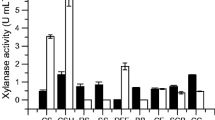
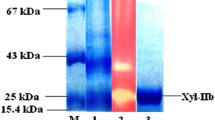
Abstract
A xylanase gene, aws-2x, was directly cloned from the genomic DNA of the alkaline wastewater sludge using degenerated PCR and modified TAIL-PCR. The deduced amino acid sequence of AWS-2x shared the highest identity (60%) with the xylanase from Chryseobacterium gleum belonging to the glycosyl hydrolase GH family 10. Recombinant AWS-2x was expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) and purified to electrophoretic homogeneity. The enzyme showed maximal activity at pH 7.5 and 55 °C, maintained more than 50% of maximal activity when assayed at pH 9.0, and was stable over a wide pH range from 4.0 to 11.0. The specific activity of AWS-2x towards hardwood xylan (beechwood and birchwood xylan) was significantly higher than that to cereal xylan (oat spelt xylan and wheat arabinoxylan). These properties make AWS-2x a potential candidate for application in the pulp and paper industry.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vardakou, M., Flint, J., Christakopoulos, P., Lewis, R. J., Gilbert, H. J., & Murray, J. W. (2005). Journal of Molecular Biology, 352, 1060–1067.
Collins, T., Gerday, C., & Feller, G. (2005). FEMS Microbiology Review, 29, 3–23.
Biely, P. (1985). Trends in Biotechnology, 3, 286–290.
Beg, Q. K., Kapoor, M., Mahajan, L., & Hoondal, G. S. (2001). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56, 326–338.
Subramaniyan, S., & Prema, P. (2002). Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 22, 33–64.
Suurnäkki, A., Tenkanen, M., Buchert, J., & Viikari, L. (1998). Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 57, 261–287.
Gessesse, A. (1998). Applied and Environment Microbiology, 64, 3533–3535.
Lorenz, P., & Schleper, C. (2002). Journal of Molecular Catalysis. B, Enzymatic, 19–20, 13–19.
Sunna, A., & Bergquist, P. (2003). Extremophiles, 7, 63–70.
Hayashi, H., Abe, T., Sakamoto, M., Ohara, H., Ikemura, T., Sakka, K., et al. (2005). Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 51, 251–259.
Brady, S. F. (2007). Nature Protocols, 2, 1297–1305.
Wang, G., Wang, Y., Yang, P., Luo, H., Huang, H., Shi, P., et al. (2010). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 87, 1383–1393.
Huang, H., Wang, G., Zhao, Y., Shi, P., Luo, H., & Yao, B. (2010). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 87, 1141–1149.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Li, N., Meng, K., Wang, Y., Shi, P., Luo, H., Bai, Y., et al. (2008). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 80, 231–240.
Luo, H., Li, J., Yang, J., Wang, H., Yang, Y., Huang, H., et al. (2009). Extremophiles, 13, 849–854.
Gessesse, A., & Gashe, B. A. (1997). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 83, 402–406.
Ratanakhanokchai, K., Kyu, K. L., & Tanticharoen, M. (1999). Applied and Environment Microbiology, 65, 694–697.
Bruce, R. A., Achenbach, L. A., & Coates, J. D. (1999). Environmental Microbiology, 1, 319–329.
Amann, R., Ludwig, W., & Schleifer, K. (1995). Microbiological Reviews, 59, 143–169.
Cottrell, M., Moore, J., & Kirchman, D. (1999). Applied and Environment Microbiology, 65, 2553–2557.
Polizeli, M. L., Rizzatti, A. C., Monti, R., Terenzi, H. F., Jorge, J. A., & Amorim, D. S. (2005). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67, 577–591.
Kampfer, P., Dreyer, U., Neef, A., Dott, W., & Busse, H. J. (2003). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53, 93–97.
Zhou, J., Huang, H., Meng, K., Shi, P., Wang, Y., Luo, H., et al. (2009). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 85, 323–333.
Zhang, G. M., Huang, J., Huang, G. R., Ma, L. X., & Zhang, X. E. (2007). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 74, 339–346.
Yin, L. J., Lin, H. H., Chiang, Y. I., & Jiang, S. T. (2010). Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 58, 557–562.
Pollet, A., Delcour, J. A., & Courtin, C. M. (2010). Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 30, 176–191.
Pell, G., Taylor, E. J., Gloster, T. M., Turkenburg, J. P., Fontes, C. M., Ferreira, L. M., et al. (2004). The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 9597–9605.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Earmarked Fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (NYCYTX-42-G2-05) and the Key Program of Transgenic Plant Breeding (2009ZX08019-002) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Conversion Funds (2009GB23260444).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Luo, H., Meng, K. et al. A Xylanase Gene Directly Cloned from the Genomic DNA of Alkaline Wastewater Sludge Showing Application Potential in the Paper Industry. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165, 35–46 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9231-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9231-1