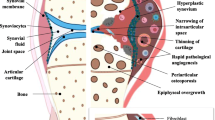
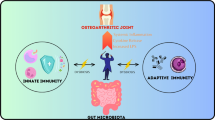
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Current technical advances enable the assessment of the complex changes in body fluid proteomes and thus allow for the discovery of biomarker signatures rather than just following differences of a single marker. In this review, we aim to summarize current approaches to discover and evaluate multi-biomarker panels for improved monitoring of chronic arthritis disease activity.
Recent Findings
Mass spectrometry and affinity proteomic methodologies have been used to identify biomarker panels in synovial fluid, serum, plasma, or urine of pediatric and adult chronic arthritis patients. Notably, despite the numerous efforts to develop new and better biomarker panels, very few have undergone extensive analytical and clinical validation and been adopted into routine use for patient benefit.
Summary
There remains a significant gap between discovery of chronic arthritis biomarker signatures and their validation for clinical use.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Wasinger VC, Cordwell SJ, Cerpa-Poljak A, Yan JX, Gooley AA, Wilkins MR, et al. Progress with gene-product mapping of the Mollicutes: Mycoplasma genitalium. Electrophoresis. 1995;16(7):1090–4.
Pennington SR, Wilkins MR, Hochstrasser DF, Dunn MJ. Proteome analysis: from protein characterization to biological function. Trends Cell Biol. 1997;7(4):168–73.
Aebersold R, Mann M. Mass-spectrometric exploration of proteome structure and function. Nature. 2016;537(7620):347–55.
Gibson DS, Rooney ME, Finnegan S, Qiu J, Thompson DC, Labaer J, et al. Biomarkers in rheumatology, now and in the future. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51(3):423–33.
Poste G. Bring on the biomarkers. Nature. 2011;469(7329):156–7.
Poste G. Biospecimens, biomarkers, and burgeoning data: the imperative for more rigorous research standards. Trends Mol Med. 2012;18(12):717–22.
Horvath AR, Lord SJ, StJohn A, Sandberg S, Cobbaert CM, Lorenz S, et al. From biomarkers to medical tests: the changing landscape of test evaluation. Clin Chim Acta. 2014;427:49–57.
Horvath AR, Bossuyt PM, Sandberg S, John AS, Monaghan PJ, Verhagen-Kamerbeek WD, et al. Setting analytical performance specifications based on outcome studies—is it possible? Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015;53(6):841–8.
Sandberg S, Fraser CG, Horvath AR, Jansen R, Jones G, Oosterhuis W, et al. Defining analytical performance specifications: Consensus Statement from the 1st Strategic Conference of the European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015;53(6):833–5.
Skates SJ, Gillette MA, LaBaer J, Carr SA, Anderson L, Liebler DC, et al. Statistical design for biospecimen cohort size in proteomics-based biomarker discovery and verification studies. J Proteome Res. 2013;12(12):5383–94.
Monaghan PJ, Lord SJ, St John A, Sandberg S, Cobbaert CM, Lennartz L, et al. Biomarker development targeting unmet clinical needs. Clin Chim Acta. 2016;460:211–9.
Lollo B, Steele F, Gold L. Beyond antibodies: new affinity reagents to unlock the proteome. Proteomics. 2014;14(6):638–44.
Langham S, Langham J, Goertz HP, Ratcliffe M. Large-scale, prospective, observational studies in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic and critical review. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11:32.
Song JW, Chung KC. Observational studies: cohort and case-control studies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(6):2234–42.
Mc Ardle A, Flatley B, Pennington SR, FitzGerald O. Early biomarkers of joint damage in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:141.
Mamdani M, Sykora K, Li P, Normand SL, Streiner DL, Austin PC, et al. Reader’s guide to critical appraisal of cohort studies: 2. Assessing potential for confounding. BMJ. 2005;330(7497):960–2.
Rissin DM, Kan CW, Campbell TG, Howes SC, Fournier DR, Song L, et al. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(6):595–9.
• Rodero MP, Decalf J, Bondet V, Hunt D, Rice GI, Werneke S, et al. Detection of interferon alpha protein reveals differential levels and cellular sources in disease. J Exp Med. 2017;214(5):1547–55. First published application of digital ELISA for quantification of interferon α.
Gold L, Ayers D, Bertino J, Bock C, Bock A, Brody EN, et al. Aptamer-based multiplexed proteomic technology for biomarker discovery. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e15004.
Lundberg M, Thorsen SB, Assarsson E, Villablanca A, Tran B, Gee N, et al. Multiplexed homogeneous proximity ligation assays for high-throughput protein biomarker research in serological material. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011;10(4):M110 004978.
Lundberg M, Eriksson A, Tran B, Assarsson E, Fredriksson S. Homogeneous antibody-based proximity extension assays provide sensitive and specific detection of low-abundant proteins in human blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(15):e102.
Collins BC, Miller CA, Sposny A, Hewitt P, Wells M, Gallagher WM, et al. Development of a pharmaceutical hepatotoxicity biomarker panel using a discovery to targeted proteomics approach. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012;11(8):394–410.
Adkins JN, Varnum SM, Auberry KJ, Moore RJ, Angell NH, Smith RD, et al. Toward a human blood serum proteome: analysis by multidimensional separation coupled with mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2002;1(12):947–55.
Silva AM, Vitorino R, Domingues MR, Spickett CM, Domingues P. Post-translational modifications and mass spectrometry detection. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;65:925-41.
Verheul MK, van Veelen PA, van Delft MAM, de Ru A, Janssen GMC, Rispens T, et al. Pitfalls in the detection of citrullination and carbamylation. Autoimmun Rev. 2018;17(2):136-41.
Kokkonen H, Soderstrom I, Rocklov J, Hallmans G, Lejon K, Rantapaa DS. Up-regulation of cytokines and chemokines predates the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(2):383–91.
Centola M, Cavet G, Shen Y, Ramanujan S, Knowlton N, Swan KA, et al. Development of a multi-biomarker disease activity test for rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60635.
Eastman PS, Manning WC, Qureshi F, Haney D, Cavet G, Alexander C, et al. Characterization of a multiplex, 12-biomarker test for rheumatoid arthritis. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;70:415–24.
Sokolove J, Bromberg R, Deane KD, Lahey LJ, Derber LA, Chandra PE, et al. Autoantibody epitope spreading in the pre-clinical phase predicts progression to rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e35296.
Chandra PE, Sokolove J, Hipp BG, Lindstrom TM, Elder JT, Reveille JD, et al. Novel multiplex technology for diagnostic characterization of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis research & therapy. 2011;13(3):R102.
Brink M, Hansson M, Mathsson L, Jakobsson PJ, Holmdahl R, Hallmans G, et al. Multiplex analyses of antibodies against citrullinated peptides in individuals prior to development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2013;65(4):899–910.
• Too CL, Murad S, Hansson M, Alm LM, Dhaliwal JS, Holmdahl R, et al. Differences in the spectrum of anti-citrullinated protein antibody fine specificities between Malaysian and Swedish patients with rheumatoid arthritis: implications for disease pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(1):58–69. Peptide array identifying disease-related antibody profiles.
Tong D, Lonnblom E, Yau ACY, Nandakumar KS, Liang B, Ge C, et al. A shared epitope of collagen type XI and type II is recognized by pathogenic antibodies in mice and humans with arthritis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:451.
Ramirez J, Inciarte-Mundo J, Cuervo A, Ruiz-Esquide V, Hernandez MV, Sanmarti R, et al. Differing local and systemic inflammatory burden in polyarticular psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis patients on anti-TNF treatment in clinical remission. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(1):74–9.
Chen J, Doyle TJ, Liu Y, Aggarwal R, Wang X, Shi Y, et al. Biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(1):28–38.
Watanabe J, Charles-Schoeman C, Miao Y, Elashoff D, Lee YY, Katselis G, et al. Proteomic profiling following immunoaffinity capture of high-density lipoprotein: association of acute-phase proteins and complement factors with proinflammatory high-density lipoprotein in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1828–37.
Smolenska Z, Smolenski RT, Zdrojewski Z. Plasma concentrations of amino acid and nicotinamide metabolites in rheumatoid arthritis—potential biomarkers of disease activity and drug treatment. Biomarkers : biochemical indicators of exposure, response, and susceptibility to chemicals. 2016;21(3):218–24.
Ahmed U, Anwar A, Savage RS, Costa ML, Mackay N, Filer A, et al. Biomarkers of early stage osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and musculoskeletal health. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9259.
Zhang X, Yuan Z, Shen B, Zhu M, Liu C, Xu W. Discovery of serum protein biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis using MALDI-TOF-MS combined with magnetic beads. Clin Exp Med. 2012;12(3):145–51.
Reindl J, Pesek J, Kruger T, Wendler S, Nemitz S, Muckova P, et al. Proteomic biomarkers for psoriasis and psoriasis arthritis. J Proteome. 2016;140:55–61.
Blaschke S, Rinke K, Maring M, Flad T, Patschan S, Jahn O, et al. Haptoglobin-alpha1, -alpha2, vitamin D-binding protein and apolipoprotein C-III as predictors of etanercept drug response in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis research & therapy. 2015;17:45.
Trocme C, Marotte H, Baillet A, Pallot-Prades B, Garin J, Grange L, et al. Apolipoprotein A-I and platelet factor 4 are biomarkers for infliximab response in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(8):1328–33.
de Jager W, Hoppenreijs EP, Wulffraat NM, Wedderburn LR, Kuis W, Prakken BJ. Blood and synovial fluid cytokine signatures in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a cross-sectional study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(5):589–98.
Kessel C, Lippitz K, Weinhage T, Hinze C, Wittkowski H, Holzinger D, et al. Proinflammatory cytokine environments can drive interleukin-17 overexpression by gamma/delta T cells in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(7):1480–94.
•• Bracaglia C, de Graaf K, Pires Marafon D, Guilhot F, Ferlin W, Prencipe G, et al. Elevated circulating levels of interferon-gamma and interferon-gamma-induced chemokines characterise patients with macrophage activation syndrome complicating systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(1):166–72. Important multiplexed biomarker profiling in pediatric rheumatology
Ling XB, Lau K, Deshpande C, Park JL, Milojevic D, Macaubas C, et al. Urine peptidomic and targeted plasma protein analyses in the diagnosis and monitoring of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Proteomics. 2010;6(4):175–93.
Gibson DS, Blelock S, Curry J, Finnegan S, Healy A, Scaife C, et al. Comparative analysis of synovial fluid and plasma proteomes in juvenile arthritis—proteomic patterns of joint inflammation in early stage disease. J Proteome. 2009;72(4):656–76.
•• Reiss WG, Devenport JN, Low JM, Wu G, Sasso EH. Interpreting the multi-biomarker disease activity score in the context of tocilizumab treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2016;36(2):295–300. Treatment directly affecting MBDA scores.
Curtis JR, van der Helm-van Mil AH, Knevel R, Huizinga TW, Haney DJ, Shen Y, et al. Validation of a novel multibiomarker test to assess rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(12):1794–803.
Todd DJ, Knowlton N, Amato M, Frank MB, Schur PH, Izmailova ES, et al. Erroneous augmentation of multiplex assay measurements in patients with rheumatoid arthritis due to heterophilic binding by serum rheumatoid factor. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(4):894–903.
Nishimoto N, Terao K, Mima T, Nakahara H, Takagi N, Kakehi T. Mechanisms and pathologic significances in increase in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor after administration of an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman disease. Blood. 2008;112(10):3959–64.
de Jager W, Bourcier K, Rijkers GT, Prakken BJ, Seyfert-Margolis V. Prerequisites for cytokine measurements in clinical trials with multiplex immunoassays. BMC Immunol. 2009;10:52.
Elshal MF, McCoy JP. Multiplex bead array assays: performance evaluation and comparison of sensitivity to ELISA. Methods. 2006;38(4):317–23.
de Jager W, Prakken BJ, Bijlsma JW, Kuis W, Rijkers GT. Improved multiplex immunoassay performance in human plasma and synovial fluid following removal of interfering heterophilic antibodies. J Immunol Methods 2005;300(1–2):124–135.
Hirata S, Dirven L, Shen Y, Centola M, Cavet G, Lems WF, et al. A multi-biomarker score measures rheumatoid arthritis disease activity in the BeSt study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52(7):1202–7.
Bakker MF, Cavet G, Jacobs JW, Bijlsma JW, Haney DJ, Shen Y, et al. Performance of a multi-biomarker score measuring rheumatoid arthritis disease activity in the CAMERA tight control study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(10):1692–7.
Hambardzumyan K, Bolce R, Saevarsdottir S, Cruickshank SE, Sasso EH, Chernoff D, et al. Pretreatment multi-biomarker disease activity score and radiographic progression in early RA: results from the SWEFOT trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1102–9.
Rech J, Hueber AJ, Finzel S, Englbrecht M, Haschka J, Manger B, et al. Prediction of disease relapses by multibiomarker disease activity and autoantibody status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis on tapering DMARD treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(9):1637–44.
•• Hambardzumyan K, Saevarsdottir S, Forslind K, Petersson IF, Wallman JK, Ernestam S, et al. A multi-biomarker disease activity score and the choice of second-line therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis after methotrexate failure. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(5):953–63. Use of MBDA for therapeutic decision-making in RA.
Fleischmann R, Connolly SE, Maldonado MA, Schiff M. Brief report: estimating disease activity using multi-biomarker disease activity scores in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with abatacept or adalimumab. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(9):2083–9.
Kessel C, Holzinger D, Foell D. Phagocyte-derived S100 proteins in autoinflammation: putative role in pathogenesis and usefulness as biomarkers. Clin Immunol. 2013;147(3):229–41.
Holzinger D, Kessel C, Omenetti A, Gattorno M. From bench to bedside and back again: translational research in autoinflammation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(10):573–85.
Foell D, Wulffraat N, Wedderburn LR, Wittkowski H, Frosch M, Gerss J, et al. Methotrexate withdrawal at 6 vs 12 months in juvenile idiopathic arthritis in remission: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2010;303(13):1266–73.
Frosch M, Strey A, Vogl T, Wulffraat NM, Kuis W, Sunderkotter C, et al. Myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 are specifically secreted during interaction of phagocytes and activated endothelium and are useful markers for monitoring disease activity in pauciarticular-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(3):628–37.
Wittkowski H, Frosch M, Wulffraat N, Goldbach-Mansky R, Kallinich T, Kuemmerle-Deschner J, et al. S100A12 is a novel molecular marker differentiating systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis from other causes of fever of unknown origin. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(12):3924–31.
Gerss J, Roth J, Holzinger D, Ruperto N, Wittkowski H, Frosch M, Wulffraat N, Wedderburn L, Stanevicha V, Mihaylova D, Harjacek M, Len C, Toppino C, Masi M, Minden K, Saurenmann T, Uziel Y, Vesely R, Apaz MT, Kuester RM, Elorduy MJR, Burgos-Vargas R, Ioseliani M, Magni-Manzoni S, Unsal E, Anton J, Balogh Z, Hagelberg S, Mazur-Zielinska H, Tauber T, Martini A, Foell D, for the Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organization (PRINTO) Phagocyte-specific S100 proteins and high-sensitivity C reactive protein as biomarkers for a risk-adapted treatment to maintain remission in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a comparative study. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71(12):1991–1997.
Holzinger D, Frosch M, Kastrup A, Prince FH, Otten MH, Van Suijlekom-Smit LW, et al. The Toll-like receptor 4 agonist MRP8/14 protein complex is a sensitive indicator for disease activity and predicts relapses in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(6):974–80.
Baillet A, Trocme C, Berthier S, Arlotto M, Grange L, Chenau J, et al. Synovial fluid proteomic fingerprint: S100A8, S100A9 and S100A12 proteins discriminate rheumatoid arthritis from other inflammatory joint diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(4):671–82.
Xia Y, Cui P, Li Q, Liang F, Li C, Yang J. Extremely elevated IL-18 levels may help distinguish systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis from other febrile diseases. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017;50(2):e5958.
Shimizu M, Nakagishi Y, Inoue N, Mizuta M, Ko G, Saikawa Y, et al. Interleukin-18 for predicting the development of macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Immunol. 2015;160(2):277–81.
Holzinger D, Kessel C, Fall N, Grom A, de jager W, Vastert S et al. S100A12 as diagnostic tool in the differential diagnosis of SJIA associated MAS vs. primary or acquired HLH. Pediatric Rheumatology 2016(Supplement 1):P297.
•• McArdle A, Qasim Butt A, Szentpetery A, de Jager W, de Roock S, FitzGerald O, et al. Developing clinically relevant biomarkers in inflammatory arthritis: a multiplatform approach for serum candidate protein discovery. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016;10(6):691–8.
Hirata S, Li W, Defranoux N, Cavet G, Bolce R, Yamaoka K, et al. A multi-biomarker disease activity score tracks clinical response consistently in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with different anti-tumor necrosis factor therapies: a retrospective observational study. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(3):344–9.
Lee YC, Hackett J, Frits M, Iannaccone CK, Shadick NA, Weinblatt ME, et al. Multibiomarker disease activity score and C-reactive protein in a cross-sectional observational study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis with and without concomitant fibromyalgia. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(4):640–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
DF declares the receipt of research grant support and honoraria from Pfizer, Novartis, Sobi, and Chugai-Roche. The UCD Conway Institute and Proteomics Core is funded by the Programme for Research in Third level Institutions, as administered by Higher Education Authority of Ireland. Research in SRP’s lab is supported by grants from the Health Research Board, Enterprise Ireland and Science Foundation Ireland and previously including the EU funded FP7 MIAMI project. Dr. Pennington reports role as Founder and CSO of Atturos (www.atturos.com) which is developing prostate cancer multiplexed protein biomarker test on MRM platform. Drs. Kessel and Foell have a patent “means and methods for diagnosing and treating inflammatory disorders” (WO 2016/178154 A1) issued to Muenster University. Dr. Foell has a patent “means and methods for diagnosing and treating inflammatory disorders” (WO 2016/178154 A1) issued to Muenster University. Angela McArdle, Emely Verweyen, Toni Weinhage, and Helmut Wittkowski declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Pediatric Rheumatology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kessel, C., McArdle, A., Verweyen, E. et al. Proteomics in Chronic Arthritis—Will We Finally Have Useful Biomarkers?. Curr Rheumatol Rep 20, 53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-018-0762-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-018-0762-0