Abstract
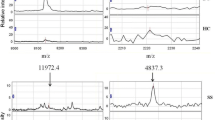
The aim of this study was to discover potential biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with magnetic beads. Proteomic fingerprint technology combining magnetic beads with MALDI-TOF-MS was used to profile and compare the proteomes in serum samples from 60 patients with RA, 35 patients with osteoarthritis and 36 healthy controls. The proteomic pattern associated with RA was identified by Biomarker Patterns Software. Model of biomarkers was constructed and evaluated through the Biomarker Patterns Software. A total of 33 discriminative peaks were identified to be related with RA, in which the 5 peaks with the mass–charge ratio (m/z) peaks at 15,715.5, 7,771.4, 8,959.4, 8,469.8 and 8,710.8 Da were used to construct a model for the diagnosis of RA by pattern recognition software. The blind testing data indicated a sensitivity of 86.7% and a specificity of 90.0% in RA diagnosis. These results demonstrated that potential protein biomarkers for RA could be discovered in serum by MALDI-TOF-MS combined with WCX magnetic beads. The diagnosis mode tree based on the five candidate biomarkers could provide a powerful and reliable diagnostic method for RA with high sensitivity and specificity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoffman IE, Peene I, Pottel H et al (2005) Diagnostic performance and predictive value of rheumatoid factor, anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies, and the HLA shared epitope for diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem 51:261–263
Pincus T, Sokka T (2009) Laboratory tests to assess patients with rheumatoid arthritis: advantages and limitations. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 35:731–734
Steiner G, Smolen J (2002) Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and their clinical significance. Arthritis Res 4:S1–S5
Lee AN, Beck CE, Hall M (2008) Rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: a review. Clin Lab Sci 21:15–18
Maurya P, Meleady P, Dowling P et al (2007) Proteomic approaches for serum biomarker discovery in cancer. Anticancer Res 27:1247–1255
Gámez-Pozo A, Sánchez-Navarro I, Nistal M et al (2009) MALDI profiling of human lung cancer subtypes. PLoS One 4:e7731
Shi L, Zhang J, Wu P et al (2009) Discovery and identification of potential biomarkers of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proteome Sci 7:7
Zhang X, Guo T, Wang H et al (2008) Potential biomarkers of acute cerebral infarction detected by SELDI-TOF-MS. Am J Clin Pathol 130:299–304
Zhou M, Veenstra T (2008) Mass spectrometry: m/z 1983–2008. Biotechniques 44:667–668, 670
Sparbier K, Wenzel T, Dihazi H et al (2009) Immuno-MALDI-TOF-MS: new perspectives for clinical applications of mass spectrometry. Proteomics 9:1442–1450
Wang P, Whiteaker JR, Paulovich AG (2009) The evolving role of mass spectrometry in cancer biomarker discovery. Cancer Biol Ther 8:1083–1094
Pietrowska M, Marczak L, Polanska J et al (2009) Mass spectrometry-based serum proteome pattern analysis in molecular diagnostics of early stage breast cancer. J Transl Med 7:60
Guo R, Pan C, Shen J et al (2011) New serum biomarkers for detection of esophageal carcinoma using Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137:513–519
Wang QT, Li YZ, Liang YF et al (2009) Construction of a multiple myeloma diagnostic model by magnetic bead-based MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry of serum and pattern recognition software. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 292:604–610
Marshall J, Kupchak P, Zhu W et al (2003) Processing of serum proteins underlies the mass spectral fingerprinting of myocardial infarction. J Proteome Res 2:361–372
Breiman L, Friedman JH, Olshen RA, Stone CJ (1984) Classification and regression trees. Wadsworth, Belmont
Van Vollenhoven RF (2009) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: state of the art 2009. Nat Rev Rheumatol 5:531–541
Wong SC, Chan CM, Ma BB et al (2009) Advanced proteomic technologies for cancer biomarker discovery. Expert Rev Proteomics 6:123–134
Choolani M, Narasimhan K, Kolla V et al (2009) Proteomic technologies for prenatal diagnostics: advances and challenges ahead. Expert Rev Proteomics 6:87–101
Wu T, Mohan C (2009) Proteomic toolbox for autoimmunity research. Autoimmun Rev 8:595–598
Kelleher MT, Fruhwirth G, Patel G et al (2009) The potential of optical proteomic technologies to individualize prognosis and guide rational treatment for cancer patients. Target Oncol 4:235–252
Peter JF, Otto AM (2010) Magnetic particles as powerful purification tool for high sensitive mass spectrometric screening procedures. Proteomics 10:628–633
Whiteaker JR, Zhao L, Zhang HY et al (2007) Antibody-based enrichment of peptides on magnetic beads for mass-spectrometry-based quantification of serum biomarkers. Anal Biochem 362:44–54
Li YZ, Hu CJ, Leng XM et al (2009) Promising diagnostic biomarkers for primary biliary cirrhosis identified with magnetic beads and MALDI-TOF-MS. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 292:455–460
Visser H, le Cessie S, Vos K et al (2002) How to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis early: a prediction model for persistent (erosive) arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:357–365
Goëb V, Thomas-L’Otellier M, Daveau R et al (2009) Candidate autoantigens identified by mass spectrometry in early rheumatoid arthritis are chaperones and citrullinated glycolytic enzymes. Arthritis Res Ther 11:R38
Huang Z, Shi Y, Cai B et al (2009) MALDI-TOF-MS combined with magnetic beads for detecting serum protein biomarkers and establishment of boosting decision tree model for diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxf) 48:626–631
Komurasaki R, Imaoka S, Tada N et al (2010) LKM-1 sera from autoimmune hepatitis patients that recognize ERp57, carboxylester-ase 1 and CYP2D6. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 25:84–92
Giusti L, Baldini C, Bazzichi L et al (2007) Proteomic diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Expert Rev Proteomics 4:757–767
Uchida T, Fukawa A, Uchida M et al (2002) Application of a novel protein biochip technology for detection and identification of rheumatoid arthritis biomarkers in synovial fluid. J Proteome Res 1:495–499
de Seny D, Fillet M, Meuwis MA et al (2005) Discovery of new rheumatoid arthritis biomarkers using the surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry proteinchip approach. Arthritis Rheum 52:3801–3812
Acknowledgments
Supported by grant 2007B225 from Medical Technology Program of Zhejiang and grant 2010C33001 from Science Technology of Zhejiang Province.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiaoxue Zhang and Bo Shen equally contribute to the work as first coauthors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yuan, Z., Shen, B. et al. Discovery of serum protein biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis using MALDI-TOF-MS combined with magnetic beads. Clin Exp Med 12, 145–151 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-011-0154-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-011-0154-5