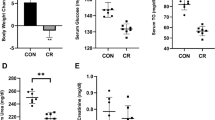
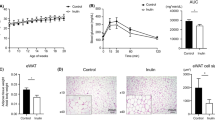
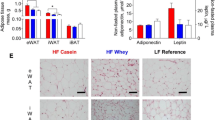
Abstract
With the change of people’s dietary structures, obesity, diabetes, and other related chronic metabolic diseases characterized by energy metabolism disorders have become a public health problem worldwide. Stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM) as a novel technology to explore energy metabolism will certainly contribute to the development of functional foods to improve energy metabolism disorders. The purpose of this review is to elaborate on the technology processes of SIRM in the research of functional foods with improved energy metabolism disorders, and to promote the applications of this technology in functional food. The research strategies for functional foods for improving energy metabolism disorders were summarized. The progress of the application of SIRM on functional foods was elaborated and policy recommendations were also provided. In conclusion, the precise property of SIRM in revealing metabolic pathways will inevitably facilitate the development of functional foods in improving energy metabolism disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used for the research described in the article.
References
Ahmed, H. A., Ticar, B. F., Black, I., Mahdi, F., Shami, A. A., Misra, S. K., Heiss, C., Paris, J. J., Sharp, J. S., Azadi, P., & Pomin, V. H. (2023). Structural characterization and biological activity of an α-glucan from the mollusk Marcia hiantina (Lamarck, 1818). Glycoconjugate Journal, 40(1), 33–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-022-10092-6
Bai, Y. H., Shi, D. X., Lu, H. Y., Yang, K. B., Zhao, H. H., Lu, B. N., & Pang, Z. R. (2021). Hypoglycemic effects of Tibetan medicine Huidouba in STZ-induced diabetic mice and db/db mice. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 13(2), 202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chmed.2021.02.001
Baumel-Alterzon, S., Katz, L. S., Brill, G., Garcia-Ocaña, A., & Scott, D. K. (2021). Nrf2: The master and captain of beta cell fate. Trends in Endocrinology Metabolism, 32(1), 7–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2020.11.002
Borges, C. V., Amorim, V. B., Ramlov, F., Ledo, C. A., Donato, M., Maraschin, M., & Amorim, E. P. (2014). Characterisation of metabolic profile of banana genotypes, aiming at biofortified Musa spp. cultivars. Food Chemistry, 145, 496–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.041
Bourgin, M., Kepp, O., & Kroemer, G. (2022). Immunostimulatory effects of vitamin B5 improve anticancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology, 11, 2031500. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2022.2031500
Brandsma, J., Bailey, A. P., Koster, G., Gould, A. P., & Postle, A. D. (2017). Stable isotope analysis of dynamic lipidomics. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Molecular Cell Biology of Lipids, 1862, 792–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.03.002
Brekke, E. M., Walls, A. B., Schousboe, A., Waagepetersen, H. S., & Sonnewald, U. (2012). Quantitative importance of the pentose phosphate pathway determined by incorporation of 13C from [2-13C]- and [3-13C]-glucose into TCA cycle intermediates and neurotransmitter amino acids in functionally intact neurons. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 32, 1788–1799. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.85
Brendel, M., Probst, F., Jaworska, A., Overhoff, F., Korzhova, V., Albert, N. L., Beck, R., Lindner, S., Gildehaus, F. J., Baumann, K., Bartenstein, P., Kleinberger, G., Haass, C., Herms, J., & Rominger, A. (2016). Glial activation and glucose metabolism in a transgenic amyloid mouse model: A triple-tracer PET study. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 57(6), 954–960. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.115.167858
Brodsky, A. N., Odenwelder, D. C., & Harcum, S. W. (2019). High extracellular lactate causes reductive carboxylation in breast tissue cell lines grown under normoxic conditions. PLoS One, 14, e0213419. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213419
Bruntz, R. C., Lane, A. N., Higashi, R. M., & Fan, T. W. (2017). Exploring cancer metabolism using stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 292, 11601–11609. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R117.776054
Bujak, R., Struck-Lewicka, W., Markuszewski, M. J., & Kaliszan, R. (2015). Metabolomics for laboratory diagnostics. Journal of Pharmceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 113, 108–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.12.017
Burca-Busaga, C. G., Betoret, N., Seguí, L., Betoret, E., & Barrera, C. (2020). Survival of Lactobacillus salivarius CECT 4063 and stability of antioxidant compounds in dried apple snacks as affected by the water activity, the addition of trehalose and high pressure homogenization. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081095
Cai, M., Zhang, J., Chen, H., & Pan, Y. X. (2022). A maternal low-protein diet during gestation induces hepatic autophagy-related gene expression in a sex-specific manner in Sprague-Dawley rats. British Journal of Nutrition, 128(4), 592–603. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521003639
Candow, D. G., Forbes, S. C., Kirk, B., & Duque, G. (2021). Current evidence and possible future applications of creatine supplementation for older adults. Nutrients, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030745
Cave, J. R., & Waterhouse, A. L. (2019). Combinatorics of proanthocyanidins in wine. Analyst, 144(14), 4395–4399. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an00439d
Celli, G. B., Ghanem, A., & Brooks, M.S.-L. (2015). Bioactive encapsulated powders for functional foods—A review of methods and current limitations. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 1825–1837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1559-z
Chambers, E. S., Byrne, C. S., Rugyendo, A., Morrison, D. J., Preston, T., Tedford, C., Bell, J. D., Thomas, L., Akbar, A. N., Riddell, N. E., Sharma, R., Thursz, M. R., Manousou, P., & Frost, G. (2019). The effects of dietary supplementation with inulin and inulin-propionate ester on hepatic steatosis in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 21(2), 372–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13500
Chandel, N. S. (2021). Amino acid metabolism. Cold Spring Harbor Perspective in Biology, 13(4). https://doi.org/10.5582/bst.2021.01061
Chen, Y., Cheng, L., Lian, R., Song, Z., & Tian, J. (2021). COVID-19 vaccine research focusses on safety, efficacy, immunoinformatics, and vaccine production and delivery: A bibliometric analysis based on VOSviewer. Bioscience Trends, 15(2), 64–73. https://doi.org/10.5582/bst.2021.01061
Cheng, T., Sudderth, J., Yang, C., Mullen, A. R., Jin, E. S., Matés, J. M., & DeBerardinis, R. J. (2011). Pyruvate carboxylase is required for glutamine-independent growth of tumor cells. the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science USA, 108, 8674–8679. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1016627108
Cheng, S., Fu, X., Wang, X., Liao, Y., Zeng, L., Dong, F., & Yang, Z. (2017). Studies on the biochemical formation pathway of the amino acid l-theanine in tea (Camellia sinensis) and other plants. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65, 7210–7216. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02437
Cheung, P. K., Ma, M. H., Tse, H. F., Yeung, K. F., Tsang, H. F., Chu, M. K. M., Kan, C. M., Cho, W. C. S., Ng, L. B. W., Chan, L. W. C., & Wong, S. C. C. (2019). The applications of metabolomics in the molecular diagnostics of cancer. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics, 19, 785–793. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737159.2019.1656530
Crown, S. B., Ahn, W. S., & Antoniewicz, M. R. (2012). Rational design of 13C-labeling experiments for metabolic flux analysis in mammalian cells. BMC Systematic Biology, 6, 43. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-6-43
Cruickshank-Quinn, C., Zheng, L. K., Quinn, K., Bowler, R., Reisdorph, R., & Reisdorph, N. (2018). Impact of blood collection tubes and sample handling time on serum and plasma metabolome and lipidome. Metabolites, 8(4), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040088
Dang, F., Jiang, Y., Pan, R., Zhou, Y., Wu, S., Wang, R., Zhuang, K., Zhang, W., Li, T., & Man, C. (2018). Administration of Lactobacillus paracasei ameliorates type 2 diabetes in mice. Food and Function, 9, 3630–3639. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo00081f
Das, P. R., Darwish, A. G., Ismail, A., Haikal, A. M., Gaijar, P., Balasubramani, S. P., Sheikh, M. B., Tsolova, V., Soliman, K. F. A., Sherif, S. M., & El-Sharkawy, I. (2022). Diversity in blueberry genotypes and developmental stages enables discrepancy in the bioactive compounds, metabolites, and cytotoxicity. Food Chemistry, 374, 131632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131632
de Toro-Martín, J., Arsenault, B. J., Després, J. P., & Vohl, M. C. (2017). Precision nutrition: A review of personalized nutritional approaches for the prevention and management of metabolic syndrome. Nutrients, 9(8), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080913a
Devi, S., Varkey, A., Sheshshayee, M. S., Preston, T., & Kurpad, A. V. (2018). Measurement of protein digestibility in humans by a dual-tracer method. American Journal of Clinical Nutrients, 107, 984–991. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqy062
Domingo-Almenara, X., & Siuzdak, G. (2020). Metabolomics data processing using XCMS. Methods of Molecular Biology, 2104, 11–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0239-3_2
Du, X., Smirnov, A., Pluskal, T., Jia, W., & Sumner, S. (2020). Metabolomics data preprocessing using ADAP and MZmine 2. Methods of Molecular Biology, 2104, 25–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0239-3_3
Dutta, D., Nayak, A., & Dutta, D. (2023). Reconnoitring the usage of agroindustrial waste in carotenoid production for food fortification: A sustainable approach to tackle vitamin A deficiency. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 16, 467–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02888-z
Emwas, A. H. (2015). The strengths and weaknesses of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry with particular focus on metabolomics research. Methods of Molecular Biology, 1277, 161–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2377-9_13
Fan, T. W., Warmoes, M. O., Sun, Q., Song, H., Turchan-Cholewo, J., Martin, J. T., Mahan, A., Higashi, R. M., & Lane, A. N. (2016). Distinctly perturbed metabolic networks underlie differential tumor tissue damages induced by immune modulator β-glucan in a two-case ex vivo non-small-cell lung cancer study. Cold Spring Harbor Molecular Case Study, 2, a000893. https://doi.org/10.1101/mcs.a000893
Fan, T. W., Higashi, R. M., Chernayavskaya, Y., & Lane, A. N. (2020). Resolving metabolic heterogeneity in experimental models of the tumor microenvironment from a stable isotope resolved metabolomics perspective. Metabolites, 10(6), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060249
Faubert, B., Tasdogan, A., Morrison, S. J., Mathews, T. P., & DeBerardinis, R. J. (2021). Stable isotope tracing to assess tumor metabolism in vivo. Nature Protocols, 16, 5123–5145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-021-00605-2
Fekete, K., Györei, E., Lohner, S., Verduci, E., Agostoni, C., & Decsi, T. (2015). Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid status in obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity Review, 16(6), 488–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12280
Feng, J., Wu, L., Ji, J., Chen, K., Yu, Q., Zhang, J., Chen, J., Mao, Y., Wang, F., Dai, W., Xu, L., Wu, J., & Guo, C. (2019). PKM2 is the target of proanthocyanidin B2 during the inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Experimental and Clinical Cancer Research, 38(1), 204. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1194-z
Flasch, M., Bueschl, C., Del Favero, G., Adam, G., Schuhmacher, R., Marko, D., & Warth, B. (2022). Elucidation of xenoestrogen metabolism by non-targeted, stable isotope-assisted mass spectrometry in breast cancer cells. Environment International, 158, 106940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106940
Frahm, A. B., Jensen, P. R., Ardenkjær-Larsen, J. H., Yigit, D., & Lerche, M. H. (2020). Stable isotope resolved metabolomics classification of prostate cancer cells using hyperpolarized NMR data. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 316, 106750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2020.106750
Fu, M., Bao, T., Yu, H., LiSha A, L., Li, H., Ba, G., & Cho, S. (2022). Metabolomics investigation on antiobesity effects of Corydalis bungeana on high-fat high-sugar diet-induced obese rats. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 14(3), 414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chmed.2022.04.001
Fu, J., Zhang, L. L., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, F., & Zou, L. (2022). Application of metabolomics for revealing the interventional effects of functional foods on metabolic diseases. Food Chemistry, 367, 130697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130697
Hauser, A. S., Attwood, M. M., Rask-Andersen, M., Schiöth, H. B., & Gloriam, D. E. (2017). Trends in GPCR drug discovery: New agents, targets and indications. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery, 16, 829–842. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2017.178
Hay, N. (2016). Reprogramming glucose metabolism in cancer: can it be exploited for cancer therapy? Nature Reviews. Cancer, 16(10), 635–649. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.77
Hernandes, V. V., Barbas, C., & Dudzik, D. (2017). A review of blood sample handling and pre-processing for metabolomics studies. Electrophoresis, 38, 2232–2241. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201700086
Hosaka, T., Nii, Y., Tomotake, H., Ito, T., Tamanaha, A., Yamasaka, Y., Sasaga, S., Edazawa, K., Tsutsumi, R., Shuto, E., Okahisa, N., Iwata, S., & Sakai, T. (2011). Extracts of common buckwheat bran prevent sucrose digestion. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology (Tokyo), 57, 441–445. https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.57.441
Hui, S., Ghergurovich, J. M., Morscher, R. J., Jang, C., Teng, X., Lu, W., Esparza, L. A., Reya, T., Le, Z., Yanxiang Guo, J., White, E., & Rabinowitz, J. D. (2017). Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate. Nature, 551, 115–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24057
Hui, S., Cowan, A. J., Zeng, X., Yang, L., TeSlaa, T., Li, X., Bartman, C., Zhang, Z., Jang, C., Wang, L., Lu, W., Rojas, J., Baur, J., & Rabinowitz, J. D. (2020). Quantitative fluxomics of circulating metabolites. Cell Metabolism, 32(4), 676–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.07.013
Ibrügger, S., Kristensen, M., Poulsen, M. W., Mikkelsen, M. S., Ejsing, J., Jespersen, B. M., Dragsted, L. O., Engelsen, S. B., & Bügel, S. (2013). Extracted oat and barley β-glucans do not affect cholesterol metabolism in young healthy adults. Journal of Nutrition, 143, 1579–1585. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.112.173054
Ijare, O. B., Hambarde, S., Brasil da Costa, F. H., Lopez, S., Sharpe, M. A., Helekar, S. A., Hangel, G., Bogner, W., Widhalm, G., Bachoo, R. M., Baskin, D. S., & Pichumani, K. (2022). Glutamine anaplerosis is required for amino acid biosynthesis in human meningiomas. Neuro-Oncology, 24, 556–568. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noab219
Jang, C., Chen, L., & Rabinowitz, J. D. (2018). Metabolomics and Isotope Tracing. Cell, 173, 822–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.055
Jibril, M. M., Haji-Hamid, A., Abas, F., Karrupan, J., Mohammed, A. S., Jaafar, A. H., Pak Dek, M. S., & Ramli, N. S. (2022). Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) leaf extract attenuates biochemical and histological parameters in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 46, e14058. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.14058
Jing, J. L., Ning, T. C. Y., Natali, F., Eisenhaber, F., & Alfatah, M. (2022). Iron supplementation delays aging and extends cellular lifespan through potentiation of mitochondrial function. Cells, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11050862
Jung, S. M., Le, J., Doxsey, W. G., Haley, J. A., Park, G., Guertin, D. A., & Jang, C. (2022). Stable isotope tracing and metabolomics to study in vivo brown adipose tissue metabolic fluxes. Methods of Molecular Biology, 2448, 119–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2087-8_8
Kawagoe, N., Kano, O., Kijima, S., Tanaka, H., Takayanagi, M., & Urita, Y. (2016). Investigation of metabolism of exogenous glucose at the early stage and onset of diabetes mellitus in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rats using [1, 2, 3–13C]glucose breath tests. PLoS One, 11(8), e0160177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160177
Kong, H., Li, M., Deng, C. M., Wu, Y. J., He, S. T., & Mu, D. L. (2023). A comprehensive overview of clinical research on dexmedetomidine in the past 2 decades: A bibliometric analysis. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 14, 1043956. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1043956
Kumar, A., Mosa, K. A., Ji, L., Kage, U., Dhokane, D., Karre, S., Madalageri, D., & Pathania, N. (2018). Metabolomics-assisted biotechnological interventions for developing plant-based functional foods and nutraceuticals. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 58, 1791–1807. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1285752
Lafarga, T., Fernández-Sevilla, J. M., González-López, C., & Acién-Fernández, F. G. (2020). Spirulina for the food and functional food industries. Food Research International, 137, 109356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109356
Lane, A. N., & Fan, T. W. (2017). NMR-based stable isotope resolved metabolomics in systems biochemistry. Archieve of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 628, 123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2017.02.009
Lee, M. H., Malloy, C. R., Corbin, I. R., Li, J., & Jin, E. S. (2019). Assessing the pentose phosphate pathway using [2, 3–13C2]-glucose. NMR Biomedicine, 32, e4096. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4096
Lee, K., Lee, Y. J., Kim, K. J., Chei, S., Jin, H., Oh, H. J., & Lee, B. Y. (2020). Gomisin N from Schisandra chinensis ameliorates lipid accumulation and induces a brown fat-like phenotype through AMP-activated protein kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. International Journal of Molecular Science, 21(6), 2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062153
Lewis, G. F., Carpentier, A. C., Pereira, S., Hahn, M., & Giacca, A. (2021). Direct and indirect control of hepatic glucose production by insulin. Cell Metabolism, 33(4), 709–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.03.007
Li, J., Hoene, M., Zhao, X., Chen, S., Wei, H., Häring, H. U., Lin, X., Zeng, Z., Weigert, C., Lehmann, R., & Xu, G. (2013). Stable isotope-assisted lipidomics combined with nontargeted isotopomer filtering, a tool to unravel the complex dynamics of lipid metabolism. Analytical Chemistry, 85, 4651–4657. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac400293y
Li, Z., & Zhang, H. (2016). Reprogramming of glucose, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism for cancer progression. Cellular and Molecular Life Science, 73, 377–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2070-4
Liang, L., Sun, F., Wang, H., & Hu, Z. (2021). Metabolomics, metabolic flux analysis and cancer pharmacology. Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 224, 107827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera
Lin, P., Lane, A. N., & Fan, T. W. (2019). Stable isotope-resolved metabolomics by NMR. Methods of Molecular Biology, 2037, 151–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9690-2_9
Lin, P., & T, W. M. F., & Lane, A. N. (2022). NMR-based isotope editing, chemoselection and isotopomer distribution analysis in stable isotope resolved metabolomics. Methods, 206, 8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2022.07.014
Linghu, T., Gao, Y., Li, A., Shi, B., Tian, J., & Qin, X. (2020). A unique insight for energy metabolism disorders in depression based on chronic unpredictable mild stress rats using stable isotope-resolved metabolomics. Journal of Pharmceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 191, 113588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113588
Linghu, T., Zhao, Y., Wu, W., Gao, Y., Tian, J., & Qin, X. (2022). Novel targets for ameliorating energy metabolism disorders in depression through stable isotope-resolved metabolomics. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Bioenergetics, 1863(7), 148578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2022.148578
Liu, G., Shi, A., Wang, N., Li, M., He, X., Yin, C., Tu, Q., Shen, X., Tao, Y., Wang, Q., & Yin, H. (2020). Polyphenolic Proanthocyanidin-B2 suppresses proliferation of liver cancer cells and hepatocellular carcinogenesis through directly binding and inhibiting AKT activity. Redox Biology, 37, 101701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101701
Liu, X., Zhao, S., Tan, L., Tan, Y., Wang, Y., Ye, Z., Hou, C., Xu, Y., Liu, S., & Wang, G. (2022). Frontier and hot topics in electrochemiluminescence sensing technology based on CiteSpace bibliometric analysis. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 201, 113932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113932
Luo, H., Cai, Z., Huang, Y., Song, J., Ma, Q., Yang, X., & Song, Y. (2021). Study on pain catastrophizing from 2010 to 2020: A bibliometric analysis via CiteSpace. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 759347. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.759347
Ma, X., & Fernández, F. M. (2022). Advances in mass spectrometry imaging for spatial cancer metabolomics. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 6, e21804. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21804
Malik, V. S., & Hu, F. B. (2022). The role of sugar-sweetened beverages in the global epidemics of obesity and chronic diseases. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology, 18(4), 205–218. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-021-00627-6
Malin, S. K., Kullman, E. L., Scelsi, A. R., Haus, J. M., Filion, J., Pagadala, M. R., Godin, J. P., Kochhar, S., Ross, A. B., & Kirwan, J. P. (2018). A whole-grain diet reduces peripheral insulin resistance and improves glucose kinetics in obese adults: A randomized-controlled trial. Metabolism, 82, 111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.12.011
McGarrah, R. W., Crown, S. B., Zhang, G. F., Shah, S. H., & Newgard, C. B. (2018). Cardiovascular metabolomics. Circulation Research, 122(9), 1238–1258. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311002
Mohammad, M. A., Maningat, P., Sunehag, A. L., & Haymond, M. W. (2015). Precursors of hexoneogenesis within the human mammary gland. American Journal of Physiology- Endocrinology and Metabolism, 308, E680-687. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00356.2014
Morigny, P., Boucher, J., Arner, P., & Langin, D. (2021). Lipid and glucose metabolism in white adipocytes: Pathways, dysfunction and therapeutics. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology, 17(5), 276–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-021-00471-8
Moszak, M., Szulińska, M., & Bogdański, P. (2020). You are what you eat-the relationship between diet, microbiota, and metabolic disorders-A review. Nutrients, 12(4), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041096
Mulukutla, B. C., Yongky, A., Le, T., Mashek, D. G., & Hu, W. S. (2016). Regulation of glucose metabolism—A perspective from cell bioprocessing. Trends in Biotechnology, 34, 638–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.04.012
Murugan, A. C., Karim, M. R., Yusoff, M. B., Tan, S. H., Asras, M. F., & Rashid, S. S. (2015). New insights into seaweed polyphenols on glucose homeostasis. Pharmaceutical Biology, 53, 1087–1097. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.959615
O’Brien, D. M. (2015). Stable isotope ratios as biomarkers of diet for health research. Annual Reviews of Nutriton, 35, 565–594. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071714-034511
Papadimitropoulos, M. P., Vasilopoulou, C. G., Maga-Nteve, C., & Klapa, M. I. (2018). Untargeted GC-MS metabolomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1738, 133–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7643-0_9
Patkova, A., Joskova, V., Havel, E., Kovarik, M., Kucharova, M., Zadak, Z., & Hronek, M. (2017). Energy, protein, carbohydrate, and lipid intakes and their effects on morbidity and mortality in critically ill adult patients: A systematic review. Advances in Nutrition, 8, 624–634. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.117.015172
Pei, S., Zhao, H., Chen, L., He, X., Hua, Q., Meng, X., Shi, R., Zhang, J., Zhang, H., Liu, R., & Li, D. (2022). Preventive effect of ellagic acid on cardiac dysfunction in diabetic mice through regulating DNA hydroxymethylation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 70, 1902–1910. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07574
Piché, M. E., Tchernof, A., & Després, J. P. (2020). Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation Research, 126, 1477–1500. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316101
Pichumani, K., Mashimo, T., Vemireddy, V., Ijare, O. B., Mickey, B. E., Malloy, C. R., Marin-Valencia, I., Baskin, D. S., Bachoo, R. M., & Maher, E. A. (2017). Measurement of 13C turnover into glutamate and glutamine pools in brain tumor patients. FEBS Letters, 591, 3548–3554. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12867
Poulose, N., Sajayan, A., Ravindran, A., Chandran, A., Priyadharshini, G. B., Selvin, J., & Kiran, G. S. (2021). Anti-diabetic potential of a stigmasterol from the seaweed Gelidium spinosum and its application in the formulation of nanoemulsion conjugate for the development of functional biscuits. Frontiers in Nutrients, 8, 694362. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.694362
Previs, S. F., & Downes, D. P. (2020). Key concepts surrounding studies of stable isotope-resolved metabolomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2104, 99–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0239-3_6
Prochownik, E. V., & Wang, H. (2021). The Metabolic Fates of Pyruvate in Normal and Neoplastic Cells. Cells, 10(4), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040762
Reitelseder, S., Tranberg, B., Agergaard, J., Dideriksen, K., Højfeldt, G., Merry, M. E., Storm, A. C., Poulsen, K. R., Hansen, E. T., van Hall, G., Lund, P., & Holm, L. (2020). Phenylalanine stable isotope tracer labeling of cow milk and meat and human experimental applications to study dietary protein-derived amino acid availability. Clinical Nutrition, 39, 3652–3662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2020.03.017
Rodríguez-Cortés, F. J., Morales-Cané, I., Rodríguez-Muñoz, P. M., Cappadona, R., De Giorgi, A., Manfredini, R., Rodríguez-Borrego, M. A., Fabbian, F., & López-Soto, P. J. (2022). Individual circadian preference, eating disorders and obesity in children and adolescents: A dangerous Liaison? A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Children (Basel), 9(2), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020167
Salgado, H. H., Remus, A., Pomar, C., Létourneau-Montminy, M. P., & Lapierre, H. (2021). Technical Note: In vivo estimation of lipogenesis using a bolus injection of [U-13C]-glucose in pigs. Journal of Animal Science, 99(6), skab148. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skab148
Sen, P., Qadri, S., Luukkonen, P. K., Ragnarsdottir, O., McGlinchey, A., Jäntti, S., Juuti, A., Arola, J., Schlezinger, J. J., Webster, T. F., Orešič, M., Yki-Järvinen, H., & Hyötyläinen, T. (2022). Exposure to environmental contaminants is associated with altered hepatic lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Hepatology, 76(2), 283–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.09.039
Seo, Y. J., Lee, K., Song, J. H., Chei, S., & Lee, B. Y. (2018). Ishige okamurae extract suppresses obesity and hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutrients, 10(11), 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111802
Shan, M., Dong, Y., Chen, J., Su, Q., & Wan, Y. (2022). Global tendency and frontiers of research on myopia from 1900 to 2020: A bibliometrics analysis. Frontiers in Public Health., 10, 846601. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022
Simões, R. V., Cabañas, M. E., Loreiro, C., Illa, M., Crispi, F., & Gratacós, E. (2018). Assessment of prenatal cerebral and cardiac metabolic changes in a rabbit model of fetal growth restriction based on 13C-labelled substrate infusions and ex vivo multinuclear HRMAS. PLoS One, 13(12), e0208784. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208784
Song, T., Song, X., Zhu, C., Patrick, R., Skurla, M., Santangelo, I., Green, M., Harper, D., Ren, B., Forester, B. P., Öngür, D., & Du, F. (2021). Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and metabolic alterations in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. Ageing Research Reviews, 72, 101503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101503
Sun, R. C., Fan, T. W., Deng, P., Higashi, R. M., Lane, A. N., Le, A. T., Scott, T. L., Sun, Q., Warmoes, M. O., & Yang, Y. (2017). Noninvasive liquid diet delivery of stable isotopes into mouse models for deep metabolic network tracing. Nature Communications, 8, 1646. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01518-z
Sylow, L., Kleinert, M., Richter, E. A., & Jensen, T. E. (2017). Exercise-stimulated glucose uptake—Regulation and implications for glycaemic control. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology, 13(3), 133–148. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.162
Tan, L., Wang, X., Yuan, K., Yin, T., Du, R., Shen, L., Zhu, Z., Yu, S., Zhang, H., & Wang, G. (2023). Structural and temporal dynamics analysis on drug-eluting stents: History, research hotspots and emerging trends. Bioactive Materials, 23, 170–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.09.009
Tang, B. L. (2020). Glucose, glycolysis, and neurodegenerative diseases. Journal Cell Physiology, 235, 7653–7662. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29682
TeSlaa, T., Bartman, C. R., Jankowski, C. S. R., Zhang, Z., Xu, X., Xing, X., Wang, L., Lu, W., Hui, S., & Rabinowitz, J. D. (2021). The source of glycolytic intermediates in mammalian tissues. Cell Metabolism, 33, 367-378.e365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.12.020
Tian, J. S., Wu, W. Z., Liu, S. B., Ling-Hu, T., Zhao, Y. H., Gao, Y., & Qin, X. M. (2022). Stable isotope-resolved metabolomics studies on corticosteroid-induced PC12 cells: A strategy for evaluating glucose catabolism in an in vitro model of depression. Journal of Proteome Research, 21, 788–797. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.1c00516
Tian, J. S., Zhao, Y. H., Ling-Hu, T., Wu, W. Z., Wang, X. X., Ji, C., Zhao, W. D., Han, Y. M., & Qin, X. M. (2023). A novel insight for high-rate and low-efficiency glucose metabolism in depression through stable isotope-resolved metabolomics in CUMS-induced rats. Journal of Affective Disorder, 331, 121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2023.03.061
Tramunt, B., Smati, S., Grandgeorge, N., Lenfant, F., Arnal, J. F., Montagner, A., & Gourdy, P. (2020). Sex differences in metabolic regulation and diabetes susceptibility. Diabetologia, 63(3), 453–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-05040-3
Tsai, S. C., Huang, Y. W., Wu, C. C., Wang, J. J., Chen, Y. T., Singhania, R. R., Chen, C. W., Dong, C. D., & Hsieh, S. L. (2022). Anti-obesity effect of Nostoc commune ethanol extract in vitro and in vivo. Nutrients, 14(5), 968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126611
Ventura-Clapier, R., Piquereau, J., Garnier, A., Mericskay, M., Lemaire, C., & Crozatier, B. (2020). Gender issues in cardiovascular diseases. Focus on energy metabolism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Basis Disease, 1866(6), 165722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165722
Vettukattil, R. (2015). Preprocessing of raw metabonomic data. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1277, 123–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2377-9_10
Volpicella, M., Leoni, C., Dileo, M. C. G., & Ceci, L. R. (2019). Progress in the analysis of food allergens through molecular biology approaches. Cells, 8(9), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091073
Wang, N., Liu, H., Liu, G., Li, M., He, X., Yin, C., Tu, Q., Shen, X., Bai, W., Wang, Q., Tao, Y., & Yin, H. (2020). Yeast β-D-glucan exerts antitumour activity in liver cancer through impairing autophagy and lysosomal function, promoting reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis. Redox Biology, 32, 101495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101495
Wang, L., Zheng, W., Yang, J., Ali, A., & Qin, H. (2022). Mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus alleviating acquired hyperlipidemia induced by high-fat diet through regulating lipid metabolism. Nutrients, 14(5), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14050954
Wang, L., Xing, X., Zeng, X., Jackson, S. R., TeSlaa, T., Al-Dalahmah, O., Samarah, L. Z., Goodwin, K., Yang, L., McReynolds, M. R., Li, X., Wolff, J. J., Rabinowitz, J. D., & Davidson, S. M. (2022). Spatially resolved isotope tracing reveals tissue metabolic activity. Nature Methods, 19(2), 223–230. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01378-y
Weng, J., Yang, M., Wang, W., Xu, X., & Tian, Z. (2020). Revealing thermodynamics and kinetics of lipid self-assembly by markov state model analysis. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(51), 21344–21352. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c09343
Williams, H. C., Piron, M. A., Nation, G. K., Walsh, A. E., Young, L. E. A., Sun, R. C., & Johnson, L. A. (2020). Oral gavage delivery of stable isotope tracer for in vivo metabolomics. Metabolites, 10(12), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120501
Wu, S. H., Li, H. B., Li, G. L., Qi, Y. J., Zhang, J., & Wang, B. Y. (2020). Panax ginseng root, not leaf, can enhance thermogenic capacity and mitochondrial function in mice. Pharmaceutical Biology, 58, 374–384. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2020.1756348
Wu, W. Z., Ling-Hu, T., Zhao, Y. H., Zhao, W. D., Ji, C., Tian, J. S., Ren, Y., & Qin, X. M. (2023). A unique insight for Xiaoyao San exerts antidepressant effects by modulating hippocampal glucose catabolism using stable isotope-resolved metabolomics. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 300, 115702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115702
Wurihan., Aodungerle., Bilige., Lili., Sirguleng., Aduqinfu., & Bai, M. (2022). Metabonomics study of liver and kidney subacute toxicity induced by garidi-5 in rats. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 14(3), 422–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chmed.2022.05.003
Xia, W., Fang, X., Gao, Y., Wu, W., Han, Y., Liu, R., Yang, H., Chen, H., & Gao, H. (2023). Advances of stable isotope technology in food safety analysis and nutrient metabolism research. Food Chemistry, 408, 135191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135191
Ying, M., Guo, C., & Hu, X. (2019). The quantitative relationship between isotopic and net contributions of lactate and glucose to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 294, 9615–9630. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.007841
Yoon, H., Shaw, J. L., Haigis, M. C., & Greka, A. (2021). Lipid metabolism in sickness and in health: Emerging regulators of lipotoxicity. Molecular Cell, 81, 3708–3730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.08.027
Yoshinaga, K., Beppu, F., Yamatani, Y., Kubo, A., Yoshinaga-Kiriake, A., Nagai, T., Yoshida, A., Kanda, J., & Gotoh, N. (2019). Effect of calcium treatment on catabolic rates of 13C-labeled fatty acids bound to the α and β positions of triacylglycerol. Journal of Oleo Science, 68, 1149–1155. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess19197
You, L., Zhang, B., & Tang, Y. J. (2014). Application of stable isotope-assisted metabolomics for cell metabolism studies. Metabolites, 4, 142–165. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4020142
Yuan, H., Li, Y., Ling, F., Guan, Y., Zhang, D., Zhu, Q., Liu, J., Wu, Y., & Niu, Y. (2020). The phytochemical epigallocatechin gallate prolongs the lifespan by improving lipid metabolism, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in high-fat diet-fed obese rats. Aging Cell, 19, e13199. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13199
Zabielski, P., Błachnio-Zabielska, A. U., Wójcik, B., Chabowski, A., & Górski, J. (2017). Effect of plasma free fatty acid supply on the rate of ceramide synthesis in different muscle types in the rat. PLoS One, 12(11), e0187136. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187136
Zamora Obando, H. R., Duarte, G. H. B., & Simionato, A. V. C. (2021). Metabolomics data treatment: basic directions of the full process. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1336, 243–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-77252-9_12
Zhang, W., Qi, S., Xue, X., Al, Naggar, & Y., Wu, L., & Wang, K. (2021). Understanding the gastrointestinal protective effects of polyphenols using foodomics-based approaches. Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 671150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.671150
Zhao, J., Yu, J., Zhi, Q., Yuan, T., Lei, X., Zeng, K., & Ming, J. (2021). Anti-aging effects of the fermented anthocyanin extracts of purple sweet potato on Caenorhabditis elegans. Food and Function, 12(24), 12647–12658. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo02671b
Züllig, T., & Köfeler, H. C. (2021). High resolution mass spectrometry in lipidomics. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 40(3), 162–176. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21627
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82174076), the Construction Project of Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory, China (2022JH13/10200026), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N2220002) and 111 Project (B16009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yue Hou, Xue-mei Qin, and Dong Liang contributed the central idea. Wenze Wu analyzed most of the data and wrote the initial draft of the paper. The remaining authors contributed to refining the ideas, carrying out additional analyses, and finalizing this paper. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11947_2023_3137_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Figure. S1. Top 25 most cited keywords of studies on functional foods in energy metabolism from 1995 to 2022. The blue color represents the timespan (1995–2022). The red color represents the year that the keyword appeared Table S1. Top 20 authors of studies on functional foods in energy metabolism from 1995 to 2022. (DOCX 168 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Meng, Q., Mi, Y. et al. A Novel Strategy for the Development of Functional Foods to Improve Energy Metabolism Disorders: Stable Isotope-Resolved Metabolomics. Food Bioprocess Technol 17, 591–605 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03137-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03137-7