Abstract
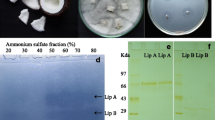
Pleurotus ostreatus is an edible white-rot fungus with lignocellulosic biomass degrading enzymes that have been studied extensively. However, until now, lipolytic enzymes from P. ostreatus, which degrade extractives in lignocellulosic biomass, have not been purified and characterized. In this study, P. ostreatus was inoculated into the rapeseed oil containing culture to induce lipase. The lipase in the culture broth was successfully purified to homogeneity by chromatographic methods. The molecular weight of the purified lipase was 27 kDa, and its optimal pH and temperature were 5.0 and 30 °C, respectively. The purified lipase showed high activity with the substrates 4-methylumbelliferyl (4-MU) decanoate (C10:0) and 4-MU oleate (C18:1), and no activity with 4-MU acetate (C2:0) and 4-MU butyrate (C4:0). The amino acid sequences and substrate specificities of the purified lipase suggested that it belonged to class III. Kinetic parameters measurements (Km and Vmax) showed that 4-MU palmitate had a high affinity for the purified lipase, and it was the substrate most efficiently hydrolyzed by the purified lipase.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ghosh, P. K., Saxena, R. K., Gupta, R., Yadav, R. P., & Davidson, S. (1996). Microbial lipases: Production and applications. Science Progress, 79(Pt 2), 119–157.
Macrae, A., & Hammond, R. (1985). Present and future applications of lipases. Biotechnology and genetic engineering reviews, 3, 193–218.
Jaeger, K. E., Dijkstra, B. W., & Reetz, M. T. (1999). Bacterial biocatalysts: Molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases. Annual Review of Microbiology, 53, 315–351.
Saxena, R. K., Sheoran, A., Giri, B., & Davidson, W. S. (2003). Purification strategies for microbial lipases. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 52, 1–18.
Singh, A. K., & Mukhopadhyay, M. (2012). Overview of fungal lipase: A review. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 166, 486–520.
Ramnath, L., Sithole, B., & Govinden, R. (2017). Classification of lipolytic enzymes and their biotechnological applications in the pulping industry. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 63, 179–192.
Okal, E. J., Aslam, M. M., Karanja, J. K., & Nyimbo, W. J. (2020). Mini review: Advances in understanding regulation of cellulase enzyme in white-rot basidiomycetes. Microbial Pathogenesis, 147, 104410.
Li, X., & Zheng, Y. (2020). Biotransformation of lignin: Mechanisms, applications and future work. Biotechnology Progress, 36, e2922.
Sjostrom, E. (1993). In Wood Chemistry (Second Edition), (Sjostrom, E., ed.), Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 51–108.
Gutiérrez, A., del Río, J. C., Martínez, M. J., & Martínez, A. T. (1999). Fungal degradation of lipophilic extractives in Eucalyptus globulus wood. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 1367–1371.
Gutierrez, A., del Rio, J. C., & Martinez, A. T. (2009). Microbial and enzymatic control of pitch in the pulp and paper industry. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 1005–1018.
Cohen, R., Persky, L., & Hadar, Y. (2002). Biotechnological applications and potential of wood-degrading mushrooms of the genus Pleurotus. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 58, 582–594.
Tellez-Tellez, M., & Diaz-Godinez, G. (2019). Omic tools to study enzyme production from fungi in the Pleurotus genus. BioResources, 14, 2420–2457.
Skocaj, M., Gregori, A., Grundner, M., Sepcic, K., & Sezun, M. (2018). Hydrolytic and oxidative enzyme production through cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus on pulp and paper industry wastes. Holzforschung, 72, 813–817.
Piscitelli, A., Tarallo, V., Guarino, L., Sannia, G., Birolo, L., & Pezzella, C. (2017). New lipases by mining of Pleurotus ostreatus genome. PLoS ONE, 12, 15.
Antošová, Z., & Sychrová, H. (2016). Yeast hosts for the production of recombinant laccases: A review. Molecular Biotechnology, 58, 93–116.
Strinska, H. N., Petrov, D. N., Panajotova, H. N., Dobreva, V. T., Zhekova, B. J., & Dobrev, G. T. (2017). Isolation and purification of lipase from Rhizopus arrhizus by ultrafiltration and fractional precipitation. Bulgarian Chemical Communications, 49, 137–143.
Riley, R., Salamov, A. A., Brown, D. W., Nagy, L. G., Floudas, D., Held, B. W., Levasseur, A., Lombard, V., Morin, E., Otillar, R., Lindquist, E. A., Sun, H., LaButti, K. M., Schmutz, J., Jabbour, D., Luo, H., Baker, S. E., Pisabarro, A. G., Walton, J. D., … Grigoriev, I. V. (2014). Extensive sampling of basidiomycete genomes demonstrates inadequacy of the white-rot/brown-rot paradigm for wood decay fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111, 9923–9928.
Castanera, R., López-Varas, L., Borgognone, A., LaButti, K., Lapidus, A., Schmutz, J., Grimwood, J., Pérez, G., Pisabarro, A. G., Grigoriev, I. V., Stajich, J. E., & Ramírez, L. (2016). Transposable elements versus the fungal genome: Impact on whole-genome architecture and transcriptional profiles. PLoS Genetics, 12, e1006108
Alfaro, M., Castanera, R., Lavín, J. L., Grigoriev, I. V., Oguiza, J. A., Ramírez, L., & Pisabarro, A. G. (2016). Comparative and transcriptional analysis of the predicted secretome in the lignocellulose-degrading basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Environmental Microbiology, 18, 4710–4726.
Verkasalo, E., Roitto, M., Möttönen, V., Tanner, J., Kumar, A., Kilpeläinen, P., Sikanen, L., & Ilvesniemi, H. (2022). Extractives of tree biomass of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) for biorefining in four climatic regions in Finland-lipophilic compounds, stilbenes, and lignans. Forests, 13, 779.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, S.N.; methodology, S.N., H.M, N.M.; validation, S.N., H.M, N.M.; investigation, S.N., H.M, N.M.; resources, S.N.; data curation, S.N., H.M, N.M.; writing-original draft preparation, S.N., H.M, N.M.; writing-review and editing, S.N.; visualization, S.N., H.M, N.M.; supervision, S.N.; project administration, S.N.; funding acquisition, S.N.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nakagame, S., Minagawa, H. & Motegi, N. Purification and Characterization of Class III Lipase from a White-Rot Fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 1085–1095 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04211-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04211-0