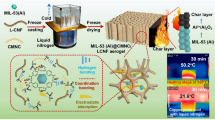
Abstract
Lignocellulosic nanofibrils (LCNF) aerogels have a three-dimensional structure, with large specific surface area, low density, which is promising to be developed into a new type of adsorbent with high absorption capacity. However, LCNF aerogels have the problem of simultaneous oil and water adsorption. This high hydrophilicity directly leads to low adsorption efficiency in oil-water systems. This paper suggests a facile and economical method for the synthesis of biocompatible CE-LCNF aerogels using LCNF and Castor oil triglycidyl ether (CE) was successfully established. The use of LCNF enabled aerogels to possess remarkably uniform pore size and structural integrity, while the introduction of hydrophobic silica produced stable superhydrophobicity for more than 50 days at room temperature. These aerogels presented desirable hydrophobicity (131.6°), excellent oil adsorption capacity (62.5 g/g) and excellent selective sorption property, making them ideal absorbents for oil spill cleaning. The effects of ratios of LCNF to CE composition, temperatures and oil viscosity on the oil adsorption performance of aerogels were estimated. The results displayed that the aerogels had the maximum adsorption capacity at 25 °C. The pseudo-secondary model had higher validity in oil adsorption kinetic theories compared to the pseudo-first-order model. The CE-LCNF aerogels were excellent super-absorbents for oil removal. Moreover, the LCNF was renewable and nontoxic, which has the potential to promote environmental applications.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, J. H., Kim, D. H., Han, S. W., Kim, B. R., Park, E. J., Jeong, M.-G., Kim, J. H., & Kim, Y. D. (2016). Fabrication of superhydrophobic fibre and its application to selective oil spill removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 289, 1–6.
Chen, J., Zhang, W., Wan, Z., Li, S., & Fei, Y. (2019). Oil spills from global tankers: Status review and future governance. Journal of Cleaner Production, 227, 20–32.
Zhang, B., Matchinski, E. J., Chen, B., Ye, X., Jing, L., & Lee, K. (2019). Marine oil spills—Oil pollution, sources and effects. World seas: An environmental evaluation. Academic Press., 3, 391–406.
Nzila, A., & Musa, M. M. (2021). Current knowledge and future challenges on bacterial degradation of the highly complex petroleum products asphaltenes and resins. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 9, 779644.
Korhonen, J. T., Kettunen, M., Ras, R. H., & Ikkala, O. (2011). Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 3, 1813–1816.
Varjani, S. J. (2017). Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresource Technology, 223, 277–286.
Deng, Y.-F., Zhang, D., Zhang, N., Huang, T., Lei, Y.-Z., & Wang, Y. (2021). Electrospun stereocomplex polylactide porous fibers toward highly efficient oil/water separation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 407, 124787.
Angelova, D., Uzunov, I., Uzunova, S., Gigova, A., & Minchev, L. (2011). Kinetics of oil and oil products adsorption by carbonized rice husks. Chemical Engineering Journal, 172, 306–311.
Wang, L., Liu, C., Huang, Q., An, Y., Fan, J., & Liu, Y. (2019). A polyamide 6–organic montmorillonite composite sponge by large-scale solution foaming as a reusable and efficient oil and organic pollutant sorbent. Soft Matter, 15, 9066–9075.
Wen, Q., Di, J., Jiang, L., Yu, J., & Xu, R. (2013). Zeolite-coated mesh film for efficient oil–water separation. Chemical Science, 4, 591–595.
Gao, R., Xiao, S., Gan, W., Liu, Q., Amer, H., Rosenau, T., Li, J., & Lu, Y. (2018). Mussel adhesive-inspired design of superhydrophobic nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels for oil/water separation. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6, 9047–9055.
Bian, H., Dong, M., Chen, L., Zhou, X., Wang, R., Jiao, L., Ji, X., & Dai, H. (2020). On-demand regulation of lignocellulosic nanofibrils based on rapid fractionation using acid hydrotrope: Kinetic study and characterization. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8, 9569–9577.
Chen, S., Chen, Y., Li, D., Xu, Y., & Xu, F. (2021). Flexible and sensitivity-adjustable pressure sensors based on carbonized bacterial nanocellulose/wood-derived cellulose nanofibril composite aerogels. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13(7), 8754–8763.
Zhang, H., Zhang, G., Zhu, H., Wang, F., Xu, G., Shen, H., & Wang, J. (2021b). Multiscale kapok/cellulose aerogels for oil adsorption: The study on structure and oil adsorption properties. Industrial Crops and Products, 171, 113902.
Li, Z., Shao, L., Hu, W., Zheng, T., Lu, L., Cao, Y., & Chen, Y. (2018). Excellent reusable chitosan/cellulose aerogel as an oil and organic solvent absorbent. Carbohydrate Polymers, 191, 183–190.
Tarrés, Q., Oliver-Ortega, H., Llop, M., Pèlach, M., Delgado-Aguilar, M., & Mutjé, P. (2016). Effective and simple methodology to produce nanocellulose-based aerogels for selective oil removal. Cellulose., 23, 3077–3088.
Wang, L., Li, K., Copenhaver, K., Mackay, S., Lamm, M. E., Zhao, X., Dixon, B., Wang, J., Han, Y., Neivandt, D., Johnson, D. A., Walker, C. C., Ozcan, S., & Gardner, D. J. (2021). Review on nonconventional fibrillation methods of producing cellulose nanofibrils and their applications. Biomacromolecules., 22, 4037–4059.
Mondal, S. (2017). Preparation, properties and applications of nanocellulosic materials. Carbohydrate Polymers, 163, 301–316.
Bian, H., Duan, S., Wu, J., Fu, Y., Yang, W., Yao, S., Zhang, Z., Xiao, H., Dai, H., & Hu, C. (2022). Lignocellulosic nanofibril aerogel via gas phase coagulation and diisocyanate modification for solvent absorption. Carbohydrate Polymers, 15(278), 119011.
Zou, X., Yao, L., Zhou, S., Chen, G., Wang, S., Liu, X., & Jiang, Y. (2022). Sulfated lignocellulose nanofibril based composite aerogel towards adsorption-photocatalytic removal of tetracycline. Carbohydrate Polymers, 296, 119970.
Fu, Q., Tan, J., Han, C., Zhang, X., Fu, B., Wang, F., & Zhu, X. (2020). Synthesis and curing properties of castor oil-based triglycidyl ether epoxy resin. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 31, 2552–2560.
Luo, J., Huang, K., Zhou, X., & Xu, Y. (2020). Preparation of highly flexible and sustainable lignin-rich nanocellulose film containing xylonic acid (XA), and its application as an antibacterial agent. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 163, 1565–1571.
Bian, H., Chen, L., Gleisner, R., Dai, H., & Zhu, J. (2017). Producing wood-based nanomaterials by rapid fractionation of wood at 80 °C using a recyclable acid hydrotrope. Green Chemistry, 19(14), 3370–3379.
Gupta, P., Singh, B., Agrawal, A. K., & Maji, P. K. (2018). Low density and high strength nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel for thermal insulation application. Materials and Design, 158, 224–236.
Feng, J., Le, D., Nguyen, S. T., Nien, V. T. C., Jewell, D., & Duong, H. M. (2016). Silica cellulose hybrid aerogels for thermal and acoustic insulation applications, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp, 506, 298–305.
Zhang, H., Wang, J., Xu, G., Xu, Y., Wang, F., & Shen, H. (2021). Ultralight, hydrophobic, sustainable, cost-effective and floating kapok/microfibrillated cellulose aerogels as speedy and recyclable oil superabsorbents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 406, 124758.
Gong, X., Wang, Y., Zeng, H., Betti, M., & Chen, L. (2019). Highly porous, hydrophobic, and compressible cellulose nanocrystals/pva aerogels as recyclable absorbents for oil-water separation. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 7, 11118–11128.
Peng, D., Zhao, J., Liang, X., Guo, X., & Li, H. (2023). Corn stalk pith-based hydrophobic aerogel for efficient oil sorption. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 448, 130954.
Thai, Q. B., Nguyen, S. T., Ho, D. K., Tran, T. D., Huynh, D. M., Do, N. H. N., Luu, T. P., Le, P. K., Le, D. K., Phan-Thien, N., & Duong, H. M. (2020). Cellulose-based aerogels from sugarcane bagasse for oil spill-cleaning and heat insulation applications. Carbohydrate Polymers, 228, 115365.
Adebajo, M. O., Frost, R. L., Kloprogge, J. T., Carmody, O., & Kokot, S. (2003). Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: A review of synthesis and absorbing properties. Journal of Porous Materials, 10, 159–170.
Wahi, R., Chuah, L. A., Choong, T. S. Y., Ngaini, Z., & Nourouzi, M. M. (2013). Oil removal from aqueous state by natural fibrous sorbent: An overview. Separation and Purification Technology, 113, 51–63.
Nguyen, S. T., Feng, J., Le, N. T., Le, A. T., Hoang, N., Tan, V. B., & Duong, H. M. (2013). Cellulose aerogel from paper waste for crude oil spill cleaning. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 52, 18386–18391.
Nguyen, S. T., Feng, J., Ng, S. K., Wong, J. P., Tan, V. B., & Duong, H. M. (2014). Advanced thermal insulation and adsorption properties of recycled cellulose aerogels. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 445, 128–134.
Feng, J., Nguyen, S. T., Fan, Z., & Duong, H. M. (2015). Advanced fabrication and oil adsorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. Chemical Engineering Journal, 270, 168–175.
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This work is supported by the Nanjing Tech University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bujun Huang: conceptualization, methodology, validation, data curation, visualization, writing—review and editing, writing—original draft.
Juncheng Jiang: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, project administration.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, B., Jiang, J. Construction of Super-Hydrophobic Lignocellulosic Nanofibrils Aerogels as Speedy Oil Absorbents. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 220–232 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04560-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04560-4