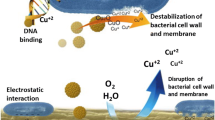
Abstract
Nanoscale particles can achieve more effective action mechanisms than microscale particles. For the synthesis of nanoparticles, pathways that consider environmental preservation are highly desirable by the consumer. Despite the lack of studies for production on an industrial scale, the exceptional functionality makes nanoparticles one of the main ways to replace synthetic additives and formulate safer foods. In this sense, this review addresses, based on bibliometric analysis, the main nanoparticles synthesized in green with properties of current interest for food matrices. The databases indicated metallic and polymeric nanoparticles as the most applied types in the food science and technology area. Metallic nanoparticles can individually or simultaneously exert antimicrobial and antioxidant activity. Furthermore, in addition to carrying bioactive compounds, polymeric nanoparticles can modulate important physical properties, such as the solubility of molecules in water and the oral perception of the product. Although in vivo studies evaluating the safety of nanoparticles are scarce, this area is in development, as green nanoparticles (GNPs) show the ability to play an essential role in food design and human health.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data are available from the corresponding author upon suitable request.
References
Aazami, M. A., Rasouli, F., & Ebrahimzadeh, A. (2021). Oxidative damage, antioxidant mechanism and gene expression in tomato responding to salinity stress under in vitro conditions and application of iron and zinc oxide nanoparticles on callus induction and plant regeneration. BMC Plant Biology, 21(1), 597. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03379-7
Abid, N., Khan, A. M., Shujait, S., Chaudhary, K., Ikram, M., Imran, M., Haider, J., Khan, M., Khan, Q., & Maqbool, M. (2022). Synthesis of nanomaterials using various top-down and bottom-up approaches, influencing factors, advantages, and disadvantages: A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 300, 102597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102597
Ahmad, M., Mudgil, P., Gani, A., Hamed, F., Masoodi, F. A., & Maqsood, S. (2019). Nano-encapsulation of catechin in starch nanoparticles: characterization, release behavior and bioactivity retention during simulated in-vitro digestion. Food Chemistry, 270, 95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.024
Alqarni, L. S., Alghamdi, M. D., Alshahrani, A. A., & Nassar, A. M. (2022). Green Nanotechnology: Recent research on bioresource-based nanoparticle synthesis and applications. Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4030999
Ansar, S., Tabassum, H., Aladwan, N. S. M., Naiman Ali, M., Almaarik, B., AlMahrouqi, S., Abudawood, M., Banu, N., & Alsubki, R. (2020). Eco friendly silver nanoparticles synthesis by Brassica oleracea and its antibacterial, anticancer and antioxidant properties. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 18564. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-74371-8
Anselmo, A. C., & Mitragotri, S. (2015). A review of clinical translation of inorganic nanoparticles. The AAPS Journal, 17(5), 1041–1054. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-015-9780-2
Bajpai, V. K., Kamle, M., Shukla, S., Mahato, D. K., Chandra, P., Hwang, S. K., Kumar, P., Huh, Y. S., & Han, Y. K. (2018). Prospects of using nanotechnology for food preservation, safety, and security. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 26(4), 1201–1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2018.06.011
Balasubramanian, S., Kala, S. M. J., & Pushparaj, T. L. (2020). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Jasminum auriculatum leaf extract and their catalytic, antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 57, 101620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101620
Balkrishna, A., Sharma, V. K., Das, S. K., Mishra, N., Bisht, L., Joshi, A., & Sharma, N. (2020). Characterization and anti-cancerous effect of Putranjiva roxburghii Seed extract mediated silver nanoparticles on human colon (HCT-116), pancreatic (PANC-1) and breast (MDA-MB 231) cancer cell lines: a comparative study. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 15, 573–585. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S230244
Bartolucci, C., Antonacci, A., Arduini, F., Moscone, D., Fraceto, L., Campos, E., Attaallah, R., Amine, A., Zanardi, C., Cubillana-Aguilera, L. M., Palacios Santander, J. M., & Scognamiglio, V. (2020). Green nanomaterials fostering agrifood sustainability. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 125, 115840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115840
Bensy, A. D. V., Christobel, G. J., Muthusamy, K., Alfarhan, A., & Anantharaman, P. (2022). Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles from Ulva lactuca and bactericidal activity against enteropathogens. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 34(3), 101888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101888
Bertolo, M. R. V., Brenelli de Paiva, L. B., Nascimento, V. M., Gandin, C. A., Neto, M. O., Driemeier, C. E., & Rabelo, S. C. (2019). Lignins from sugarcane bagasse: Renewable source of nanoparticles as Pickering emulsions stabilizers for bioactive compounds encapsulation. Industrial Crops and Products, 140, 111591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111591
Boostani, S., Hosseini, S. M. H., Golmakani, M.-T., Marefati, A., Abdul Hadi, N. B., & Rayner, M. (2020). The influence of emulsion parameters on physical stability and rheological properties of Pickering emulsions stabilized by hordein nanoparticles. Food Hydrocolloids, 101, 105520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105520
Calabrese, V., Courtenay, J. C., Edler, K. J., & Scott, J. L. (2018). Pickering emulsions stabilized by naturally derived or biodegradable particles. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 12, 83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2018.07.002
Camargos, C. H. M., & Rezende, C. A. (2021). Antisolvent versus ultrasonication: Bottom-up and top-down approaches to produce lignin nanoparticles (LNPs) with tailored properties. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 193, 647–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.094
Chandrasekaran, M., Kim, K. D., & Chun, S. C. (2020). Antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles: a review. Processes, 8(9), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8091173
Cheong, A. M., Tan, K. W., Tan, C. P., & Nyam, K. L. (2016). Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed oil-in-water Pickering nanoemulsions stabilised by mixture of sodium caseinate, Tween 20 and β-cyclodextrin. Food Hydrocolloids, 52, 934–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.09.005
Da Cunha, J. A., de Ávila Scheeren, C., Fausto, V. P., de Melo, L. D. W., Henneman, B., Frizzo, C. P., de Almeida Vaucher, R., Castagna de Vargas, A., & Baldisserotto, B. (2018). The antibacterial and physiological effects of pure and nanoencapsulated Origanum majorana essential oil on fish infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Microbial Pathogenesis, 124, 116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.08.040
Dasgupta, N., Ranjan, S., Mundekkad, D., Ramalingam, C., Shanker, R., & Kumar, A. (2015). Nanotechnology in agro-food: From field to plate. Food Research International, 69, 381–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.01.005
Dauthal, P., & Mukhopadhyay, M. (2016a). Noble metal nanoparticles: plant-mediated synthesis, mechanistic aspects of synthesis, and applications. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 55(36), 9557–9577. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b00861
Dauthal, P., & Mukhopadhyay, M. (2016b). Phyto-synthesis and structural characterization of catalytically active gold nanoparticles biosynthesized using Delonix regia leaf extract. 3 Biotech, 6(2), 118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0432-8
De Silva, R. T., Mantilaka, M. M. M. G. P. G., Ratnayake, S. P., Amaratunga, G. A. J., & de Silva, K. M. N. (2017). Nano-MgO reinforced chitosan nanocomposites for high performance packaging applications with improved mechanical, thermal and barrier properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 157, 739–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.038
Deschênes, L., & Ells, T. (2020). Bacteria-nanoparticle interactions in the context of nanofouling. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 277, 102106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102106
Divya, K., & Jisha, M. S. (2018). Chitosan nanoparticles preparation and applications. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 16(1), 101–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0670-y
Đorđević, V., Balanč, B., Belščak-Cvitanović, A., Lević, S., Trifković, K., Kalušević, A., Kostić, I., Komes, D., Bugarski, B., & Nedović, V. (2015). Trends in encapsulation technologies for delivery of food bioactive compounds. Food Engineering Reviews, 7(4), 452–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-014-9106-7
Duvall, M. D. (2012). FDA regulation of nanotechnology. https://www.bdlaw.com/content/uploads/2018/06/fda-regulation-of-nanotechnology.pdf
Durval, I. J. B., Meira, H. M., de Veras, B. O., Rufino, R. D., Converti, A., & Sarubbo, L. A. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a biosurfactant from Bacillus cereus UCP 1615 as stabilizing agent and its application as an antifungal agent. Fermentation, 7(4), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040233
El-Batal, A. I., Mosallam, F. M., & El-Sayyad, G. S. (2018). Synthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles by fluconazole drug and gamma rays to inhibit the growth of multidrug-resistant microbes. Journal of Cluster Science, 29(6), 1003–1015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-1411-5
El-Sheikh, M. A. (2017). New technique in starch nanoparticles synthesis. Carbohydrate Polymers, 176, 214–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.033
Enescu, D., Cerqueira, M. A., Fucinos, P., & Pastrana, L. M. (2019). Recent advances and challenges on applications of nanotechnology in food packaging. A literature review. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 134, 110814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.110814
Esfanjani, A. F., & Jafari, S. M. (2017). Nanoencapsulation of phenolic compounds and antioxidants. In Nanoencapsulation of Food Bioactive Ingredients (pp. 63–101). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809740-3.00002-7
Falsafi, S. R., Karaca, A. C., Deng, L., Wang, Y., Li, H., Askari, G., & Rostamabadi, H. (2022). Insights into whey protein-based carriers for targeted delivery and controlled release of bioactive components. Food Hydrocolloids, 133, 108002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.108002
Fuciños, C., Míguez, M., Fuciños, P., Pastrana, L. M., Rúa, M. L., & Vicente, A. A. (2017). Creating functional nanostructures: Encapsulation of caffeine into α-lactalbumin nanotubes. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 40, 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2016.07.030
Ganesan, V., Hariram, M., Vivekanandhan, S., & Muthuramkumar, S. (2020). Periconium sp. (endophytic fungi) extract mediated sol-gel synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for antimicrobial and antioxidant applications. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 105, 104739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104739
Ganje, M., Jafari, S. M., Tamadon, A. M., Niakosari, M., & Maghsoudlou, Y. (2019). Mathematical and fuzzy modeling of limonene release from amylose nanostructures and evaluation of its release kinetics. Food Hydrocolloids, 95, 186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.04.045
Ge, S., Xiong, L., Li, M., Liu, J., Yang, J., Chang, R., Liang, C., & Sun, Q. (2017). Characterizations of Pickering emulsions stabilized by starch nanoparticles: Influence of starch variety and particle size. Food Chemistry, 234, 339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.150
Gómez-Llorente, H., Hervás, P., Pérez-Esteve, É., Barat, J. M., & Fernández-Segovia, I. (2022). Nanotechnology in the agri-food sector: Consumer perceptions. NanoImpact, 26, 100399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2022.100399
Granata, G., Stracquadanio, S., Leonardi, M., Napoli, E., Consoli, G. M. L., Cafiso, V., Stefani, S., & Geraci, C. (2018). Essential oils encapsulated in polymer-based nanocapsules as potential candidates for application in food preservation. Food Chemistry, 269, 286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.140
Gu, R., Li, C., Shi, X., & Xiao, H. (2022). Naturally occurring protein/polysaccharide hybrid nanoparticles for stabilizing oil-in-water Pickering emulsions and the formation mechanism. Food Chemistry, 395, 133641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133641
Guo, Y., Xu, L., Liu, H., Li, Y., Che, C.-M., & Li, Y. (2015). Self-assembly of functional molecules into 1D crystalline nanostructures. Advanced Materials, 27(6), 985–1013. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201403846
Gutiérrez, G., Morán, D., Marefati, A., Purhagen, J., Rayner, M., & Matos, M. (2020). Synthesis of controlled size starch nanoparticles (SNPs). Carbohydrate Polymers, 250, 116938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116938
Hadidi, M., Pouramin, S., Adinepour, F., Haghani, S., & Jafari, S. M. (2020). Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with clove essential oil: Characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Carbohydrate Polymers, 236, 116075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116075
Hamad, A. F., Han, J.-H., Kim, B.-C., & Rather, I. A. (2018). The intertwine of nanotechnology with the food industry. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 25(1), 27–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.09.004
Hathout, R. M., & Metwally, A. A. (2019). Gelatin Nanoparticles (pp. 71–78). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9516-5_6
He, J., Xie, Y., Zhong, J., Chen, W., Fang, S., Chen, X., Peng, S., Liu, W., & Liu, C. (2023). Improving shikonin solubility and stability by encapsulation in natural surfactant-coated shikonin nanoparticles. Journal of Food Science, 88(2), 825–836. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.16445
He, X., Deng, H., Hwang, H., & min. (2019). The current application of nanotechnology in food and agriculture. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 27(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2018.12.002
He, X., Fu, P., Aker, W. G., & Hwang, H.-M. (2018). Toxicity of engineered nanomaterials mediated by nano–bio–eco interactions. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part C, 36(1), 21–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2017.1418793
Hekmati, M., Hasanirad, S., Khaledi, A., & Esmaeili, D. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using extracts of Allium rotundum l, Falcaria vulgaris Bernh, and Ferulago angulate Boiss, and their antimicrobial effects in vitro. Gene Reports, 19, 100589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100589
Jadoun, S., Arif, R., Jangid, N. K., & Meena, R. K. (2021). Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19(1), 355–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01074-x
Jamali, S. N., Assadpour, E., Feng, J., & Jafari, S. M. (2021). Natural antimicrobial-loaded nanoemulsions for the control of food spoilage/pathogenic microorganisms. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 295, 102504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102504
Jamkhande, P. G., Ghule, N. W., Bamer, A. H., & Kalaskar, M. G. (2019). Metal nanoparticles synthesis: An overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 53, 101174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101174
Jayakumar, A., Radoor, S., Siengchin, S., Shin, G. H., & Kim, J. T. (2023). Recent progress of bioplastics in their properties, standards, certifications and regulations: A review. Science of The Total Environment, 878, 163156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163156
Jayarambabu, N., Akshaykranth, A., Venkatappa Rao, T., Venkateswara Rao, K., & Rakesh Kumar, R. (2020). Green synthesis of Cu nanoparticles using Curcuma longa extract and their application in antimicrobial activity. Materials Letters, 259, 126813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126813
Jha, A. K., Prasad, K., Kumar, V., & Prasad, K. (2009). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using eclipta leaf. Biotechnology Progress, 25(5), 1476–1479. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.233
Jiang, Y., Zhang, C., Yuan, J., Wu, Y., Li, F., Li, D., & Huang, Q. (2019). Effects of pectin polydispersity on zein/pectin composite nanoparticles (ZAPs) as high internal-phase Pickering emulsion stabilizers. Carbohydrate Polymers, 219, 77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.025
Kassem, A., Ayoub, G. M., & Malaeb, L. (2019). Antibacterial activity of chitosan nano-composites and carbon nanotubes: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 668, 566–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.446
Kenari, R. E., Amiri, Z. R., Motamedzadegan, A., Milani, J. M., Farmani, J., & Farahmandfar, R. (2020). Optimization of Iranian golpar (Heracleum persicum) extract encapsulation using sage (Salvia macrosiphon) seed gum: Chitosan as a wall materials and its effect on the shelf life of soybean oil during storage. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 14(5), 2828–2839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-020-00528-8
Khen, A., Hadjersi, T., Brihi, N., Moulai, F., Fellahi, O., Naama, S., Ifires, M., & Manseri, A. (2022). Preparation of SiNWs/rGO/CuO nanocomposites as effective photocatalyst for degradation of ciprofloxacin assisted with peroxymonosulfate. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 32(3), 1078–1091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02184-x
Khezerlou, A., Alizadeh-Sani, M., Azizi-Lalabadi, M., & Ehsani, A. (2018). Nanoparticles and their antimicrobial properties against pathogens including bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses. Microbial Pathogenesis, 123, 505–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.08.008
Khoshakhlagh, K., Koocheki, A., Mohebbi, M., & Allafchian, A. (2017). Development and characterization of electrosprayed Alyssum homolocarpum seed gum nanoparticles for encapsulation of d-limonene. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 490, 562–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.067
Ko, E. B., & Kim, J.-Y. (2021). Application of starch nanoparticles as a stabilizer for Pickering emulsions: Effect of environmental factors and approach for enhancing its storage stability. Food Hydrocolloids, 120, 106984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106984
Koul, B., Poonia, A. K., Yadav, D., & Jin, J.-O. (2021). Microbe-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles: Applications and future prospects. Biomolecules, 11(6), 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060886
Król, A., Railean-Plugaru, V., Pomastowski, P., & Buszewski, B. (2019). Phytochemical investigation of Medicago sativa L. extract and its potential as a safe source for the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: The proposed mechanism of formation and antimicrobial activity. Phytochemistry Letters, 31, 170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2019.04.009
Kuang, L., Burgess, B., Cuite, C. L., Tepper, B. J., & Hallman, W. K. (2020). Sensory acceptability and willingness to buy foods presented as having benefits achieved through the use of nanotechnology. Food Quality and Preference, 83, 103922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2020.103922
Kumar, H., Bhardwaj, K., Nepovimova, E., Kuča, K., Singh Dhanjal, D., Bhardwaj, S., Bhatia, S. K., Verma, R., & Kumar, D. (2020). Antioxidant functionalized nanoparticles: a combat against oxidative stress. Nanomaterials, 10(7), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071334
Kumari, S., Yadav, B. S., & Yadav, R. B. (2020). Synthesis and modification approaches for starch nanoparticles for their emerging food industrial applications: A review. Food Research International, 128, 108765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108765
Lamabam, S. D., & Thangjam, R. (2018). Progress and challenges of nanotechnology in food engineering. In Impact of Nanoscience in the Food Industry (pp. 87–112). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811441-4.00004-2
lashin, I., Hasanin, M., Hassan, S. A. M., & Hashem, A. H. (2021). Green biosynthesis of zinc and selenium oxide nanoparticles using callus extract of Ziziphus spina-christi: Characterization, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activity. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01873-4
Lead, J. R., Doak, S. H., & Clift, M. J. D. (Eds.). (2021). Nanotoxicology in humans and the environment. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79808-6
Lee, Y.-S., Tarté, R., & Acevedo, N. C. (2021). Synergistic effects of starch nanoparticles and chitin nanofibers on the stability of oil-in-water Pickering emulsions. Food Chemistry, 363, 130301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130301
Leena, M. M., Anukiruthika, T., Moses, J. A., & Anandharamakrishnan, C. (2022). Co-delivery of curcumin and resveratrol through electrosprayed core-shell nanoparticles in 3D printed hydrogel. Food Hydrocolloids, 124, 107200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107200
Li, C.-W., Li, L.-L., Chen, S., Zhang, J.-X., & Lu, W.-L. (2020). Antioxidant nanotherapies for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00200
Li, H., Li, F., Yang, F., Fang, Y., Xin, Z., Zhao, L., & Hu, Q. (2008). Size effect of Se-enriched green tea particles on in vitro antioxidant and antitumor activities. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(12), 4529–4533. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0731200
Liang, X., Cao, K., Li, W., Li, X., McClements, D. J., & Hu, K. (2021). Tannic acid-fortified zein-pectin nanoparticles: Stability, properties, antioxidant activity, and in vitro digestion. Food Research International, 145, 110425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110425
Liao, W., Badri, W., Dumas, E., Ghnimi, S., Elaissari, A., Saurel, R., & Gharsallaoui, A. (2021). Nanoencapsulation of essential oils as natural food antimicrobial agents: An overview. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 5778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135778
Liu, C., Cheng, F., & Yang, X. (2017). Fabrication of a soybean Bowman-Birk inhibitor (BBI) nanodelivery carrier to improve bioavailability of curcumin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(11), 2426–2434. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00097
Mahmud, J., Sarmast, E., Shankar, S., & Lacroix, M. (2022). Advantages of nanotechnology developments in active food packaging. Food Research International, 154(12), 111023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111023
Manikandan, N. A., Pakshirajan, K., & Pugazhenthi, G. (2020). Preparation and characterization of environmentally safe and highly biodegradable microbial polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) based graphene nanocomposites for potential food packaging applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 154, 866–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.084
Marta, H., Rizki, D. I., Mardawati, E., Djali, M., Mohammad, M., & Cahyana, Y. (2023). Starch nanoparticles: Preparation, properties and applications. Polymers, 15(5), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051167
Maťátková, O., Michailidu, J., Miškovská, A., Kolouchová, I., Masák, J., & Čejková, A. (2022). Antimicrobial properties and applications of metal nanoparticles biosynthesized by green methods. Biotechnology Advances, 58, 107905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107905
McClements, D. J., & Xiao, H. (2017). Is nano safe in foods? Establishing the factors impacting the gastrointestinal fate and toxicity of organic and inorganic food-grade nanoparticles. Npj Science of Food, 1(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-017-0005-1
Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajjadi, M., Sajadi, S. M., & Issaabadi, Z. (2019). Green Nanotechnology (pp. 145–198). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813586-0.00005-5
Nieto-Maldonado, A., Bustos-Guadarrama, S., Espinoza-Gomez, H., Z. Flores-López, L., Ramirez-Acosta, K., Alonso-Nuñez, G., & Cadena-Nava, R. D. (2022). Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using different plant extracts and their antibacterial activity. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(2), 107130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107130
Ning, F., Ge, Z., Qiu, L., Wang, X., Luo, L., Xiong, H., & Huang, Q. (2020). Double-induced se-enriched peanut protein nanoparticles preparation, characterization and stabilized food-grade Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 99, 105308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105308
Odeniyi, M. A., Okumah, V. C., Adebayo-Tayo, B. C., & Odeniyi, O. A. (2020). Green synthesis and cream formulations of silver nanoparticles of Nauclea latifolia (African peach) fruit extracts and evaluation of antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 15, 100197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2019.100197
Ovais, M., Khalil, A. T., Islam, N. U., Ahmad, I., Ayaz, M., Saravanan, M., Shinwari, Z. K., & Mukherjee, S. (2018). Role of plant phytochemicals and microbial enzymes in biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102(16), 6799–6814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9146-7
Pascoli, M., de Lima, R., & Fraceto, L. F. (2018). Zein nanoparticles and strategies to improve colloidal stability: A mini-review. Frontiers in Chemistry, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00006
Pasupuleti, V. R. (2021). Nanoscience and nanotechnology advances in food industry. Global Trends, Opportunities, and Sustainability Challenges. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91001-9.00011-6
Pauluk, D., Padilha, A. K., Khalil, N. M., & Mainardes, R. M. (2019). Chitosan-coated zein nanoparticles for oral delivery of resveratrol: Formation, characterization, stability, mucoadhesive properties and antioxidant activity. Food Hydrocolloids, 94, 411–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.03.042
Periakaruppan, R., & S, M. P., C, P., P, R., S, G. R., & Danaraj, J. (2022). Biosynthesis of silica nanoparticles using the leaf extract of Punica granatum and assessment of its antibacterial activities against human pathogens. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 194(11), 5594–5605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-03994-6
Pisoschi, A. M., Pop, A., Cimpeanu, C., Turcuş, V., Predoi, G., & Iordache, F. (2018). Nanoencapsulation techniques for compounds and products with antioxidant and antimicrobial activity - a critical view. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 157, 1326–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.08.076
Prakash, B., Kujur, A., Yadav, A., Kumar, A., Singh, P. P., & Dubey, N. K. (2018). Nanoencapsulation: an efficient technology to boost the antimicrobial potential of plant essential oils in food system. Food Control, 89, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.01.018
Primožič, M., Knez, Ž, & Leitgeb, M. (2021). (Bio)nanotechnology in food science-food packaging. Nanomaterials, 11(2), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020292
Rajesh, M.K., Muralikrishna, K.S. , Nair, S. S., Kumar, B. K., Subrahmanya, T.M., Sonu, K.P., Subaharan, K., Sweta, H., Prasada, T.S. K., Chandran, .N., Karunasagar, I., Hebbar, K.B.,& Karun, A. (2020). Facile coconut inflorescence sap mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its diverse antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 111, 110834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.11083
Rajeshkumar, S., & Rinitha, G. (2018). Nanostructural characterization of antimicrobial and antioxidant copper nanoparticles synthesized using novel Persea americana seeds. OpenNano, 3, 18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onano.2018.03.001
Rajeshkumar, S., Santhoshkumar, J., Parameswari, R. P., Saravanan, S., Balusamy, S. R., & Arunachalam, K. (2022). Degradation of toxic dye and antimicrobial and free radical potential of environmental benign zinc oxide nanoparticles. Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications, 2022, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4513208
Rambaran, T., & Schirhagl, R. (2022). Nanotechnology from lab to industry – a look at current trends. Nanoscale Advances, 4(18), 3664–3675. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NA00439A
Saharan, V., Mehrotra, A., Khatik, R., Rawal, P., Sharma, S. S., & Pal, A. (2013). Synthesis of chitosan based nanoparticles and their in vitro evaluation against phytopathogenic fungi. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 62, 677–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.10.012
Sahoo, M., Vishwakarma, S., Panigrahi, C., & Kumar, J. (2021). Nanotechnology: Current applications and future scope in food. Food Frontiers, 2(1), 3–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/fft2.58
Sahoo, N., Sahoo, R. K., Biswas, N., Guha, A., & Kuotsu, K. (2015). Recent advancement of gelatin nanoparticles in drug and vaccine delivery. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 81, 317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.006
Samrot, A. V., Ram Singh, S. P., Deenadhayalan, R., Rajesh, V. V., Padmanaban, S., & Radhakrishnan, K. (2022). Nanoparticles, a double-edged sword with oxidant as well as antioxidant properties–A review. Oxygen, 2(4), 591–604. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2040039
Sangolkar, R. D., Kawadkar, D. K., Bhanvase, B. A., Sonawane, S. H., & Potoroko, I. (2019). Ultrasound assisted encapsulation of peppermint flavor in gum Arabic: Study of process parameters. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 42(7). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.13269
Sanpui, P., Murugadoss, A., Prasad, P. V. D., Ghosh, S. S., & Chattopadhyay, A. (2008). The antibacterial properties of a novel chitosan-Ag-nanoparticle composite. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 124(2), 142–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.03.004
Sedaghat Doost, A., Nikbakht Nasrabadi, M., Kassozi, V., Dewettinck, K., Stevens, C. V., & Van der Meeren, P. (2019). Pickering stabilization of thymol through green emulsification using soluble fraction of almond gum – Whey protein isolate nano-complexes. Food Hydrocolloids, 88, 218–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.10.009
Shafey, A. M. E. (2020). Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles from plant leaf extracts and their applications: a review. Green Processing and Synthesis, 9(1), 304–339. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2020-0031
Shah, S. S., Shaikh, M. N., Khan, M. Y., Alfasane, M. A., Rahman, M. M., & Aziz, M. A. (2021). Present status and future prospects of jute in nanotechnology: a review. The Chemical Record, 21(7), 1631–1665. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202100135
Sharkawy, A., Barreiro, M. F., & Rodrigues, A. E. (2020). Chitosan-based Pickering emulsions and their applications: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 250, 116885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116885
Sharma, P., Pant, S., Dave, V., Tak, K., Sadhu, V., & Reddy, K. R. (2019). Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles by Tinospora cardifolia to produce nature-friendly copper nano-coated fabric and their antimicrobial evaluation. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 160, 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2019.03.007
Sharma, R., & Tripathi, A. (2022). Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its key applications in various sectors. Materials Today: Proceedings, 48, 1626–1632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.09.512
Shokry, M., Hathout, R. M., & Mansour, S. (2018). Exploring gelatin nanoparticles as novel nanocarriers for Timolol Maleate: Augmented in-vivo efficacy and safe histological profile. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 545(1–2), 229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.04.059
Singh, T., Shukla, S., Kumar, P., Wahla, V., & Bajpai, V. K. (2017). Application of nanotechnology in food science: Perception and overview. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8(AUG), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01501
Sun, R., Lu, J., & Nolden, A. (2021). Nanostructured foods for improved sensory attributes. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 108, 281–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.011
Syafiq, R., Sapuan, S. M., Zuhri, M. Y. M., Ilyas, R. A., Nazrin, A., Sherwani, S. F. K., & Khalina, A. (2020). Antimicrobial Activities of starch-based biopolymers and biocomposites incorporated with plant essential oils: a review. Polymers, 12(10), 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102403
Talegaonkar, S., Pandey, S., Rai, N., Rawat, P., Sharma, H., & Kumari, N. (2016). Exploring nanoencapsulation of aroma and flavors as new frontier in food technology. In Encapsulations (pp. 47–88). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804307-3.00002-8
Tauseef, A., Hisam, F., Hussain, T., Caruso, A., Hussain, K., Châtel, A., & Chénais, B. (2022). Nanomicrobiology: Emerging trends in microbial synthesis of nanomaterials and their applications. Journal of Cluster Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02256-z
Trifković, K., Đorđević, V., Balanč, B., Kalušević, A., Lević, S., Bugarski, B., & Nedović, V. (2016). Novel approaches in nanoencapsulation of aromas and flavors. In Encapsulations (pp. 363–419). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804307-3.00009-0
Truong, T. H., Alcantara, K. P., Bulatao, B. P. I., Sorasitthiyanukarn, F. N., Muangnoi, C., Nalinratana, N., Vajragupta, O., Rojsitthisak, P., & Rojsitthisak, P. (2022). Chitosan-coated nanostructured lipid carriers for transdermal delivery of tetrahydrocurcumin for breast cancer therapy. Carbohydrate Polymers, 288, 119401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119401
Tufail, M. S., Liaqat, I., Andleeb, S., Naseem, S., Zafar, U., Sadiqa, A., Liaqat, I., Ali, N. M., Bibi, A., Arshad, N., & Saleem, G. (2022). Biogenic synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles against human pathogens. Journal of Oleo Science, 71(2), ess21291. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess21291
Vaiserman, A., Koliada, A., Zayachkivska, A., & Lushchak, O. (2020). Nanodelivery of natural antioxidants: An anti-aging perspective. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00447
Villena de Francisco, E., & García-Estepa, R. M. (2018). Nanotechnology in the agrofood industry. Journal of Food Engineering, 238, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.05.024
Vitta, Y., Figueroa, M., Calderon, M., & Ciangherotti, C. (2020). Synthesis of iron nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Eucalyptus robusta Sm and evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. Materials Science for Energy Technologies, 3, 97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2019.10.014
Voci, S., Gagliardi, A., Fresta, M., & Cosco, D. (2022). Ascorbic acid-loaded gliadin nanoparticles as a novel nutraceutical formulation. Food Research International, 161, 111869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111869
Wang, M., Li, S., Chen, Z., Zhu, J., Hao, W., Jia, G., Chen, W., Zheng, Y., Qu, W., & Liu, Y. (2021). Safety assessment of nanoparticles in food: Current status and prospective. Nano Today, 39, 101169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101169
Wasilewska, A., Klekotka, U., Zambrzycka, M., Zambrowski, G., Święcicka, I., & Kalska-Szostko, B. (2023). Physico-chemical properties and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles fabricated by green synthesis. Food Chemistry, 400, 133960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133960
Wiggers, H. A., Fin, M. T., Khalil, N. M., & Mainardes, R. M. (2022). Polyethylene glycol-stabilized zein nanoparticles containing gallic acid. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 60(2), 145–154. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.60.02.22.6981
Wu, S., Rajeshkumar, S., Madasamy, M., & Mahendran, V. (2020). Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Cissus vitiginea and its antioxidant and antibacterial activity against urinary tract infection pathogens. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 48(1), 1153–1158. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2020.1817053
Xiao, J., Li, Y., & Huang, Q. (2016). Recent advances on food-grade particles stabilized Pickering emulsions: fabrication, characterization and research trends. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 55, 48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2016.05.010
Xu, B., Liu, C., Sun, H., Wang, X., & Huang, F. (2020). Oil-in-water Pickering emulsions using a protein nano-ring as high-grade emulsifiers. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 187, 110646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110646
Xu, Y., Wei, Z., & Xue, C. (2023). Pickering emulsions stabilized by zein–gallic acid composite nanoparticles: Impact of covalent or non-covalent interactions on storage stability, lipid oxidation and digestibility. Food Chemistry, 408, 135254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135254
Yanat, M., & Schroën, K. (2021). Preparation methods and applications of chitosan nanoparticles; with an outlook toward reinforcement of biodegradable packaging. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 161, 104849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2021.104849
Yang, H., Su, Z., Meng, X., Zhang, X., Kennedy, J. F., & Liu, B. (2020). Fabrication and characterization of Pickering emulsion stabilized by soy protein isolate-chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polymers, 247, 116712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116712
Yang, T., Liu, T.-X., Li, X.-T., & Tang, C.-H. (2019). Novel nanoparticles from insoluble soybean polysaccharides of Okara as unique Pickering stabilizers for oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 94, 255–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.03.035
Yasmin, R., Shah, M., Khan, S. A., & Ali, R. (2017). Gelatin nanoparticles: a potential candidate for medical applications. Nanotechnology Reviews, 6(2), 191–207. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2016-0009
Ying, S., Guan, Z., Ofoegbu, P. C., Clubb, P., Rico, C., He, F., & Hong, J. (2022). Green synthesis of nanoparticles: Current developments and limitations. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 26, 102336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2022.102336
Yuan, Y., Ma, M., Xu, Y., & Wang, D. (2022). Surface coating of zein nanoparticles to improve the application of bioactive compounds: a review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 120, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.12.025
Zayed, M. F., Mahfoze, R. A., El-kousy, S. M., & Al-Ashkar, E. A. (2020). In-vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of metal nanoparticles biosynthesized using optimized Pimpinella anisum extract. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 585, 124167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124167
Zeng, A., Wang, B., Zhang, C., Yang, R., Yu, S., & Zhao, W. (2022). Physicochemical properties and antibacterial application of silver nanoparticles stabilized by whey protein isolate. Food Bioscience, 46, 101569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101569
Zhang, B., Wang, Y., & Lu, R. (2023). Pickering emulsion stabilized by casein–caffeic acid covalent nanoparticles to enhance the bioavailability of curcumin in vitro and in vivo. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 103(7), 3579–3591. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.12447
Zhang, D., Zhou, Z., Du, J., Liao, X., Xu, G., Hong, Y., & Xiong, J. (2022). Evaluation of antibacterial and antifungal properties of Lonicera japonica Thunb. Leaves mediated silver nanoparticles and mechanism investigation. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 46(10). https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.16896
Zhang, L., Han, C., Liu, M., Yang, H., Zhang, F., Liu, B., & Meng, X. (2020). The formation, stability of DHA/EPA nanoemulsion prepared by emulsion phase inversion method and its application in apple juice. Food Research International, 133, 109132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109132
Zhang, Z., Vriesekoop, F., Yuan, Q., & Liang, H. (2014). Effects of nisin on the antimicrobial activity of d-limonene and its nanoemulsion. Food Chemistry, 150, 307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.160
Zhou, G., & Hu, W. (2018). Public acceptance of and willingness-to-pay for nanofoods in the U.S. Food Control, 89, 219–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.02.004
Zhou, R., Zhao, L., Wang, Y., Hameed, S., Ping, J., Xie, L., & Ying, Y. (2020). Recent advances in food-derived nanomaterials applied to biosensing. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 127, 115884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115884
Zhao, D., Zhao, Q., Xu, Z., Shi, X. (2022). Preparation of temperature‐sensitive fragrance nanocapsules and its controllable release property. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 37(5) 285–292. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.3711
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), grant #2022/05719-2 and 2021/05508-9, and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for the fellowship given to the students.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Marcelo Gomes Soares: Conceptualization, writing–original draft, writing–review and editing. Gabriel Bevilaqua Cicalese: Writing–original draft, writing–review and editing. Marieli de Lima: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, supervision, writing–review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Soares, M.G., Bevilaqua, G.C. & de Lima, M. Potential Applications of Environmentally Friendly Nanoparticles in Food Matrices: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol 16, 2742–2760 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03101-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03101-5