Abstract
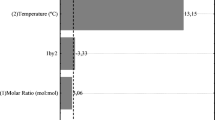
In this research, eugenyl acetate, a compound with flavoring, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties, was obtained from essential oil of clove (Syzygium aromaticum) via liquid lipase-mediated acetylation. Clove essential oil was extracted by drag water vapor from dry flower buds and its physic-chemical characteristics were analyzed. For the enzymatic synthesis, an extensive evaluation of reaction parameters was accomplished through employment of distinct reaction temperatures, acetic anhydride to eugenol molar ratios, enzyme loads, and three different lipases (a lyophilized enzyme produced by solid-state fermentation of sunflower seed with Penicillium sumatrense microorganism and other two commercial lipases — Lipozyme TL 100L and CALB L). The product eugenyl acetate was confirmed by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR Distortionless Enhancement by Polarization Transfer (DEPT 135), and Heteronuclear Multiple Bond Correlation (HMBC). Through optimized conditions (55 °C, acetic anhydride to eugenol molar ratio of 1:1, 10 wt% of Lipozyme TL 100L), 91.80% of conversion after 2 h was achieved to the eugenyl acetate production. With the results obtained, it was possible to conclude that the use of lipases in liquid formulation is a promising alternative for the synthesis of essential esters largely applied on food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
dos Santos, P., Zabot, G. L., Meireles, M. A. A., Mazutti, M. A., & Martínez, J. (2016). Synthesis of eugenyl acetate by enzymatic reactions in supercritical carbon dioxide. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 114, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2016.06.018.
da Silva Corrêa, L., Henriques, R. O., Rios, J. V., Lerin, L. A., de Oliveira, D., & Furigo, A. (2020). Lipase-catalyzed esterification of geraniol and citronellol for the synthesis of terpenic esters. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 190(2), 574–583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03102-1.
Musthafa, K. S., Hmoteh, J., Thamjarungwong, B., & Voravuthikunchai, S. P. (2016). Antifungal potential of eugenyl acetate against clinical isolates of Candida species. Microbial Pathogenesis, 99, 19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.07.012.
Silva, M. J. A., Loss, R. A., Laroque, D. A., Lerin, L. A., Pereira, G. N., Thon, É., Oliveira, J. V., Ninow, J. L., Hense, H., & Oliveira, D. (2015). Lipozyme TL IM as catalyst for the synthesis of eugenyl acetate in solvent-free acetylation. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 176(3), 782–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1611-5.
Machado, J. R., Pereira, G. N., dos Santos de Oliveira, P., Zenevicz, M. C., Lerin, L., & dos Reis Barreto de Oliveira, R., … de Oliveira, D. (2017). Synthesis of eugenyl acetate by immobilized lipase in a packed bed reactor and evaluation of its larvicidal activity. Process Biochemistry, 58, 114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.04.031.
Kaur, B., & Chakraborty, D. (2013). Biotechnological and molecular approaches for vanillin production: A review. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 169(4), 1353–1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-0066-1.
Zhao, L., Jiang, Y., Fang, H., Zhang, H., Cheng, S., Rajoka, M. S. R., & Wu, Y. (2019). Biotransformation of isoeugenol into vanillin using immobilized recombinant cells containing isoeugenol monooxygenase active aggregates. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 189(2), 448–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-02996-1.
Dev, M., Ghosh, M., Bhattacharyya, D., & Kumar. (2021). Physico-chemical, antimicrobial, and organoleptic properties of roasted aromatic spice (Clove Bud) in baked product. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 193(6), 1813–1835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03504-0.
Kadarohman, A., Hernani, Rohman, I., Kusrini, R., & Astuti, R. M. (2012). Combustion characteristics of diesel fuel on one cylinder diesel engine using clove oil, eugenol, and eugenyl acetate as fuel bio-additives. Fuel, 98, 73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.03.037.
Cortés-Rojas, D. F., Souza, C. R. F., & Oliveira, W. P. (2014). Encapsulation of eugenol rich clove extract in solid lipid carriers. Journal of Food Engineering, 127, 34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.11.027.
Pandey, S. K., Tandon, S., Ahmad, A., Singh, A. K., & Tripathi, A. K. (2013). Structure-activity relationships of monoterpenes and acetyl derivatives against Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. Pest Management Science, 69(11), 1235–1238. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3488.
Cansian, R. L., Vanin, A. B., Orlando, T., Piazza, S. P., Puton, B. M. S., Cardoso, R. I., Gonçalves, I. L., Honaiser, T. C., Paroul, N., & Oliveira, D. (2017). Toxicity of clove essential oil and its ester eugenyl acetate against Artemia salina. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 77(1), 155–161. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.12215.
Musthafa, K. S., & Voravuthikunchai, S. P. (2016). Eugenyl acetate inhibits growth and virulence factors of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 31(6), 448–454. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.3336.
Carrasco, A. H., Espinoza, C. L., Cardile, V., Gallardo, C., Cardona, W., Lombardo, L., et al. (2008). Eugenol and its synthetic analogues inhibit cell growth of human cancer cells (Part I). Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 19(3), 543–548. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532008000300024.
Mhetras, N., Mapare, V., & Gokhale, D. (2021). Cold active lipases: Biocatalytic tools for greener technology. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 193(7), 2245–2266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03516-w.
Wancura, J. H. C., Tres, M. V., Jahn, S. L., & Oliveira, J. V. (2020). Lipases in liquid formulation for biodiesel production: Current status and challenges. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 67(4), 648–667. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1835.
Rosset, D. V., Wancura, J. H. C., Ugalde, G. A., Oliveira, J. V., Tres, M. V., Kuhn, R. C., & Jahn, S. L. (2019). Enzyme-catalyzed production of FAME by hydroesterification of soybean oil using the novel soluble lipase NS 40116. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 188(4), 914–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-02966-7.
Wancura, J. H. C., Fantinel, A. L., Ugalde, G. A., Donato, F. F., Vladimir de Oliveira, J., Tres, M. V., & Jahn, S. L. (2021). Semi-continuous production of biodiesel on pilot scale via enzymatic hydroesterification of waste material: Process and economics considerations. Journal of Cleaner Production, 285(124838), 124838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124838.
Shuai, W., Das, R. K., Naghdi, M., Brar, S. K., & Verma, M. (2017). A review on the important aspects of lipase immobilization on nanomaterials. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 64(4), 496–508. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1515.
Vanin, A. B., Orlando, T., Piazza, S. P., Puton, B. M. S., Cansian, R. L., Oliveira, D., & Paroul, N. (2014). Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of clove essential oil and eugenyl acetate produced by enzymatic esterification. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 174(4), 1286–1298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1113-x.
Tischer, J. S., Possan, H., Luiz, J., Malagutti, N. B., Martello, R., Valério, A., Dalmagro, J., de Oliveira, D., & Oliveira, J. V. (2019). Synthesis of eugenyl acetate through heterogeneous catalysis. Journal of Essential Oil Research, 31(4), 312–318. https://doi.org/10.1080/10412905.2019.1566098.
Laroque, D. A., Maria, J. A., Silva, R. A. L., & Pereira, G. N. (2015). Synthesis of eugenyl acetate in solvent-free acetylation: Process optimization and kinetic evaluation. Journal of Chemical Engineering & Process Technology, 6(4), 10000247. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7048.1000247.
Remonatto, D., Santin, C. M. T., de Oliveira, D., Di Luccio, M., & de Oliveira, J. V. (2016). FAME production from waste oils through commercial soluble lipase Eversa® catalysis. Industrial Biotechnology, 12(4), 254–262. https://doi.org/10.1089/ind.2016.0002.
Cesarini, S., Diaz, P., & Nielsen, P. M. (2013). Exploring a new, soluble lipase for FAMEs production in water-containing systems using crude soybean oil as a feedstock. Process Biochemistry, 48(3), 484–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.02.001.
Stringari, D. (2009), PhD Thesis, Federal University of Paraná. Curitiba, BR.
United States Pharmacopeial Convention. (2018). The United States Pharmacopeia: USP 41 - National formulary NF 36. Available from: https://www.worldcat.org/title/united-states-pharmacopeia-2018-usp-41-the-national-formulary-nf-36/oclc/1013752699. Accessed 20 Feb 2021.
Radünz, M., da Trindade, M. L. M., Camargo, T. M., Radünz, A. L., Borges, C. D., Gandra, E. A., & Helbig, E. (2019). Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of unencapsulated and encapsulated clove (Syzygium aromaticum, L.) essential oil. Food Chemistry, 276, 180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.173.
Chiaradia, V., Paroul, N., Cansian, R. L., Júnior, C. V., Detofol, M. R., Lerin, L. A., Oliveira, J. V., & Oliveira, D. (2012). Synthesis of eugenol esters by lipase-catalyzed reaction in solvent-free system. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 168(4), 742–751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9814-5.
Engel, R. G. et al. (2015) Introduction to spectroscopy, 5th ed., Cengage Learning, São Paulo, Brazil.
Santos, A. L., Chierice, G. O., Alexander, K. S., Riga, A., & Matthews, E. (2009). Characterization of the raw essential oil eugenol extracted from Syzygium aromaticum L. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 96(3), 821–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0030-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Leandro Santolin: Investigation; Writing (original draft preparation)
Karina G. Fiametti: Conceptualization; Investigation; Supervision
Viviane da Silva Lobo: Data Curation; Resources
João H. C. Wancura: Writing (review and editing), Validation
J. Vladimir Oliveira: Validation; Resources
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent to Participate
All authors agree mutually with the participation and publication of this work and declare that this is an original research.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santolin, L., Fiametti, K.G., da Silva Lobo, V. et al. Enzymatic Synthesis of Eugenyl Acetate from Essential Oil of Clove Using Lipases in Liquid Formulation as Biocatalyst. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 193, 3512–3527 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03610-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03610-z