M, Hondo R, Ueda F (2002) Simultaneous analysis for multiple heavy metals in contaminated biological samples. Biol Trace Elem Res 87:211–223
Acknowledgment
This study was funded by grant No. 13660328 in 2001-2003 and grant No. 20580344-0001 (2008) from the Japanese Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mochizuki, M., Kudo, E., Kikuchi, M. et al. A Basic Study on the Biological Monitoring for Vanadium—Effects of Vanadium on Vero Cells and the Evaluation of Intracellular Vanadium Contents. Biol Trace Elem Res 142, 117–126 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8741-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8741-y