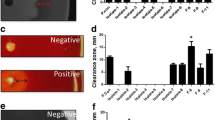
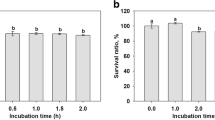
Abstract
The aims of the study were to degrade the anti-nutritional factors (ANFs) such as phytic acid, glycinin, and β-conglycinin and improve the values of soybean meal (SBM). Firstly, in this study, a strain PY-4B which exhibited the best enzymatic activities of protease (403.3 ± 17.8 U/mL) and phytase (62.9 ± 2.9 U/mL) was isolated and screened among the isolates. Based on the analysis of physiological and biochemical characteristics and 16S rDNA sequence, the strain PY-4B was identified and named as Pseudomonas PY-4B. Next, Pseudomonas PY-4B was applied to fermentation of SBM. The results showed that the contents of glycinin and β-conglycinin were decreased by 57–63%, and the phytic acid was remarkably degraded by 62.5% due to the fermentation of SBM by Pseudomonas PY-4B. The degradation of glycinin and β-conglycinin resulted in increase of contents of water-soluble proteins and amino acids in fermented SBM. Moreover, Pseudomonas PY-4B exhibited no hemolytic activity and slight inhibitory effect on the growth of pathogen Staphylococcus aureus and the wide range of pH tolerance (3 to 9). In summary, our study indicates that isolated strain Pseudomonas PY-4B is a safe and applicable strain and has the ability to effectively degrade the ANFs (phytic acid, glycinin, and β-conglycinin) in SBM by fermentation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Amino acids
- ANFs:
-
Anti-nutritional factors
- FSBM:
-
Fermented soybean meal
- PSM:
-
Phytase screening media
- SBM:
-
Soybean meal
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- SMKP:
-
Skimmed milk powder solid medium
- TMB:
-
3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine
- VP:
-
Voges-Proskauer
References
Wang, J., Mai, K., & Ai, Q. (2022). Conventional soybean meal as fishmeal alternative in diets of Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus): Effects of functional additives on growth, immunity, antioxidant capacity and disease resistance. Antioxidants (Basel), 11(5), 951.
Nguyen, H. P., Do, T. V., & Tran, H. D. (2020). Dietary replacement of fish meal by defatted and fermented soybean meals with taurine supplementation for pompano fish: Effects on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and biological parameters in a long-term feeding period. Journal of Animal Science, 98(12), skaa367.
Saz, J. M., & Marina, M. L. (2007). High performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis in the analysis of soybean proteins and peptides in foodstuffs. Journal of Separation Science, 30(4), 431–451.
Gupta, Y. P. (1987). Anti-nutritional and toxic factors in food legumes: A review. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 37(3), 201–228.
Punjabi, M., Bharadvaja, N., Jolly, M., Dahuja, A., & Sachdev, A. (2018). Development and evaluation of low phytic acid soybean by siRNA triggered seed specific silencing of inositol polyphosphate 6-/3-/5-kinase gene. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 804.
Haefner, S., Knietsch, A., Scholten, E., Braun, J., Lohscheidt, M., & Zelder, O. (2005). Biotechnological production and applications of phytases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 68(5), 588–597.
Torres, J., Domínguez, S., Cerdá, M. F., Obal, G., Mederos, A., Irvine, R. F., Díaz, A., & Kremer, C. (2005). Solution behaviour of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in the presence of multivalent cations. Prediction of a neutral pentamagnesium species under cytosolic/nuclear conditions. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 99(3), 828–840.
Singh, A., Meena, M., Kumar, D., Dubey, A. K., & Hassan, M. I. (2015). Structural and functional analysis of various globulin proteins from soy seed. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 55(11), 1491–1502.
Véron, V., Panserat, S., Le Boucher, R., Labbé, L., Quillet, E., Dupont-Nivet, M., & Médale, F. (2016). Long-term feeding a plant-based diet devoid of marine ingredients strongly affects certain key metabolic enzymes in the rainbow trout liver. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 42(2), 771–785.
Singh, A. K., Rehal, J., Kaur, A., & Jyot, G. (2015). Enhancement of attributes of cereals by germination and fermentation: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 55(11), 1575–1589.
Yao, Y., Li, H., Li, J., Zhu, B., & Gao, T. (2021). Anaerobic solid-state fermentation of soybean meal with Bacillus sp. to improve nutritional quality. Frontiers in Nutrition, 8, 706977.
Feng, Y., Wang, L., Khan, A., Zhao, R., Wei, S., & Jing, X. (2020). Fermented wheat bran by xylanase-producing Bacillus cereus boosts the intestinal microflora of broiler chickens. Poultry Science, 99(1), 263–271.
Shi, C., Zhang, Y., Lu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2017). Solid-state fermentation of corn-soybean meal mixed feed with Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium for degrading antinutritional factors and enhancing nutritional value. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 8, 50.
Soumeh, E. A., Mohebodini, H., Toghyani, M., Shabani, A., Ashayerizadeh, A., & Jazi, V. (2019). Synergistic effects of fermented soybean meal and mannan-oligosaccharide on growth performance, digestive functions, and hepatic gene expression in broiler chickens. Poultry Science, 98(12), 6797–6807.
Olukomaiya, O., Fernando, C., Mereddy, R., Li, X., & Sultanbawa, Y. (2019). Solid-state fermented plant protein sources in the diets of broiler chickens: A review. Animal Nutrition, 5(4), 319–330.
Li, Y., Guo, B., Li, C., Wang, W., Wu, Z., Liu, G., & Cai, H. (2020). Isolation of a highly efficient antigenic-protein-degrading Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and assessment of its safety. Animals, 10(7), 1144.
Chen, L., Vadlani, P. V., & Madl, R. L. (2014). High-efficiency removal of phytic acid in soy meal using two-stage temperature-induced Aspergillus oryzae solid-state fermentation. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 94(1), 113–118.
Nualkul, M., Yuangsoi, B., Hongoh, Y., Yamada, A., & Deevong, P. (2022). Improving the nutritional value and bioactivity of soybean meal in solid-state fermentation using Bacillus strains newly isolated from the gut of the termite Termes propinquus. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 369(1), fnac044.
Gao, S., Pan, L., Zhang, M., Huang, F., Zhang, M., & He, Z. (2020). Screening of bacterial strains from the gut of pacific white shrimp (litopenaeus vannamei) and their efficiencies in improving the fermentation of soybean meal. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 367(2), fnaa017.
Rosado, Azevedo, D., Cruz, D., Elsas, V., & Seldin. (1998). Phenotypic and genetic diversity of paenibacillus azotofixans strains isolated from the rhizoplane or rhizosphere soil of different grasses. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 84(2), 216–226.
Wang, R., Dong, P., Zhu, Y., Yan, M., & Guo, H. (2020). Bacterial community dynamics reveal its key bacterium, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ZB, involved in soybean meal fermentation for efficient water-soluble protein production. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 135, 110068.
Hernandez-Patlan, D., Solis-Cruz, B., Latorre, J. D., Merino-Guzman, R., Morales Rodríguez, M., Ausland, C., Hernandez-Velasco, X., Ortiz Holguin, O., Delgado, R., Hargis, B. M., Singh, P., & Tellez-Isaias, G. (2022). Whole-genome sequence and interaction analysis in the production of six enzymes from the three Bacillus strains present in a commercial direct-fed microbial (Norum™) using a bliss independence test. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 9, 784387.
Zhao, G., Hou, L., & Lu, M. (2012). Construction of the mutant strain in Aspergillus oryzae 3.042 for abundant proteinase production by the N+ ion implantation mutagenesis. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 47(3), 504–510.
Neveling, D. P., Ahire, J. J., Laubscher, W., Rautenbach, M., & Dicks, L. M. T. (2020). Genetic and phenotypic characteristics of a multi-strain probiotic for broilers. Current Microbiology, 77(3), 369–387.
Wang, M. Q., Wang, Z., Yu, L. N., Zhang, C. S., Bi, J., & Sun, J. (2019). Pseudomonas qingdaonensis sp. nov., an aflatoxin-degrading bacterium, isolated from peanut rhizospheric soil. Archives of Microbiology, 201(5), 673–678.
Nübling, S., Schmidt, H., & Weiss, A. (2016). Variation of the Pseudomonas community structure on oak leaf lettuce during storage detected by culture-dependent and-independent methods. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 216, 95–103.
Frühbeck, G., Alonso, R., Marzo, F., & Santidrián, S. (1995). A modified method for the indirect quantitative analysis of phytate in foodstuffs. Analytical Biochemistry, 225(2), 206–212.
Wu, S., Zhao, M., Gao, S., Xu, Y., Zhao, X., Liu, M., & Liu, X. (2021). Change regularity of taste and the performance of endogenous proteases in shrimp (Penaens vannamei) head during autolysis. Foods, 10(5), 1020.
Mothana, A. A., Al-Shamahy, H. A., Mothana, R. A., Khaled, J. M., Al-Rehaily, A. J., Al-Mahdi, A. Y., & Lindequist, U. (2022). Streptomyces sp. 1S1 isolated from southern coast of the red sea as a renewable natural resource of several bioactive compounds. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 30(2), 162–171.
Zhang, W., Lai, S., Zhou, Z., Yang, J., Liu, H., Zhong, Z., Fu, H., Ren, Z., Shen, L., Cao, S., Deng, L., & Peng, G. (2022). Screening and evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic potential from local Holstein raw milk. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 918774.
Saadi, S., Saari, N., Ghazali, H. M., & Abdulkarim, M. S. (2022). Mitigation of antinutritional factors and protease inhibitors of defatted winged bean-seed proteins using thermal and hydrothermal treatments: Denaturation/unfolding coupled hydrolysis mechanism. Current Research in Food Science, 5, 207–221.
Lu, F., Alenyorege, E., Ouyang, N., Zhou, A., & Ma, H. (2022). Simulated natural and high temperature solid-state fermentation of soybean meal: A comparative study regarding microorganisms, functional properties and structural characteristics. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 159, 113125.
Garrido-Galand, S., Asensio-Grau, A., Calvo-Lerma, J., Heredia, A., & Andrés, A. (2021). The potential of fermentation on nutritional and technological improvement of cereal and legume flours: A review. Food Research International, 145, 110398.
Liu, L., Chen, X., Hao, L., Zhang, G., Jin, Z., Li, C., Yang, Y., Rao, J., & Chen, B. (2022). Traditional fermented soybean products: Processing, flavor formation, nutritional and biological activities. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 62(7), 1971–1989.
Dai, C., Hou, Y., Xu, H., Huang, L., Dabbour, M., Mintah, B. K., He, R., & Ma, H. (2022). Effect of solid-state fermentation by three different Bacillus species on composition and protein structure of soybean meal. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 102(2), 557–566.
Liu, Z., Guan, X., Zhong, X., Zhou, X., & Yang, F. (2021). Bacillus velezensis DP-2 isolated from Douchi and its application in soybean meal fermentation. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 101(5), 1861–1868.
Mei, C., Chretien, R. L., Amaradasa, B. S., He, Y., Turner, A., & Lowman, S. (2021). Characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacterial endophytes and plant growth promotion in vitro and in greenhouse. Microorganisms, 9(9), 1935.
Adhikari, P., Jain, R., Sharma, A., & Pandey, A. (2021). Plant growth promotion at low temperature by phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas spp. isolated from high-altitude himalayan soil. Microbial Ecology, 82(3), 677–687.
Nam, S. J., Kim, Y. O., Ko, T. K., Kang, J. K., Chun, K. H., Auh, J. H., Lee, C. S., Lee, I. K., Park, S., & Oh, B. C. (2014). Molecular and biochemical characteristics of β-propeller phytase from marine Pseudomonas sp. BS10–3 and its potential application for animal feed additives. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 24(10), 1413–1420.
Zambare, V., Nilegaonkar, S., & Kanekar, P. (2011). A novel extracellular protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa MCM B-327: Enzyme production and its partial characterization. New Biotechnology, 28(2), 173–181.
Zheng, L., Li, D., Li, Z. L., Kang, L. N., Jiang, Y. Y., Liu, X. Y., Chi, Y. P., Li, Y. Q., & Wang, J. H. (2017). Effects of Bacillus fermentation on the protein microstructure and anti-nutritional factors of soybean meal. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 65(6), 520–526.
Xie, F., Feng, F., Liu, D., Quan, S., Liu, L., Zhang, X., & Chen, G. (2022). Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 35 M can exclusively produce and secrete proteases when cultured in soybean-meal-based medium. Colloids and Surfaces B, Biointerfaces, 209(Pt 2), 112188.
Hou, X., Shen, Z., Li, N., Kong, X., Sheng, K., Wang, J., & Wang, Y. (2020). A novel fungal beta-propeller phytase from nematophagous Arthrobotrys oligospora: Characterization and potential application in phosphorus and mineral release for feed processing. Microbial Cell Factories, 19(1), 84.
Funding
This work was supported by Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (2021C04016) and Pioneer and Leading Goose R&D Program of Zhejiang (2022C04020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Y.L. conducted experiments. H.Y.L. and Z.M. wrote the original draft. T.H. and J.T.W. designed the experiments. Z.M. revised this article. X.Y.Y. polished English and checked the final version. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, H., Han, T., Wang, J. et al. Screening and Identification of a Strain with Protease and Phytase Activities and Its Application in Soybean Meal Fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 790–803 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04568-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04568-w