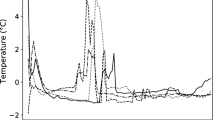
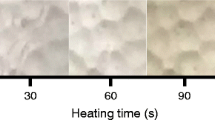
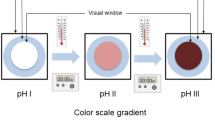
Abstract
Quality deterioration of frozen foods that have been exposed to inadequate temperature control and temporary defrosting cannot be correctly determined by appearance and organoleptic properties alone. Hence, the applicability of a time temperature indicator/integrator (TTI) in the pseudo-visualization of quality deterioration was investigated in this study. The objective of this study was to determine the applicability of a Maillard reaction-based TTI as a monitoring tool for temperature history and quality deterioration of frozen foods during the distribution. The Maillard reaction-based TTI (mixing D-xylose, glycine, and dipotassium hydrogen phosphate aqueous solution) was used to investigate the nature of the responses under sub-zero temperatures. The TTI shows a long-term (~ 15 months) color response at freezing temperatures (ca. −24 °C) and flexibility of the response in the range of −24 to 20 °C, which are validated by the relationship between reaction temperature and reaction rate on an Arrhenius plot (R2 > 0.90). The response of the TTI under sub-zero temperatures, which normally takes a few months to longer than a year, can be predicted by extrapolating the relational expression between temperature and concentration determined from the color change behavior from chilled to 25 °C (R2 > 0.99). In experiments under multiple temperature abuse conditions between −18 °C and 10 °C, the color difference of the TTI increased from 0 to 64–67. The TTI response successfully corresponded to quality deterioration of frozen foods (shrimp and chicken): increases in total viable counts (≥ 7.0 log CFU/g) and total volatile basic nitrogen (≥ 20 mg%). This study demonstrates the usefulness of the Maillard reaction-based TTI as a temperature-monitoring method in the distribution of frozen foods.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
18 June 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02861-w
References
Ahmad, I., & Jeenanunta, C. (2015). Application of support vector classification algorithms for the prediction of quality level of frozen shrimps (Litopenaeus vannamei) suitable for sensor-based time-temperature monitoring. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(1), 134–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1377-8
American Frozen Food Institute (AFFI). (2021). Growth drivers for frozen: Convenience, sustainability and personalization. https://affi.org/growth-drivers-for-frozen-convenience-sustainability-and-personalization/. Accessed on 20 February 2022.
Archer, D. (2004). Freezing: An underutilized food safety technology? International Journal of Food Microbiology, 90(2), 127–138.
Bharti, A. (2014). Examining market challenges pertaining to cold chain in the frozen food industry in Indian retail sector. Journal of Management Sciences and Technology, 2(1), 33–40.
Bobelyn, E., Hertog, M. L., & Nicolaï, B. M. (2006). Applicability of an enzymatic time temperature integrator as a quality indicator for mushrooms in the distribution chain. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 42(1), 104–114.
Byun, J., Min, J., Kim, I., Kim, J., & Chung, M. (2003). Comparison of indicators of microbial quality of meat during aerobic cold storage. Journal of Food Protection, 66, 1733–1737.
Codex Alimentarius Commission. (1994). Code of practice for the processing and handling of quick frozen foods (CAC/RCP 8–1976). Codex Alimentarius, 5, 451–468.
Conway, E. J. (1939). Micro-diffusion analysis and volumetric error, pp 139–144. Crosby Lockwood and Son Ltd, London, U.K.
Chun, J. Y., Choi, M. J., Lee, S. J., & Hong, G. P. (2013). Applications of time-temperature integrator (TTI) as a quality indicator of grounded pork patty. Food Science of Animal Resources, 33(4), 439–447.
de la Cruz Quiroz, R., Rodriguez-Martinez, V., Velazquez, G., Perez, G. M., Fagotti, F., Welti-Chanes, J., & Torres, J. A. (2020). Residential refrigerator performance based on microbial indicators of ground beef preservation assessed using predictive microbiology tools. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(12), 2172–2185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02551-5
Fengjuan, X., Lei, G., Zhenxing, L., Hong, L., & Xiangzhao, M. (2017). Development and application of a tyrosinase-based time-temperature indicator (TTI) for determining the quality of turbot sashimi. Journal of Ocean University of China, 16(5), 847–854.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). (2005). Freezing of fruits and vegetables an agri-business alternative for rural and semi-rural areas. FAO Agricultural Services Bulletin 158. https://www.fao.org/3/y5979e/y5979e00.htm#Contents. Accessed on 6 March 2022.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (1992). Bacteriological analytical manual (7th ed.). Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
Fu, X., Belwal, T., Cravotto, G., & Luo, Z. (2020). Sono-physical and sono-chemical effects of ultrasound: Primary applications in extraction and freezing operations and influence on food components. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 60, 104726.
Giannakourou, M., & Taoukis, P. (2002). Systematic application of time temperature integrators as tools for control of frozen vegetable quality. Journal of Food Science, 67(6), 2221–2228.
Giannakourou, M., & Taoukis, P. (2003). Application of a TTI-based distribution management system for quality optimization of frozen vegetables at the consumer end. Journal of Food Science, 68(1), 201–209.
Giannoglou, M., Touli, A., Platakou, E., Tsironi, T., & Taoukis, P. (2014). Predictive modeling and selection of TTI smart labels for monitoring the quality and shelf-life of frozen seafood. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 26, 294–301.
Han, J. Y., Kim, M. J., Shim, S. D., & Lee, S. J. (2012). Application of fuzzy reasoning to prediction of beef sirloin quality using time temperature integrators (TTIs). Food Control, 24(1–2), 148–153.
Hao, L., Lee, M., Jeon, H., Koo, J., Hwang, S., Oh, D., & Park, J. (2021). Tamper-proof time-temperature indicator for inspecting ultracold supply chain. ACS Omega, 6(12), 8598–8604.
Hayase, F., Takahashi, Y., Tominaga, S., Miura, M., Gomyo, T., & Kato, H. (1999). Identification of blue pigment formed in a D-xylose-glycine reaction system. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 63(8), 1512–1514.
Hsiao, H. I., & Chang, J. N. (2017). Developing a microbial time–temperature indicator to monitor total volatile basic nitrogen change in chilled vacuum-packed grouper fillets. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 41(5), e13158.
Hu, B., Li, L., Hu, Y., Zhao, D., Li, Y., Yang, M., Jia, A., Chen, S., Li, B., & Zhang, X. (2020). Development of a novel Maillard reaction-based time-temperature indicator for monitoring the fluorescent AGE content in reheated foods. Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 10(18), 10402–10410.
International Commission for the Microbiological Specifications of Foods (ICMSF). (1986). Sampling for microbial analysis: Principles and specific applications (2nd ed., pp. 130–154). Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Jafry, A., Lim, H., Sung, W., & Lee, J. (2017). Flexible time–temperature indicator: A versatile platform for laminated paper-based analytical devices. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 21(3), 1–13.
Jaiswal, R., Mendiratta, S., Talukder, S., Chand, S., & Saini, B. (2019). Application of urease based enzymatic time temperature indicator (TTI) as thermal abuse marker for frozen chicken meat quality. The Pharma Innovation Journal, 8(6), 331–334.
Jaiswal, R., Mendiratta, S., Talukder, S., Soni, A., Chand, S., & Saini, B. (2020). Application of lipase based enzymatic time temperature indicator (TTI) as quality marker for frozen chicken meat. Food Science and Technology Research, 26(1), 9–16.
James, C., Purnell, G., & James, S. J. (2015). A review of novel and innovative food freezing technologies. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(8), 1616–1634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1542-8
Japan Food Hygiene Association. (1991). Standard methods of analysis in food safety regulation, pp 269–271.
Jhuanga, J., Linb, S., Chenb, L., Loub, S., Chenb, S., & Chenb, H. (2020a). Development of immobilized laccase-based time temperature indicator by electrospinning zein fiber. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 23, 100436.
Jhuanga, J., Loub, S., Linb, S., Chenb, S., Chenb, L., & Chenb, H. (2020b). Immobilizing laccase on electrospun chitosan fiber to prepare time-temperature indicator for food quality monitoring. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 63, 102370.
Kim, K., Kim, E., & Lee, S. (2012). New enzymatic time-temperature integrator (TTI) that uses laccase. Journal of Food Engineering, 113(1), 118–123.
Kim, M. J., Park, H. R., & Lee, S. J. (2016). Guideline for proper usage of time temperature integrator (TTI) avoiding underestimation of food deterioration in terms of temperature dependency: A case with a microbial TTI and milk. Food Science and Biotechnology, 25(3), 713–719.
Kim, Y. A., Jung, S. W., Park, H. R., Chung, K. Y., & Lee, S. J. (2012). Application of a prototype of microbial time temperature indicator (TTI) to the prediction of ground beef qualities during storage. Food Science of Animal Resources, 32(4), 448–457.
Koutsoumanis, K., & Gougouli, M. (2015). Use of time temperature integrators in food safety management. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 43(2), 236–244.
Kreyenschmidt, J., Christiansen, H., Hubner, A., Raab, V., & Petersen, B. (2010). A novel photochromic time-temperature indicator to support cold chain management. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 45(2), 208–215.
Lee, J., & Harada, R., Kawamura, S., & Koseki, S. (2018a). Development of a novel time-temperature integrator/indicator (TTI) based on the maillard reaction for visual thermal monitoring of the cooking process. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(1), 185–193.
Lee, J., Kawamura, S., & Koseki, S. (2018b). Quantitative evaluation of changes in color during Maillard reaction for development of novel time-temperature integrators/indicators. Food Science and Technology Research, 24(2), 283–287.
Lee, J., Koo, Y., Cho, H., Cha, H., Shin, D., Oh, T., & Lee, S. (2021). Cysteine-loaded pH-responsive liposome/gold nanoparticles as a time-temperature indicator with instantaneous color change. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 73, 102794.
Luo, Z., Yanqun, Xu., & Ye, Q. (2015). Effect of nano-SiO2-LDPE packaging on biochemical, sensory, and microbiological quality of Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei during chilled storage. Fisheries Science, 81(5), 983–993.
Luo, Z., Qin, Y., & Ye, Q. (2015). Effect of nano-TiO2-LDPE packaging on microbiological and physicochemical quality of Pacific white shrimp during chilled storage. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 50(7), 1567–1573.
Mataragas, M., Bikouli, V., Korre, M., Sterioti, A., & Skandamis, P. (2019). Development of a microbial time temperature indicator for monitoring the shelf life of meat. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 52, 89–99.
Meng, J., Qian, J., & Tang, Y. (2018). A solid-state time-temperature indicator used in chilled fresh pork monitoring. Packaging Technology and Science, 31(5), 353–360.
Miura, M., & Gomyo, T. (1982). Formation of blue pigment in the earlier stage of browning in the system composed of D-xylose and glycine. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi, 56(6), 417–425.
Montanari, R. (2008). Cold chain tracking: A managerial perspective. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 19(8), 425–431.
Ndraha, N., Hsiao, H., Vlajic, J., Yang, M., & Lin, H. (2018). Time-temperature abuse in the food cold chain: Review of issues, challenges, and recommendations. Food Control, 89, 12–21.
Pandian, A., Chaturvedi, S., & Chakraborty, S. (2020). Applications of enzymatic time–temperature indicator (TTI) devices in quality monitoring and shelf-life estimation of food products during storage. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 15(2), 1523–1540.
Pearson, D. (1976). The chemical analysis of foods (No. Ed. 7). Longman Group Ltd.
Rajan, V., Gurubathan, K., & Shukla, V. (2017). Development and evaluation of time-temperature integrator for monitoring high temperature thawing of frozen buffalo meat. Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, 41(4), 496–505.
Rokugawa, H., & Fujikawa, H. (2015). Evaluation of a new Maillard reaction type time-temperature integrator at various temperatures. Food Control, 57, 355–361.
Saenjaiban, A., Singtisan, T., Suppakul, P., Jantanasakulwong, K., Punyodom, W., & Rachtanapun, P. (2020). Novel color change film as a time–temperature indicator using polydiacetylene/silver nanoparticles embedded in carboxymethyl cellulose. Polymers, 12(10), 1–14.
Sakai, K., Lee, J., Kocharunchitt, C., Ross, T., Jenson, I., Koyama, K., & Koseki, S. (2020). Development of a Maillard reaction–based time-temperature integrator/indicator (TTI) for visual monitoring of chilled beef during long-term storage and distribution. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(12), 2094–2103.
Sánchez-Valencia, J., Sánchez-Alonso, I., Martinez, I., & Careche, M. (2015). Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance of proton (1H LF NMR) relaxometry for monitoring the time and temperature history of frozen hake (Merluccius merluccius L.) muscle. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(10), 2137–2145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1569-x
Syamaladevi, R., Manahiloh, K., Muhunthan, B., & Sablani, S. (2012). Understanding the influence of state/phase transitions on ice recrystallization in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) during frozen storage. Food Biophysics, 7(1), 57–71.
Taoukis, P. (2001). Modelling the use of time-temperature indicators in distribution and stock rotation. Food Process Modelling, 19, 402–431.
Taoukis, P., & Labuza, T. (1989). Applicability of time-temperature indicators as shelf life monitors of food products. Journal of Food Science, 54(4), 783–788.
Taoukis, P., & Labuza, T. (2003). Time-temperature indicators (TTI). In: Novel Food Packaging Techniques, 6, 103–126.
Taoukis, P., Labuza, T., & Saguy, I. (1997). Kinetics of food deterioration and shelf-life prediction. In: The Handbook of Food Engineering Practice, Valentas. K., Rotstein. E. and Singh. R. (eds), CRC Press Boca Raton New York, 9, 367–409.
Tingman, W., Jian, Z., & Xiaoshuan, Z. (2010). Fish product quality evaluation based on temperature monitoring in cold chain. African Journal of Biotechnology, 9(37), 6146–6151.
Tsai, T., Chen, S., Chen, L., Lin, S., Lou, S., Chen, Y., & Chen, H. (2021). Enzymatic time-temperature indicator prototype developed by immobilizing laccase on electrospun fibers to predict lactic acid bacterial growth in milk during storage. Nanomaterials, 11(5), 1160.
Tsironi, T., Dermesonlouoglou, E., Giannakourou, M., & Taoukis, P. (2009). Shelf life modelling of frozen shrimp at variable temperature conditions. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 42(2), 664–671.
Tsironi, T., Giannoglou, M., Platakou, E., & Taoukis, P. (2016). Evaluation of time temperature integrators for shelf-life monitoring of frozen seafood under real cold chain conditions. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 10, 46–53.
Tsironi, T., Stamatiou, A., Giannoglou, M., Velliou, E., & Taoukis, P. (2011). Predictive modelling and selection of time temperature integrators for monitoring the shelf life of modified atmosphere packed gilthead seabream fillet. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 44(4), 1156–1163.
Tsironi, T., Stoforos, N., & Taoukis, P. (2020). Quality and shelf-life modeling of frozen fish at constant and variable temperature conditions. Foods, 9(12), 1893.
Uddin, Z., & Boonsupthip, W. (2019). Development and characterization of a new nonenzymatic colored time–temperature indicator. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 42(4), e13027.
Ullah, J., Takhar, P., & Sablani, S. (2014). Effect of temperature fluctuations on ice-crystal growth in frozen potatoes during storage. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 59, 1186–1190.
Vaikousi, H., Biliaderis, C., & Koutsoumanis, K. (2008). Development of a microbial time/temperature indicator prototype for monitoring the microbiological quality of chilled foods. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(10), 3242–3250.
Vaikousi, H., Biliaderis, C., & Koutsoumanis, K. (2009). Applicability of a microbial time temperature indicator (TTI) for monitoring spoilage of modified atmosphere packed minced meat. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 133(3), 272–278.
Wang, Y., Liang, H., Xu, R., Lu, B., Song, X., & Liu, B. (2020). Effects of temperature fluctuations on the meat quality and muscle microstructure of frozen beef. International Journal of Refrigeration, 116, 1–8.
Wang, Y., Lu, L., & Gunasekaran, S. (2017). Biopolymer/gold nanoparticles composite plasmonic thermal history indicator to monitor quality and safety of perishable bioproducts. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 92, 109–116.
World Food Logistics Organization (WFLO). (2008). Frozen foods handling & storage. WFLO Commodity Storage Manual.
Yamamoto, T., & Isshiki, K. (2012). Development of the indicator using Maillard reaction to warn against the temperature rise of the chilled food. Japanese Journal of Food Chemistry and Safety, 19(2), 84–87.
Yang, J., & Xu, Y. (2021). Prediction of fruit quality based on the RGB values of time–temperature indicator. Journal of Food Science, 86(3), 932–941.
Ye, B., Chen, J., Ye, H., Zhang, Y., Yang, Q., Yu, H., Fu, L., & Wang, Y. (2022). Development of a time–temperature indicator based on Maillard reaction for visually monitoring the freshness of mackerel. Food Chemistry, 373, 131448.
Yin, Z., Sun, Q., Zhang, X., & Jing, H. (2014). Optimised formation of blue Maillard reaction products of xylose and glycine model systems and associated antioxidant activity. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 94(7), 1332–1339.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsujihashi, M., Tanaka, S., Koayama, K. et al. Application of Time–Temperature Indicator/Integrator Based on the Maillard Reaction to Frozen Food Distribution. Food Bioprocess Technol 15, 1343–1358 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02821-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02821-4