Abstract
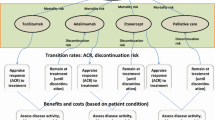
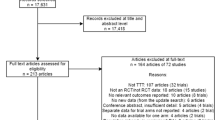
The objective of the work reported in this paper was to critically assess how sequential disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) have been modelled in the context of economic evaluation of the use of DMARDs for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A secondary purpose was to identify the methodological challenges of modelling sequential therapies. Systematic searches of 10 databases were undertaken in February 2013. Studies were included if they were in the English language and a full comparative economic evaluation was reported. They were appraised by use of the Drummond checklist (Appendix to this paper). Data extracted included economic evaluation data, data relating to sequential treatment, and data on the modelling methods used. Fifty-seven studies were identified, with 25 (44 %) modelling a sequence of treatments. Forty-three (75 %) were cost–utility analyses. Eleven (19 %) were UK studies and 11 (19 %) were US. The remainder were mainly European (26 (46 %)). A distinction was made between studies of recent-onset RA (14 (25 %)) and those of established RA (42 (74 %)). One study (1 %) was unclear. Individual-level models were more likely to meet the Drummond criteria and evaluate sequences. No study identified an optimum sequence of multiple treatments given a set of treatment options. The level of reporting of the methods and evidence used to assess the effect of downstream treatments in the sequence was generally poor. When lifelong models and downstream treatment sequences were considered, evidence gaps were identified. The review discovered that methods have not been consistently applied, leading to varied estimates of cost-effectiveness. Treatment sequences have not been fully considered and modelled, potentially resulting in inaccurate estimates of cost-effectiveness.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Symmons D. The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United Kingdom: new estimates for a new century. Rheumatology. 2002;41:793–800. Available from: http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/41/7/793
Wolfe F, Michaud K. Predicting mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.11024/full
Burton W, Morrison A, Maclean R, Ruderman E. Systematic review of studies of productivity loss due to rheumatoid arthritis. Occup. Med. (Lond). 2006;56:18–27. Available from: http://occmed.oxfordjournals.org/content/56/1/18.short
Kobelt G, Jönsson L, Lindgren P, Young A, Eberhardt K. Modeling the progression of rheumatoid arthritis: a two-country model to estimate costs and consequences of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:2310–9. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12355478
Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollenhoven R, et al. The PREMIER study: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previo. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:26–37. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.21519/full
Charles PJ, Smeenk RJ, De Jong J, Feldmann M, Maini RN. Assessment of antibodies to double-stranded DNA induced in rheumatoid arthritis patients following treatment with infliximab, a monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha: findings in open-label and randomized placebo-controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2383–90. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11083258
St Clair EW, van der Heijde DMFM, Smolen JS, Maini RN, Bathon JM, Emery P, et al. Combination of infliximab and methotrexate therapy for early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3432–43. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15529377
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;343:1594–602. Available from: http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejm200011303432202
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, et al. A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;343:1586–93. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11096165
Maini R, Clair ES, Breedveld F, Furst D. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a. Lancet. 1999; Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673699052460
Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, Bulpitt KJ, Fleischmann RM, Fox RI, et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;340:253–9. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9920948
Weinblatt ME, Keystone EC, Furst DE, Moreland LW, Weisman MH, Birbara CA, et al. Adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in patients taking concomitant methotrexate: the ARMADA trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:35–45. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.10697/full
Gartlehner G, Hansen RA, Jonas BL, Thieda P, Lohr KN. The comparative efficacy and safety of biologics for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J. Rheumatol. 2006;33:2398–408. Available from: http://www.jrheum.org/content/33/12/2398.short
Singh JA, Christensen R, Wells GA, Suarez-Almazor ME, Buchbinder R, Lopez-Olivo MA, et al. A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of biologics for rheumatoid arthritis: a Cochrane overview. CMAJ. 2009;181:787–96. Available from: http://www.cmaj.ca/content/181/11/787.short
Wiens A, Venson R, Correr CJ, Otuki MF, Pontarolo R. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacotherapy. 2010;30:339–53. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1592/phco.30.4.339/abstract
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (TA130). 2007.
Brennan A, Akehurst R. Modelling in health economic evaluation. Pharmacoeconomics. 2000; Available from: http://www.med.mcgill.ca/epidemiology/courses/EPIB654/Summer2010/Modeling/Brennan PharmEco00.pdf
Bansback N, Ara R, Karnon J, Anis A. Economic evaluations in rheumatoid arthritis: a critical review of measures used to define health States. Pharmacoeconomics. 2008;26:395–408. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18429656
National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions. Rheumatoid arthritis: national clinical guideline for management and treatment in adults. London; 2009.
Drummond MF, Sculpher MJ, Torrance GW. Methods for the Economic Evaluation of Health Care Programmes. Oxford University Press; 2005. p. 379. Available from: http://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=xyPLJIiEn7cC&pgis=1
Chen Y-F, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W, et al. A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness. Health Technol. Assess. England: West Midlands Health Technology Assessment Collaboration (WMHTAC), Department of Public Health and Epidemiology, University of Birmingham, UK.; 2006. p. iii–229. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=17049139
Davies A, Cifaldi MA, Segurado OG, Weisman MH. Cost-effectiveness of sequential therapy with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in early rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. Canada: United BioSource Corporation, London, UK. andy.davies@oxfordoutcomes.com; 2009. p. 16–26. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=19012363
Finckh A, Bansback N, Marra CA, Anis AH, Michaud K, Lubin S, et al. Treatment of very early rheumatoid arthritis with symptomatic therapy, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or biologic agents: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. United States: Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland.; 2009. p. 612–21. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=19884622
Hartman M, van Ede A, Severens JL, Laan RFJM, van de Putte L, van der Wilt GJ. Economic evaluation of folate supplementation during methotrexate treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. [Internet]. J. Rheumatol. Canada: Department of Medical Technology Assessment, University Medical Centre, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. M.Moret@mta.umcn.nl; 2004. p. 902–8. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=15124248
Kobelt G, Lekander I, Lang A, Raffeiner B, Botsios C, Geborek P. Cost-effectiveness of etanercept treatment in early active rheumatoid arthritis followed by dose adjustment. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care. England: Lund University and European Health Economics.; 2011. p. 193–200. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=21736857
Maetzel A, Strand V, Tugwell P, Wells G, Bombardier C. Cost effectiveness of adding leflunomide to a 5-year strategy of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. United States: University Health Network Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. maetzel@uhnres.utoronto.ca; 2002. p. 655–61. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=12522841
Schipper LG, Kievit W, den Broeder AA, van der Laar MA, Adang EMM, Fransen J, et al. Treatment strategies aiming at remission in early rheumatoid arthritis patients: starting with methotrexate monotherapy is cost-effective. Rheumatology (Oxford). England: Department of Rheumatology, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, Sint Maartenskliniek Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. lschipper@reuma.umcn.nl; 2011. p. 1320–30. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=21371999
Spalding JR, Hay J. Cost effectiveness of tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors as first-line agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics. New Zealand: Astellas Pharma US, Deerfield, Illinois, USA.; 2006. p. 1221–32. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=17129076
Verhoeven AC, Bibo JC, Boers M, Engel GL, van der Linden S. Cost-effectiveness and cost-utility of combination therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: randomized comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone. COBRA Trial Group. Combinatietherapie Bij Reumat. Br. J. Rheumatol. ENGLAND: Department of Internal Medicine and Rheumatology, Maastricht University Hospital, The Netherlands.; 1998. p. 1102–9. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=9825750
Kobelt G, Lindgren P, Young A. Modelling the costs and effects of leflunomide in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Health Econ. 2002;3:180–7. Available from: MEDLINE:15609143.
Korthals-de Bos IBC, van Tulder MW, Boers M, Verhoeven AC, Ader HJ, Bibo J, et al. Indirect and total costs of early rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulfasalazine with sulfasalazine alone. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:S313. Available from: WOS:000172495901623.
Tosh JC, Wailoo AJ, Scott DL, Deighton CM. Cost-effectiveness of combination nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2011;38(8):1593–600. Available from: http://www.jrheum.org/content/38/8/1593.abstract
Schädlich PK, Zeidler H, Zink A, Gromnica-Ihle E, Schneider M, Straub C, et al. Modelling cost effectiveness and cost utility of sequential DMARD therapy including leflunomide for rheumatoid arthritis in Germany: II. The contribution of leflunomide to efficiency. Pharmacoeconomics. 2005;23:395–420. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15853438
Van den Hout WB, Goekoop-Ruiterman YPM, Allaart CF, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Hazes JMM, Kerstens PJSM, et al. Cost-utility analysis of treatment strategies in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. Arthritis Care Res. United States: Department of Medical Decision Making, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands. Hout@lumc.nl; 2009;61:291–9. Available from: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cin20&AN=2010215566&site=ehost-live
Deighton C, O’Mahony R, Tosh J, Turner C, Rudolf M. Management of rheumatoid arthritis: summary of NICE guidance. BMJ. 2009;338:b702. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3266846&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
National Insitute for Health and Care Excellence. Guide to the methods of technology appraisal. 2013. Available from: http://www.nice.org.uk/media/D45/1E/GuideToMethodsTechnologyAppraisal2013.pdf
Kavanaugh A, Heudebert G, Cush J, Jain R. Cost evaluation of novel therapeutics in rheumatoid arthritis (CENTRA): A decision analysis model. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;25:297–307. Available from: WOS:A1996UE92700002.
Anis AH, Tugwell PX, Wells GA, Stewart DG. A cost effectiveness analysis of cyclosporine in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. CANADA: Health Research Centre, St. Paul’s Hospital, Vancouver, Ottawa, Canada.; 1996. p. 609–16. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=8730113
Bansback NJ, Brennan A, Ghatnekar O. Cost effectiveness of adalimumab in the treatment of patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden. Ann. Rheum. Dis. England: Health Economics and Decision Science, ScHARR, University of Sheffield, Regent Court, 40 Regent Street, Sheffield S1 4DA UK. n.j.bansback@sheffield.ac.uk; 2005. p. 995–1002. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=15550533
Barbieri M, Wong JB, Drummond M. The cost effectiveness of infliximab for severe treatment-resistant rheumatoid arthritis in the UK. Pharmacoeconomics. New Zealand: Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, Spain.; 2005. p. 607–18. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=15960556
Barton P, Jobanputra P, Wilson J, Bryan S, Burls A. The use of modelling to evaluate new drugs for patients with a chronic condition: the case of antibodies against tumour necrosis factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Health Technol. Assess. (Rockv). 2004;8(11):1–104. Available from: http://www.hta.ac.uk/1296
Benucci M, Gobbi F, Sabadini L, Saviola G, Baiardi P, Manfredi M. The Economic Burden of Biological Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis in Clinical Practice: Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Sub-Cutaneous Anti-Tnf Alpha Treatment in Italian Patients. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2009;22:1147–52. Available from: WOS:000274293700034.
Benucci M, Saviola G, Baiardi P, Manfredi M. Cost-effectiveness treatment with Rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in real life. Rheumatol. Int. Germany: Rheumatology Unit, Department of Internal Medicine, Ospedale di S. Giovanni di Dio, Azienda Sanitaria di Firenze, Via Torregalli 3, 50143 Florence, Italy. maubenucci@tiscali.it; 2011. p. 1465–9. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=20473760
Beresniak A, Ariza-Ariza R, Garcia-Llorente JF, Ramirez-Arellano A, Dupont D. Modelling cost-effectiveness of biologic treatments based on disease activity scores for the management of rheumatoid arthritis in Spain. Int. J. Inflam. 2011;2011:727634. Available from: MEDLINE:21785694.
Brennan A, Bansback N, Nixon R, Madan J, Harrison M, Watson K, et al. Modelling the cost effectiveness of TNF-alpha antagonists in the management of rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Registry. Rheumatology (Oxford). England: Health Economics and Decision Science, School of Health and Related Research (ScHARR), The University of Sheffield, UK. a.brennan@sheffield.ac.uk; 2007. p. 1345–54. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=17562686
Brennan A, Bansback N, Reynolds A, Conway P. Modelling the cost-effectiveness of etanercept in adults with rheumatoid arthritis in the UK. Rheumatology (Oxford). England: Operational Research, School of Health and Related Research, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, South Yorkshire, UK. A.B.rennan@Sheffield.ac.uk; 2004. p. 62–72. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=12890861
Chiou C-F, Choi J, Reyes CM. Cost-effectiveness analysis of biological treatments for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev. Pharmacoeconomics Outcomes Res. 2004;4:June.
Choi HK, Seeger JD, Kuntz KM. A cost-effectiveness analysis of treatment options for patients with methotrexate-resistant rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. UNITED STATES: Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston 02114, USA.; 2000. p. 2316–27. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=11037892
Choi HK, Seeger JD, Kuntz KM. A cost effectiveness analysis of treatment options for methotrexate-naive rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. Canada: Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston 02114, USA. HCHOI@PARTNERS.ORG; 2002. p. 1156–65. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=12064828
Cimmino MA, Leardini G, Salaffi F, Intorcia M, Bellatreccia A, Dupont D, et al. Assessing the cost-effectiveness of biologic agents for the management of moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis in anti-TNF inadequate responders in Italy: a modelling approach. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. Italy: Department of Internal Medicine, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy.; 2011. p. 633–41. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=21813056
Clark W, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Burls A. The clinical and cost-effectiveness of anakinra for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults: a systematic review and economic analysis. Health Technol. Assess. England: Medicines Evaluation Unit, Department of Medicines Management, Keele University, UK.; 2004. p. iii–105. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=15130461
Coyle D, Judd M, Blumenauer B, Cranney A, Maetzel A, Tugwell P, et al. Infliximab and etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation (Technology Report no 64). Ottawa: Canadian Coordinating Office for Health Technology Assessment; 2006.
Diamantopoulos A, Benucci M, Capri S, Berger W, Wintfeld N, Giuliani G, et al. Economic evaluation of tocilizumab combination in the treatment of moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis in Italy. J. Med. Econ. 2012;15:June.
Hallinen TA, Soini EJO, Eklund K, Puolakka K. Cost-utility of different treatment strategies after the failure of tumour necrosis factor inhibitor in rheumatoid arthritis in the Finnish setting. Rheumatology (Oxford). England: ESiOR Oy, Kuopio, Finland. taru.hallinen@esior.fi; 2010. p. 767–77. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=20100793
Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Burls A. The effectiveness of infliximab and etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. England: Department of Public Health and Epidemiology, University of Birmingham, UK.; 2002. p. 1–110. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=12387732
Kielhorn A, Porter D, Diamantopoulos A, Lewis G. UK cost-utility analysis of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis that failed to respond adequately to a biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. England: F. Hoffmann La-Roche Ltd, Basel, Switzerland. adrian.kielhorn@roche.com; 2008. p. 2639–50. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=18687164
Kievit W, Fransen J, Adang EM, Kuper HH, Jansen TL, De Gendt CMA, et al. Evaluating guidelines on continuation of anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment after 3 months: clinical effectiveness and costs of observed care and different alternative strategies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. England: Department of Rheumatology, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, The Netherlands. w.kievit@reuma.umcn.nl; 2009. p. 844–9. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=18625616
Kobelt G, Eberhardt K, Geborek P. TNF inhibitors in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice: costs and outcomes in a follow up study of patients with RA treated with etanercept or infliximab in southern Sweden. Ann. Rheum. Dis. England: Karolinska Institute, Huddinge Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden. gisela.kobelt@he-europa.com; 2004. p. 4–10. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=14672883
Kobelt G, Jonsson L, Young A, Eberhardt K. The cost-effectiveness of infliximab (Remicade) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden and the United Kingdom based on the ATTRACT study. Rheumatology (Oxford). England: HDI France, Speracedes, France. gisela.kobelt@easynet.fr; 2003. p. 326–35. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=12595631
Kobelt G, Lindgren P, Singh A, Klareskog L. Cost effectiveness of etanercept (Enbrel) in combination with methotrexate in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis based on the TEMPO trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. England: European Health Economics SAS, 492 chemin des Laurens, F-06530 Speracedes, France. gisela.kobelt@he-europe.com; 2005. p. 1174–9. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=15708879
Lekander I, Borgstrom F, Svarvar P, Ljung T, Carli C, van Vollenhoven RF. Cost-effectiveness of real-world infliximab use in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care. England: i3 Innovus and MMC, LIME, Stockholm, Sweden. ingrid.lekander@i3innovus.com; 2010. p. 54–61. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=20059781
Lindgren P, Geborek P, Kobelt G. Modeling the cost-effectiveness of treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with rituximab using registry data from Southern Sweden. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care. England: i3/innovus, Klarabergsviadukten 90D, SE-111 64 Stockholm, Sweden. Peter.Lindgren@3innovus.com; 2009. p. 181–9. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=19331709
Maetzel A, Strand V, Tugwell P, Wells G, Bombardier C. Economic comparison of leflunomide and methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an evaluation based on a 1-year randomised controlled trial. Pharmacoeconomics. New Zealand: Arthritis and Immune Disorder Research Centre, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. maetzel@uhnres.utoronto.ca; 2002. p. 61–70. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=11817993
Malottki K, Barton P, Tsourapas A, Uthman AO, Liu Z, Routh K, et al. Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol. Assess. England: West Midlands Health Technology Assessment Collaboration, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, UK.; 2011. p. 1–278. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=21439251
Marra CA, Marion SA, Guh DP, Najafzadeh M, Wolfe F, Esdaile JM, et al. Not all “Quality-adjusted life years” are equal. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2007;60:616–24. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895435606003593
Merkesdal S, Kirchhoff T, Wolka D, Ladinek G, Kielhorn A, Rubbert-Roth A. Cost-effectiveness analysis of rituximab treatment in patients in Germany with rheumatoid arthritis after etanercept-failure. Eur. J. Health Econ. Germany: Division of Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology, Working Group for Health Economics and Clinical Epidemiology, Hannover Medical School, Carl-Neuberg-Strasse 1, OE 6830, 30625, Hannover, Germany. merkesdal.sonja@mh-hannover.de; 2010;11:95–104. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=19967426
Nuijten MJ, Engelfriet P, Duijn K, Bruijn G, Wierz D, Koopmanschap M. A cost-cost study comparing etanercept with infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics. New Zealand: MEDTAP International, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. nuijten@medtap.nl; 2001. p. 1051–64. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=11735673
Osiri M, Kamolratanakul P, Maetzel A, Tugwell P. Cost effectiveness analysis of disease modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2007;27:1063–9. Available from: WOS:000248813000011.
Rubio-Terrés C, Domínguez-Gil A. Pharmacoeconomic analysis of the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide in comparison with the combination of infliximab and methotrexate. J. Drug Assess. Pharmacoeconomics Unit, Scientific Dept, Aventis Pharma, SA, Madrid, Spain; 2001;4:39–54. Available from: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cin20&AN=2003131286&site=ehost-live
Russell A, Beresniak A, Bessette L, Haraoui B, Rahman P, Thorne C, et al. Cost-effectiveness modeling of abatacept versus other biologic agents in DMARDS and anti-TNF inadequate responders for the management of moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. Germany: University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada.; 2009. p. 403–12. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=19089488
Saraux A, Gossec L, Goupille P, Bregman B, Boccard E, Dupont D, et al. Cost-effectiveness modelling of biological treatment sequences in moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis in France. Rheumatology (Oxford). England: Department of Rheumatology, Brest University, CHU Brest, Brest, France.; 2010. p. 733–40. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=20081224
Shini VK, Aboobacker S, Pahuja S, Revikumar KG, Bhasi R. Pharmacoeconomic study of DMARDs in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2010;5(3):148–54.
Soini EJ, Hallinen TA, Puolakka K, Vihervaara V, Kauppi MJ. Cost-effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept, and tocilizumab as first-line treatments for moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Econ. 2012;15:340–51. Available from: MEDLINE:22168785.
Tanno M, Nakamura I, Ito K, Tanaka H, Ohta H, Kobayashi M, et al. Modeling and cost-effectiveness analysis of etanercept in adults with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan: a preliminary analysis. Mod. Rheumatol. Japan: Department of Rheumatology, Yugawara Kosei-Nenkin Hospital, 438 Miyakami, Yugawara-cho, Ashigarashimo-gun, Kanagawa, 259-0314, Japan. yknb-l12@i-younet.ne.jp; 2006. p. 77–84. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=16633926
Vera-Llonch M, Massarotti E, Wolfe F, Shadick N, Westhovens R, Sofrygin O, et al. Cost-effectiveness of abatacept in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists. J. Rheumatol. Canada: From Policy Analysis Inc., Brookline, MA 02445, USA.; 2008. p. 1745–53. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=18634164
Vera-Llonch M, Massarotti E, Wolfe F, Shadick N, Westhovens R, Sofrygin O, et al. Cost-effectiveness of abatacept in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to methotrexate. Rheumatology (Oxford). England: Policy Analysis Inc., Brookline, MA 02445, USA.; 2008. p. 535–41. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=18356179
Wailoo AJ, Bansback N, Brennan A, Michaud K, Nixon RM, Wolfe F. Biologic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis in the Medicare program: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Arthritis Rheum. United States: Health Economics and Decision Science, ScHARR, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK. a.j.wailoo@sheffield.ac.uk; 2008. p. 939–46. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=medl&NEWS=N&AN=18383356
Welsing PMJ, Severens JL, Hartman M, van Riel PLCM, Laan RFJM. Modeling the 5-year cost effectiveness of treatment strategies including tumor necrosis factor-blocking agents and leflunomide for treating rheumatoid arthritis in the Netherlands. Arthritis Rheum. United States: University Medical Center Nijmegen, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. P.Welsing@reuma.umcn.nl; 2004. p. 964–73. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=15593319
Wong JB, Singh G, Kavanaugh A. Estimating the cost-effectiveness of 54 weeks of infliximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Med. United States: Division of Clinical Decision Making, Department of Medicine, Tupper Research Institute, Tufts-New England Medical Center, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02111, USA. jwong@lifespan.org; 2002. p. 400–8. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=12401535
Benucci M, Saviola G, Manfredi M, Sarzi-Puttini P, Atzeni F. Cost effectiveness analysis of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. A systematic review literature. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2011;2011:845496. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3228304&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
Merkesdal S, Ruof J, Mittendorf T, Zeidler H. Cost-effectiveness of TNF-α-blocking agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. Ashley Publications Ltd London, UK; 2004;5:1881–6. Available from: http://informahealthcare.com/doi/abs/10.1517/14656566.5.9.1881
Harrison MJM, Bansback NJN, Marra CA, Drummond M, Tugwell PS, Boonen A. Valuing health for clinical and economic decisions: directions relevant for rheumatologists. J. Rheumatol. 2011;38:1770–5. Available from: http://jrheum.org/content/38/8/1770.short
Hernández Alava M, Wailoo A, Wolfe F, Michaud K. The relationship between EQ-5D, HAQ and pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:944–50. Available from: http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2013/01/25/rheumatology.kes400.full?keytype=ref&ijkey=IFzd0zj0pdZWOzP
Scott DL, Khoshaba B, Choy EH, Kingsley GH. Limited correlation between the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and EuroQol in rheumatoid arthritis: questionable validity of deriving quality adjusted life. Ann. Rheum. 2007;66:1534–7. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2111609&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
Sullivan SD, Alfonso-Cristancho R, Carlson J, Mallya U, Ringold S. Economic consequences of sequencing biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. J. Med. Econ. 2013;16:391–6. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23298329
Madan J, Ades AE, Welton NJ. An overview of models used in economic analyses of biologic therapies for arthritis--from current diversity to future consensus. Rheumatology. 2011;50:iv10–iv18. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21859700
Tosh J, Brennan A, Wailoo A, Bansback N. The Sheffield rheumatoid arthritis health economic model. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50 Suppl 4:iv26–31. Available from: http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/50/suppl_4/iv26
Krieger S. Multiple sclerosis therapeutic pipeline: opportunities and challenges. Mt. Sinai J. Med;78:192–206. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21425264
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D, et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am. J. Psychiatry. American Psychiatric Association; 2006;163:1905–17. Available from: http://journals.psychiatryonline.org/article.aspx?volume=163&page=1905
Acknowledgments
Jonathan Tosh is funded by a National Institute for Health Research Doctoral Research Fellowship. This article presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Compliance With Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Jonathan Tosh reports grants from the National Institute for Health Research, during the conduct of the study. Matt Stevenson and Ron Akehurst declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Health Economics and Quality of Life
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tosh, J., Stevenson, M. & Akehurst, R. Health Economic Modelling of Treatment Sequences for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Curr Rheumatol Rep 16, 447 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-014-0447-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-014-0447-2