Abstract
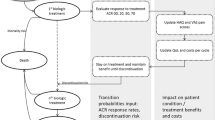
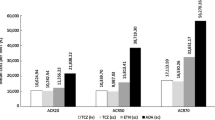
The study aims to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of adding tocilizumab (TCZ) first line to a treatment sequence for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), who had an inadequate response to one or more traditional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and are intolerant to methotrexate (MTX), or in whom continued treatment with MTX is considered inappropriate. An individual simulation model was applied to project lifetime costs and outcomes for 10,000 patients from a payer’s perspective. The analysis compared the standard treatment pathway (STP) with a similar pathway, where treatment was initiated with TCZ. QALYs were used as primary efficacy outcomes. Efficacy data were obtained from the ADACTA trial and a network meta-analysis. Clinical practice standards were derived from an expert panel of Greek rheumatologists. Results indicate that a treatment sequence starting with TCZ yields 1.17 more QALYs (9.38 vs. 8.21) at an additional cost of €33,744 (€119,840 vs. €86,096) compared with the STP. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was €28,837/QALY gained. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis confirms robustness of these findings as consistently below a threshold of €45,000. The results of the analysis suggest that TCZ, when used as a first-line biologic monotherapy, can be a cost-effective treatment option for the management of active RA in patients in need of biologic monotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365(23):2205–2219
Andrianakos A, Trontzas P, Christoyannis F et al (2006) Prevalence and management of rheumatoid arthritis in the general population of Greece—the ESORDIG study. Rheumatology 45:1549–1554
McIntosh E (1996) The cost of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 35:781–790
Kinsgley G, Scott IC, Scott DL (2011) Quality of life and the outcome of established rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 25:585–606
Young A, Dixey J, Kulinskaya E, Cox N, Davies P, Devlin J, Emery P, Gough A, James D, Prouse P, Williams P, Winfield J (2002) Which patients stop working because of rheumatoid arthritis? Results of five years’ follow up in 732 patients from the Early RA Study (ERAS). Ann Rheum Dis 61(4):335–340
Sokka T, Kautiainen H, Pincus T, Verstappen SM, Aggarwal A, Alten R, Andersone D, Badsha H, Baecklund E, Belmonte M, Craig-Müller J, da Mota LM, Dimic A, Fathi NA, Ferraccioli G, Fukuda W, Géher P, Gogus F, HajjajHassouni N, Hamoud H, Haugeberg G, Henrohn D, Horslev-Petersen K, Ionescu R, Karateew D, Kuuse R, Laurindo IM, Lazovskis J, Luukkainen R, Mofti A, Murphy E, Nakajima A, Oyoo O, Pandya SC, Pohl C, Predeteanu D, Rexhepi S, Sharma B, Shono E, Sibilia J, Sierakowski S, Skopouli FN, Stropuviene S, Toloza S, Valter I, Woolf A, Yamanaka H (2010) Work disability remains a major problem in rheumatoid arthritis in the 2000s: data from 32 countries in the QUEST-RA study. Arthritis Res Ther 12(2):R42
Wailoo AJ, Bansback N, Brennan A, Michaud K, Nixon RM, Wolfe F (2008) Biologic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis in the medicare program: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Arthritis Rheum 58(4):939–946
Beresniak A, Ariza-Ariza R, Garcia-Llorente JF, Ramirez-Arellano A, Dupont D (2011) Modelling cost-effectiveness of biologic treatments based on disease activity scores for the management of rheumatoid arthritis in Spain. Int J Inflamm. Article ID 727634, 9. doi:10.4061/2011/727634
Furneri G, Mantovani LG, Belisari A, Mosca M, Cristiani M, Bellelli S, Cortesi PA, Turchetti G (2012) Systematic literature review on economic implications and pharmacoeconomic issues of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 4(Suppl 73):S72–S84
Okuda Y (2008) Review of tocilizumab in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biol Targets Ther 2(1):75–82
Nishimoto N, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Azuma J, Kishimoto T (2009) Study of active controlled tocilizumab monotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate (SATORI): significant reduction in disease activity and serum vascular endothelial growth factor by IL-6 receptor inhibition therapy. Mod Rheumatol 19(1):12–19
Nishimoto N, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Azuma J (2009) Long-term safety and efficacy of tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, in monotherapy, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (the STREAM study): evidence of safety and efficacy in a 5-year extension study. Ann Rheum Dis 68(10):1580–1584
Nishimoto N, Ito K, Takagi N (2010) Safety and efficacy profiles of tocilizumab monotherapy in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: meta-analysis of six initial trials and five long-term extensions. Mod Rheumatol 20(3):222–232
Nishimoto N, Hashimoto J, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Murata N, van der Heijde D, Kishimoto T (2007) Study of active controlled monotherapy used for rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor (SAMURAI): evidence of clinical and radiographic benefit from an x ray reader-blinded randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab. Ann Rheum Dis 66(9):1162–1167
Jones G, Sebba A, Gu J, Lowenstein MB, Calvo A, Gomez-Reino JJ, Siri DA, Tomsic M, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Genovese MC (2010) Comparison of tocilizumab monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION study. Ann Rheum Dis 69(01):88–96
Gabay C, Emery P, van Vollenhoven R, Dikranian A, Alten R, Pavelka K, Klearman M, Musselman D, Agarwal S, Green J, Kavanaugh A (2013) Tocilizumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (ADACTA): a randomised, double-blind, controlled phase 4 trial. Lancet 381(9877):1541–1550
Maini RN, Taylor PC, Szechinski J, Pavelka K, Bröll J, Balint G, Emery P, Raemen F, Petersen J, Smolen J, Thomson D, Kishimoto T (2006) Double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, tocilizumab, in European patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had an incomplete response to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 54(9):2817–2829
Bykerk VP, Östör AJ, Alvaro-Gracia J, Pavelka K, Ivorra JAR, Graninger W, Bensen W, Nurmohamed MT, Krause A, Bernasconi C, Stancati A, Sibilia J (2012) Tocilizumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate responses to DMARDs and/or TNF inhibitors: a large, open-label study close to clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 71(12):1950–1954
Dougados M, Kissel K, Sheeran T, Tak PP, Conaghan PG, Mola EM, Schett G, Amital H, Navarro-Sarabia F, Hou A, Bernasconi C, Huizinga TWJ (2013) Adding tocilizumab or switching to tocilizumab monotherapy in methotrexate inadequate responders: 24-week symptomatic and structural results of a 2-year randomised controlled strategy trial in rheumatoid arthritis (ACT-RAY). Ann Rheum Dis 72(1):43–50
Gabriel S, Drummond M, Maetzel A, Boers M, Coyle D, Welch V, Tugwell P (2003) OMERACT 6 Economics Working Group report: a proposal for a reference case for economic evaluation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 30(4):886–890
Brennan A, Chick SE, Davies R (2006) A taxonomy of model structures for economic evaluation of health technologies. Health Econ 15(12):1295–1310
Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, Saag KG (2012) 2012 Update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 64(5):625–639
Maska L, Anderson J, Michaud K (2011) Measures of functional status and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ), Modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (MHAQ), Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ), Health Assessment Questionnaire II (HAQ‐II), Improved Health Assessment Questionnaire (Improved HAQ), and Rheumatoid Arthritis Quality of Life (RAQoL). Arthritis Care Res 63(S11):S4–S13
Buckley, F (2012). Presentation 2171-ACR 2012, 10–14 Nov, Washington
NHS reference costs 2010/2011, Department of Health (2011) Publications policy and guidance. Retrieved March 1, 2013, from Department of Health: http://www.dh.gov.uk
Malottki K, Barton P, Tsourapas A, Uthman AO, Liu Z, Routh K, Connock M, Jobanputra P, Moore D, Fry-Smith A, Chen YF (2011) Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 15(14):1–278. doi:10.3310/hta15140
Brennan A, Bansback N, Reynolds A, Conway P (2004) Modelling the cost-effectiveness of etanercept in adults with rheumatoid arthritis in the UK. Rheumatology 43(1):62–72
Gabriel SE (2008) Why do people with rheumatoid arthritis still die prematurely? Ann Rheum Dis 67(Suppl 3):iii30–iii34
Wolfe F (1994) The mortality of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 4:481–494
Barton P, Jobanputra P, Wilson J, Bryan S, Burls A (2004) The use of modelling to evaluate new drugs for patients with a chronic condition: the case of antibodies against tumour necrosis factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Health Technol Assess 8(11):iii1–iii91
Singh JA, Wells GA, Christensen R, et al (2011) Adverse effects of biologics: a network meta-analysis and Cochrane overview (review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2:CD008794
Hernández Alava M, Wailoo AJ, Ara R (2012) Tails from the peak district: adjusted limited dependent variable mixture models of EQ-5D questionnaire health state utility values. Value Health J Int Soc Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res 15(3):550
Sisk JE, Moskowitz AJ, Whang W, Lin JD, Fedson DS, McBean AM, Plouffe JF, Cetron MS, Butler JC (1997) Cost-effectiveness of vaccination against pneumococcal bacteremia among elderly people. JAMA 278:1333–1339
Ara R, Brazier J (2010) Populating an economic model with health state utility values: moving towards better practice. Value Health 13(5):509–518
Welsing PMJ, Severens JL, Hartman M, van Riel PL, Laan RF (2004) Modeling the 5-year cost effectiveness of treatment strategies including tumour necrosis factor-blocking agents and leflunomide for treating rheumatoid arthritis in the Netherlands. Arthritis Rheum 51:964–973
Stavropoulou L, Arzoumanidou D, Athanasakis K, Kyriopoulos J (2013) Estimating the cost of IV infusions for RA patients in the Greek National Health System., poster presentation, 9th PanHellenic Congress on Management, Economics and Health Policy, 5–7 Dec, Athens
Kobelt G, Eberhardt K, Jönsson L, Jönsson B (1999) Economic consequences of the progression of rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden. Arthritis Rheum 42(2):347–356
Kobelt G (2005) Modelling the effect of function and disease activity on costs and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 44(9):1169–1175
Karamanoli E (2011) Debt crisis strains Greece’s ailing health system. Lancet 378(9788):303–304
Carlson JJ, Ogale S, Dejonckheere F, Sullivan S (2015) Cost-effectiveness of tocilizumab monotherapy vs. adalimumab monotherapy in the treatment of severe active rheumatoid arthritis. Value Health. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2014.10.013
Ertenli I (2012) Cost-effectiveness of tocilizumab for the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis (ra) patients with inadequate response to anti-TNF treatment in Turkey (abstract). Value Health 15(7):A445
Navarro Sarabia F, Blanco FJ, Álvaro-Gracia J, García Meijide J, Poveda J, Ruiz-beato E (2012) Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of tocilizumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy in reducing disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (abstract). Value Health 15(7):A444
Monteiro I, Café A, Encarnação R, Diamantopoulos A, Dejonckheere F (2012) Cost-utility of tocilizumab monotherapy in methotrexate intolerant/contra-indicated, moderate/severe rheumatoid arthritis patients in Portugal (abstract). Value Health 15(7):A447
Gibbons C, Diamantopoulos A, Pang H, Huertas C, Dejonckheere F (2012) Tocilizumab in methotrexate-intolerant or contraindicated patients—a cost-utility model for Scotland. Ann Rheum Dis 71(Suppl3):454
Harland D, Gibbons C, Diamantopoulos A, Pang H, Huertas C, Dejonckheere F (2012) Tocilizumab in methotrexate-intolerant or contraindicated patients—a cost-utility model for the UK (abstract). Value Health 15(7):A448
Ancuta I, Baculaea S, Szkultecka-Debek M (2009) Cost-effectiveness evaluation of tocilizumab in Romanian setting. Manag Health 13(3):7–10
Diamantopoulos A, Finckh A, Huizinga T, Sungher DK, Sawyer L, Neto D, Dejonckheere F (2014) Tocilizumab in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a cost-effectiveness analysis in the UK. Pharmacoeconomics 32(8):775–787
Yelin E, Wanke LA (1999) An assessment of the annual and long-term direct costs of rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of poor function and functional decline. Arthritis Rheum 42(6):1209–1218
Acknowledgments
The present study was financially supported by Roche Hellas S.A.
Conflict of interest
The Department of Health Economics of the National School of Public Health was financially supported via research grant from Roche Hellas S.A. for the completion of this study. AK, FT, KT and JK are affiliated to the Department of Health Economics of the National School of Public Health. TK and EV have disclosed that they are former employees of Roche Hellas S.A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athanasakis, K., Tarantilis, F., Tsalapati, K. et al. Cost-utility analysis of tocilizumab monotherapy in first line versus standard of care for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in Greece. Rheumatol Int 35, 1489–1495 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-015-3253-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-015-3253-x