Abstract
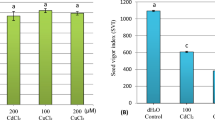
The influence of copper excess on germination rate, growth, minerals, carbohydrates, and amino acids supply in embryonic axis of bean seed was investigated. Compared to the control, Cu treatment caused a reduction in germination percent, embryo length, and accumulation of Ca, Fe, K, Mn, Zn, total soluble sugars, glucose, fructose, sucrose, and amino acids. Moreover, the nutrient concentrations, as well as the electrical conductivity were determined in the germination medium to quantify the extent of solute leakage. Such nutrients were lost in the imbibition medium at the expense of suitable mobilization to the growing embryonic axis. This was associated with an enhancement in accumulation of malondialdehyde, major product of lipoperoxidation process which can be due to the stimulation in lipoxygenase activity in Cu-poisoned tissues.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woolhouse HW (1983) Toxicity and tolerance in the responses of plants to metals. In: Lange OL, Nobel PS, Osmond CB, Ziegler H (eds) Encyclopaedia of plant physiology, 12C. Springer, Berlin, pp 245–300
Van Assche F, Clijsters H (1990) Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ 13:195–206
Fernande JC, Henriques FS (1991) Biochemical, physiological and structural effects of excess copper in plants. Bot Rev 57:246–273
Gaetke LM, Chow CK (2003) Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology 189:147–163
Mazhoudi S, Chaoui A, Ghorbal MH, El Ferjani E (1997) Response of antioxidant enzymes to excess copper in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum, Mill.). Plant Sci 127:129–137
Gupta M, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H (1999) Copper affect the enzymes of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and its related metabolites in the root of Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Plant 106:262–267
Lambardii L, Sebastiani L (2005) Copper toxicity in Prunus cerasifera: growth and antioxidant enzyme responses of in vitro grown plant. Plant Sci 168:797–802
Xiong ZT, Liu C, Geng B (2006) Phytotoxic effects of copper on nitrogen metabolism and plant growth in Brassica pekinensis Rupr. Ecotox Environ Saf 64:273–280
Ernst WHO (1998) Effects of heavy metals in plants at the cellular and organismic level ecotoxicology. In: Gerrit S, Bernd M (eds) III. Bioaccumulation and biological effects of chemicals, Wiley and Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, pp 587–620
Carlson CL, Adriano DC, Sajwan KS, Abels SL, Thoma DP, Driver JT (1991) Effects of selected trace metals on germinating seeds of six plant species. Water Air Soil Pollut 59:231–240
Mihoub A, Chaoui A, El Ferjani E (2005) Biochemical changes associated with cadmium and copper stress in germinating pea seeds (Pisum sativum L.). C R Biol 328:33–41
Ahsan N, Lee SH, Lee DG, Lee H, Lee SW, Bahk JD, Lee BH (2007) Physiological and protein profiles alternation of germinating rice seedlings exposed to acute cadmium toxicity. C R Biol 330:735–746
Rahoui S, Chaoui A, El Ferjani E (2008) Differential sensitivity to cadmium in germinating seeds of three cultivars of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Acta Physiol Plant 30:451–456
Smiri M, Chaoui A, El Ferjani E (2009) Respiratory metabolism in the embryonic axis of germinating pea seed exposed to cadmium. J Plant Physiol 166:259–269
Bewley DJ (1997) Seed germination and dormancy. Plant Cell 9:1055–1066
Murray DR, Peoples MB, Waters SP (1979) Proteolysis in the axis of the germinating pea seed. I. Changes in protein degrading enzyme activities of the radicle and primary root. Planta 147:111–116
Moore S, Stein WH (1954) A modified ninhydrin reagent for the photometric determination of aminoacids and related compounds. J Biol Chem 211:907–913
McCready RM, Guggolz J, Silviera V, Owens HS (1950) Determination of starch and amylose in vegetables. Application to pea. Anal Chem 22:1156–1158
Dishe Z, Borenfreund E (1951) A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J Biol Chem 192:583–587
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem and Biophy 125:189–198
Surrey K (1964) Spectrohotometric method for determination of lipoxygenase activity. Plant Physiol 39:65–69
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Pretorius JC, Small JGC (1993) The effect of soaking injury in bean seeds on carbohydrate levels and sucrose phosphate synthase activity during germination. Plant Physiol Biochem 31:25–34
Powell WW, Raymond BT (1981) Soaking injury and its reversal with polyethylene glycol in relation to respiratory metabolism in high and low vigour soybean seeds. Physiol Plant 53:263–268
Perry DA, Harrison JG (1970) The deleterious effect of water and low temperature on germination of pea seed. J Exp Bot 67:504–512
Mocquot B, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H, Mench M (1996) Copper toxicity in young maize (Zea mays L.) plants: effects on growth, mineral and chlorophyll contents, and enzyme activities. Plant Soil 128:287–300
Chaoui A, Ghorbal MH, El Ferjani E (1997) Effects of cadmium-zinc interactions on hydroponically grown bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Sci 126:21–28
Yoshihara T, Hodoshima H, Miyano Y, Shoji K, Shimada H, Goto F (2006) Cadmium inducible Fe deficiency responses observed from macro and molecular views in tobacco plants. Plant Cell Rep 25:365–373
Mishra P, Dubey RS (2008) Effect of aluminium on metabolism of starch and sugars in growing rice seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 30(3):265–275
Monerri C, Garcia-Luis A, Guardiola JL (1986) Sugar and starch changes in pea cotyledons during germination. Physiol Plant 67:49–54
Weckx J, Clijsters H (1996) Oxidative damage and defence mechanisms in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris as a result of root assimilation of toxic amounts of copper. Physiol Plant 96:506–512
Chaoui A, El Ferjani E (2005) Effects of cadmium and copper on antioxidant capacities, lignification and auxin degradation in leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedling. C R Biol 328:23–31
Agrawal SB, Mishra S (2009) Effects of supplemental ultraviolet-B and cadmium on growth, antioxidants and yield of Pisum sativum L. Ecotox Environ Saf 72:610–618
Posmyk MM, Kontek R, Janas KM (2009) Antioxidants enzymes activity and phenolic compounds content in red cabbage seedlings exposed to copper stress. Ecotox Environ Saf 72:596–602
Gora L, Clijsters H (1989) Effects of copper and zinc on the ethylene metabolism in Phaseolus vulgaris L. In: Clijsters H, De Proft M, Marclle R, Van Poucke M (eds) Biochemical and physiological aspects of ethylene production n lower and higher plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 219–228
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was received from the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research, and Technology (99/UR/09-18). The authors wish to thank Dr. Othman Bousandal for help regarding atomic absorption spectrophotometric analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sfaxi-Bousbih, A., Chaoui, A. & El Ferjani, E. Unsuitable Availability of Nutrients in Germinating Bean Embryos Exposed to Copper Excess. Biol Trace Elem Res 135, 295–303 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8505-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8505-8