Abstract
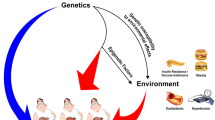
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) afflicts more than one third of the population in affluent societies, paralleling the dramatic escalation in global obesity prevalence. NAFLD is thus a leading cause for end-stage liver disease, cancer, and liver transplantation and an estimated 20 million patients worldwide will eventually die of their liver disease Rinella and Charlton (Hepatology 2016;64:19–22). Furthermore, NAFLD increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. NAFLD comprises a complex disease phenotype ranging from simple steatosis, through to steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and ultimately, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. NAFLD is also characterized by considerable inter-individual variability in disease spectrum and outcomes. Thus, NAFLD best resembles a complex disease trait resulting from the dynamic interaction of environmental factors (e.g., caloric intake and composition, energy expenditure, the microbiome) acting on a susceptible polygenic host background. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and candidate gene studies have enriched our understanding of genetic factors contributing to the known inter-individual variation in NAFLD phenotypes including hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. The role of other types of genetic variations and epigenetics are also now being unraveled. In this review, we summarize current knowledge about genetic and epigenetic associations of NAFLD and its potential clinical implications and future challenges in the field.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
Rinella M, Charlton M. The globalization of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: prevalence and impact on world health. Hepatology. 2016;64:19–22.
Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:547–55.
Armstrong MJ, Adams LA, Canbay A, Syn WK. Extrahepatic complications of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2014;59:1174–97.
Serfaty L, Lemoine M. Definition and natural history of metabolic steatosis: clinical aspects of NAFLD, NASH and cirrhosis. Diabetes Metab. 2008;34:634–7.
Singh S, Allen AM, Wang Z, Prokop LJ, Murad MH, Loomba R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:643–54.
Eslam M, George J. Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of NASH. Hepatol Int. 2016;10:394–406.
Loomba R, Schork N, Chen CH, Bettencourt R, Bhatt A, Ang B, et al. Heritability of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis based on a prospective twin study. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1784–93.
Schwimmer JB, Celedon MA, Lavine JE, Salem R, Campbell N, Schork NJ, et al. Heritability of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1585–92.
Willner IR, Waters B, Patil SR, Reuben A, Morelli J, Riely CA. Ninety patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: insulin resistance, familial tendency, and severity of disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:2957–61.
Mohanty SR, Troy TN, Huo D, O'Brien BL, Jensen DM, Hart J. Influence of ethnicity on histological differences in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2009;50:797–804.
Schneider AL, Lazo M, Selvin E, Clark JM. Racial differences in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the U.S. population. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22:292–9.
Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–95.
Bambha K, Belt P, Abraham M, Wilson LA, Pabst M, Ferrell L, et al. Ethnicity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2012;55:769–80.
Tabibian JH, Lazo M, Durazo FA, Yeh HC, Tong MJ, Clark JM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease across ethno-racial groups: do Asian-American adults represent a new at-risk population? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:501–9.
•• Romeo S, Kozlitina J, Xing C, Pertsemlidis A, Cox D, Pennacchio LA, et al. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1461–5. A landmark GWAS describes the discovery of PNPLA3, the most roubst risk varint for NAFLD.
Speliotes EK, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Wu J, Hernaez R, Kim LJ, Palmer CD, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variants associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that have distinct effects on metabolic traits. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1001324.
Speliotes EK, Butler JL, Palmer CD, Voight BF, Consortium G, Consortium MI, et al. PNPLA3 variants specifically confer increased risk for histologic nonalcoholic fatty liver disease but not metabolic disease. Hepatology. 2010;52:904–12.
Trepo E, Nahon P, Bontempi G, Valenti L, Falleti E, Nischalke HD, et al. Association between the PNPLA3 (rs738409 C>G) variant and hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence from a meta-analysis of individual participant data. Hepatology. 2014;59:2170–7.
Eslam M, Mangia A, Berg T, Chan HL, Irving WL, Dore GJ, et al. Diverse impacts of the rs58542926 E167K variant in TM6SF2 on viral and metabolic liver disease phenotypes. Hepatology. 2016;64(1):34–46.
Kitamoto T, Kitamoto A, Yoneda M, Hyogo H, Ochi H, Nakamura T, et al. Genome-wide scan revealed that polymorphisms in the PNPLA3, SAMM50, and PARVB genes are associated with development and progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Japan. Hum Genet. 2013;132:783–92.
Xu RF, Tao AY, Zhang SS, Deng YB, Chen GZ. Association between patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (PNPLA3) polymorphisms and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a HuGE review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9284.
Nobili V, Liccardo D, Bedogni G, Salvatori G, Gnani D, Bersani I, et al. Influence of dietary pattern, physical activity, and I148M PNPLA3 on steatosis severity in at-risk adolescents. Genes Nutr. 2014;9:392.
Davis JN, Le KA, Walker RW, Vikman S, Metz DS, Weigensberg MJ, et al. Increased hepatic fat in overweight Hispanic youth influenced by interaction between genetic variation in PNPLA3 and high dietary carbohydrate and sugar consumption. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92:1522–7.
Santoro N, Savoye M, Kim G, Marotto K, Shaw MM, Pierpont B, et al. Hepatic fat accumulation is modulated by the interaction between the rs738409 variant in the PNPLA3 gene and the dietary Omega6/Omega3 PUFA intake. PLoS One. 2012;7:e37827.
Marzuillo P, Grandone A, Perrone L, del Giudice EM. Weight loss allows the dissection of the interaction between abdominal fat and PNPLA3 (adiponutrin) in the liver damage of obese children. J Hepatol. 2013;59:1143–4.
Romeo S, Sentinelli F, Dash S, Yeo GSH, Savage DB, Leonetti F, et al. Morbid obesity exposes the association between PNPLA3 I148M (rs738409) and indices of hepatic injury in individuals of European descent. Int J Obes. 2010;34:190–4.
Dongiovanni P, Petta S, Mannisto V, Mancina RM, Pipitone R, Karja V, et al. Statin use and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in at risk individuals. J Hepatol. 2015;63:705–12.
Nishioji K, Mochizuki N, Kobayashi M, Kamaguchi M, Sumida Y, Nishimura T, et al. The impact of PNPLA3 rs738409 genetic polymorphism and weight Gain >= 10 kg after age 20 on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-obese japanese individuals. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0140427.
Stender S, Kozlitina J, Nordestgaard BG, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC. Adiposity amplifies the genetic risk of fatty liver disease conferred by multiple loci. Nat Genet. 2017;49:842–7.
Huang Y, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH. Expression and characterization of a PNPLA3 protein isoform (I148M) associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:37085–93.
Pingitore P, Pirazzi C, Mancina RM, Motta BM, Indiveri C, Pujia A, et al. Recombinant PNPLA3 protein shows triglyceride hydrolase activity and its I148M mutation results in loss of function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;841(4):574–80.
Pirazzi C, Valenti L, Motta BM, Pingitore P, Hedfalk K, Mancina RM, et al. PNPLA3 has retinyl-palmitate lipase activity in human hepatic stellate cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:4077–85.
BasuRay S, Smagris E, Cohen J, Hobbs HH. The PNPLA3 variant associated with fatty liver disease (I148M) accumulates on lipid droplets by evading ubiquitylation. Hepatology. 2017;66(4):1111–24.
Smagris E, BasuRay S, Li J, Huang Y, Lai KM, Gromada J, et al. Pnpla3I148M knockin mice accumulate PNPLA3 on lipid droplets and develop hepatic steatosis. Hepatology. 2015;61:108–18.
Santoro N, Kursawe R, D'Adamo E, Dykas DJ, Zhang CK, Bale AE, et al. A common variant in the patatin-like phospholipase 3 gene (PNPLA3) is associated with fatty liver disease in obese children and adolescents. Hepatology. 2010;52:1281–90.
Huang Y, He S, Li JZ, Seo YK, Osborne TF, Cohen JC, et al. A Feed-forward loop amplifies nutritional regulation of PNPLA3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:7892–7.
Liu YL, Reeves HL, Burt AD, Tiniakos D, McPherson S, Leathart JB, et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 influences hepatic fibrosis progression in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4309.
Dongiovanni P, Petta S, Maglio C, Fracanzani AL, Pipitone R, Mozzi E, et al. Transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 gene variant disentangles nonalcoholic steatohepatitis from cardiovascular disease. Hepatology. 2015;61:506–14.
•• Kozlitina J, Smagris E, Stender S, Nordestgaard BG, Zhou HH, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, et al. Exome-wide association study identifies a TM6SF2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet. 2014;46:352–6. The first work to discover a variant in the TM6SF2 loci as a risk varint for NAFLD.
Holmen OL, Zhang H, Fan Y, Hovelson DH, Schmidt EM, Zhou W, et al. Systematic evaluation of coding variation identifies a candidate causal variant in TM6SF2 influencing total cholesterol and myocardial infarction risk. Nat Genet. 2014;46:345–51.
Luukkonen PK, Zhou Y, Nidhina Haridas PA, Dwivedi OP, Hyotylainen T, Ali A, et al. Impaired hepatic lipid synthesis from polyunsaturated fatty acids in TM6SF2 E167K variant carriers with NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2017;67:128–36.
Kim DS, Jackson AU, Li YK, Stringham HM, Kuusisto J, Kangas AJ, et al. Novel association of TM6SF2 rs58542926 genotype with increased serum tyrosine levels and decreased apolipoprotein B-100 particles in Finns. J Lipid Res. 2017;58(7):1471–81.
Fan Y, Lu H, Guo Y, Zhu T, Garcia-Barrio MT, Jiang Z, et al. Hepatic transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 regulates cholesterol metabolism in mice. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1208–18.
Smagris E, Gilyard S, BasuRay S, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH. Inactivation of Tm6sf2, a gene defective in fatty liver disease, impairs lipidation but not secretion of very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:10659–76.
Petta S, Miele L, Bugianesi E, Camma C, Rosso C, Boccia S, et al. Glucokinase regulatory protein gene polymorphism affects liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One. 2014;9:e87523.
Beer NL, Tribble ND, McCulloch LJ, Roos C, Johnson PR, Orho-Melander M, et al. The P446L variant in GCKR associated with fasting plasma glucose and triglyceride levels exerts its effect through increased glucokinase activity in liver. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:4081–8.
•• Buch S, Stickel F, Trepo E, Way M, Herrmann A, Nischalke HD, et al. A genome-wide association study confirms PNPLA3 and identifies TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 as risk loci for alcohol-related cirrhosis. Nat Genet. 2015;47:1443–8. The first work to discover a variant in the MBOAT7 loci as a risk variant for alcohol-related cirrhosis.
Mancina RM, Dongiovanni P, Petta S, Pingitore P, Meroni M, Rametta R, et al. The MBOAT7-TMC4 variant rs641738 increases risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in individuals of European descent. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1219–1230.e1216.
Luukkonen PK, Zhou Y, Hyotylainen T, Leivonen M, Arola J, Orho-Melander M, et al. The MBOAT7 variant rs641738 alters hepatic phosphatidylinositols and increases severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in humans. J Hepatol. 2016;65:1263–5.
Thabet K, Asimakopoulos A, Shojaei M, Romero-Gomez M, Mangia A, Irving WL, et al. MBOAT7 rs641738 increases risk of liver inflammation and transition to fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12757.
Thabet K, Chan HL, Petta S, Mangia A, Berg T, Boonstra A, et al. The membrane-bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing 7 variant rs641738 increases inflammation and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2017;65(6):1840–50.
Suppiah V, Moldovan M, Ahlenstiel G, Berg T, Weltman M, Abate ML, et al. IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1100–4.
•• Eslam M, Hashem AM, Leung R, Romero-Gomez M, Berg T, Dore GJ, et al. Interferon-lambda rs12979860 genotype and liver fibrosis in viral and non-viral chronic liver disease. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6422. The first work to discover a ‘core’ risk variant that correlates with fibrosis progression independent of disease etiology.
Petta S, Grimaudo S, Camma C, Cabibi D, Di Marco V, Licata G, et al. IL28B and PNPLA3 polymorphisms affect histological liver damage in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2012;56:1356–62.
•• Eslam M, McLeod D, Kelaeng KS, Mangia A, Berg T, Thabet K, et al. IFN-lambda3, not IFN-lambda4, likely mediates IFNL3-IFNL4 haplotype-dependent hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. Nat Genet. 2017;49:795–800. This work describes the discovery of the caustive protein for this genetic area assocaition.
Angulo P, Lindor KD. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17(Suppl):S186–90.
Kim H, Haluzik M, Asghar Z, Yau D, Joseph JW, Fernandez AM, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist treatment in a transgenic model of type 2 diabetes reverses the lipotoxic state and improves glucose homeostasis. Diabetes. 2003;52:1770–8.
Chen S, Li Y, Li S, Yu CA. Val227Ala substitution in the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPAR alpha) gene associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and decreased waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:1415–8.
Dongiovanni P, Rametta R, Fracanzani AL, Benedan L, Borroni V, Maggioni P, et al. Lack of association between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma2 polymorphisms and progressive liver damage in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a case control study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:102.
Valenti L, Motta BM, Alisi A, Sartorelli R, Buonaiuto G, Dongiovanni P, et al. LPIN1 rs13412852 polymorphism in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;54:588–93.
Fawcett KA, Grimsey N, Loos RJ, Wheeler E, Daly A, Soos M, et al. Evaluating the role of LPIN1 variation in insulin resistance, body weight, and human lipodystrophy in U.K. populations. Diabetes. 2008;57:2527–33.
Auinger A, Valenti L, Pfeuffer M, Helwig U, Herrmann J, Fracanzani AL, et al. A promoter polymorphism in the liver-specific fatty acid transport protein 5 is associated with features of the metabolic syndrome and steatosis. Horm Metab Res. 2010;42:854–9.
Petta S, Valenti L, Svegliati-Baroni G, Ruscica M, Pipitone RM, Dongiovanni P, et al. Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 rs3480 A>G polymorphism, irisin, and liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(8):2660–9.
Gupta AC, Misra R, Sakhuja P, Singh Y, Basir SF, Sarin SK. Association of adiponectin gene functional polymorphisms (−11377C/G and +45T/G) with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gene. 2012;496:63–7.
Zain SM, Mohamed Z, Mahadeva S, Cheah PL, Rampal S, Chin KF, et al. Impact of leptin receptor gene variants on risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its interaction with adiponutrin gene. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:873–9.
Al Sayegh F, Almahmeed W, Al Humood S, Marashi M, Bahr A, Al Mahdi H, et al. Global risk profile verification in patients with venous thromboembolism (GRIP VTE) in 5 Gulf countries. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2009;15:289–96.
Anstee QM, Darlay R, Leathart JB, Clement J, Clement K, Aithal GP, et al. Genome-wide association analysis confirms importance of PNPLA3 and identifies novel variants associated with histologically progressive steatohepatitis in NAFLD. Hepatology. 2012;56:265a–6a.
Dongiovanni P, Valenti L, Rametta R, Daly AK, Nobili V, Mozzi E, et al. Genetic variants regulating insulin receptor signaling are associated with the severity of liver damage in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 2010;59:267–73.
Carulli L, Canedi I, Rondinella S, Lombardini S, Ganazzi D, Fargion S, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: interleukin-6-174G/C polymorphism is associated with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Liver Dis. 2009;41:823–8.
Tokushige K, Takakura M, Tsuchiya-Matsushita N, Taniai M, Hashimoto E, Shiratori K. Influence of TNF gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients with NASH and simple steatosis. J Hepatol. 2007;46:1104–10.
Nozaki Y, Saibara T, Nemoto Y, Ono M, Akisawa N, Iwasaki S, et al. Polymorphisms of interleukin-1 beta and beta 3-adrenergic receptor in Japanese patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004;28:106S–10S.
Braunersreuther V, Viviani GL, Mach F, Montecucco F. Role of cytokines and chemokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:727–35.
Kiziltas S, Ata P, Colak Y, Mesci B, Senates E, Enc F, et al. TLR4 gene polymorphism in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in comparison to healthy controls. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2014;12:165–70.
Miele L, Beale G, Patman G, Nobili V, Leathart J, Grieco A, et al. The Kruppel-like factor 6 genotype is associated with fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:282–91.
Patin E, Kutalik Z, Guergnon J, Bibert S, Nalpas B, Jouanguy E, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants associated with progression of liver fibrosis from HCV infection. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1244–52. e1241–1212
Petta S, Valenti L, Marra F, Grimaudo S, Tripodo C, Bugianesi E, et al. MERTK rs4374383 polymorphism affects the severity of fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64:682–90.
Redon R, Pena NG, Crescencio FR. Leaching in metal nanoparticle catalysis. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2014;8:31–51.
Zain SM, Mohamed R, Cooper DN, Razali R, Rampal S, Mahadeva S, et al. Genome-wide analysis of copy number variation identifies candidate gene loci associated with the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One. 2014;9:e95604.
Anstee QM, Targher G, Day CP. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:330–44.
Hochberg Z, Feil R, Constancia M, Fraga M, Junien C, Carel JC, et al. Child health, developmental plasticity, and epigenetic programming. Endocr Rev. 2011;32:159–224.
Nobili V, Marcellini M, Marchesini G, Vanni E, Manco M, Villani A, et al. Intrauterine growth retardation, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:2638–40.
Donma MM, Donma O. Low birth weight: a possible risk factor also for liver diseases in adult life? Med Hypotheses. 2003;61:435–8.
Thompson MD, Cismowski MJ, Trask AJ, Lallier SW, Graf AE, Rogers LK, et al. Enhanced steatosis and fibrosis in liver of adult offspring exposed to maternal high-fat diet. Gene Expr. 2016;17(1):47–59.
Burgueno AL, Cabrerizo R, Mansilla NG, Sookoian S, Pirola CJ. Maternal high-fat intake during pregnancy programs metabolic-syndrome-related phenotypes through liver mitochondrial DNA copy number and transcriptional activity of liver PPARGC1A. J Nutr Biochem. 2013;24:6–13.
Sheldon RD, Nicole Blaize A, Fletcher JA, Pearson KJ, Donkin SS, Newcomer SC, et al. Gestational exercise protects adult male offspring from high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis. J Hepatol. 2016;64:171–8.
Gibbs JR, van der Brug MP, Hernandez DG, Traynor BJ, Nalls MA, Lai SL, et al. Abundant quantitative trait loci exist for DNA methylation and gene expression in human brain. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1000952.
Choi SW, Friso S. Epigenetics: a new bridge between nutrition and health. Adv Nutr. 2010;1:8–16.
Li YY. Genetic and epigenetic variants influencing the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:6546–51.
Ahrens M, Ammerpohl O, von Schonfels W, Kolarova J, Bens S, Itzel T, et al. DNA methylation analysis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease suggests distinct disease-specific and remodeling signatures after bariatric surgery. Cell Metab. 2013;18:296–302.
Murphy SK, Yang H, Moylan CA, Pang H, Dellinger A, Abdelmalek MF, et al. Relationship between methylome and transcriptome in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:1076–87.
Deminice R, da Silva RP, Lamarre SG, Kelly KB, Jacobs RL, Brosnan ME, et al. Betaine supplementation prevents fatty liver induced by a high-fat diet: effects on one-carbon metabolism. Amino Acids. 2015;47:839–46.
Sookoian S, Puri P, Castano GO, Scian R, Mirshahi F, Sanyal AJ, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with a state of betaine-insufficiency. Liver Int. 2017;37:611–9.
Horvath S, Erhart W, Brosch M, Ammerpohl O, von Schonfels W, Ahrens M, et al. Obesity accelerates epigenetic aging of human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:15538–43.
Sookoian S, Rosselli MS, Gemma C, Burgueno AL, Fernandez Gianotti T, Castano GO, et al. Epigenetic regulation of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: impact of liver methylation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha promoter. Hepatology. 2010;52:1992–2000.
Kitamoto T, Kitamoto A, Ogawa Y, Honda Y, Imajo K, Saito S, et al. Targeted-bisulfite sequence analysis of the methylation of CpG islands in genes encoding PNPLA3, SAMM50, and PARVB of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2015;63:494–502.
Donati B, Motta BM, Pingitore P, Meroni M, Pietrelli A, Alisi A, et al. The rs2294918 E434K variant modulates patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 expression and liver damage. Hepatology. 2016;63:787–98.
Sorm F, Piskala A, Cihak A, Vesely J. 5-Azacytidine, a new, highly effective cancerostatic. Experientia. 1964;20:202–3.
Lal G, Zhang N, van der Touw W, Ding Y, Ju W, Bottinger EP, et al. Epigenetic regulation of Foxp3 expression in regulatory T cells by DNA methylation. J Immunol. 2009;182:259–73.
Chen ZJ, Pikaard CS. Epigenetic silencing of RNA polymerase I transcription: a role for DNA methylation and histone modification in nucleolar dominance. Genes Dev. 1997;11:2124–36.
Colak Y, Yesil A, Mutlu HH, Caklili OT, Ulasoglu C, Senates E, et al. A potential treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with SIRT1 activators. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2014;23:311–9.
Cohen HY, Miller C, Bitterman KJ, Wall NR, Hekking B, Kessler B, et al. Calorie restriction promotes mammalian cell survival by inducing the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science. 2004;305:390–2.
Brooks CL, Gu W. How does SIRT1 affect metabolism, senescence and cancer? Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:123–8.
Frescas D, Valenti L, Accili D. Nuclear trapping of the forkhead transcription factor FoxO1 via Sirt-dependent deacetylation promotes expression of glucogenetic genes. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:20589–95.
Schroeder TM, Westendorf JJ. Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote osteoblast maturation. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20:2254–63.
Mukhopadhyay P, Horvath B, Rajesh M, Varga ZV, Gariani K, Ryu D, et al. PARP inhibition protects against alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2017;66:589–600.
Huang K, Du M, Tan X, Yang L, Li X, Jiang Y, et al. PARP1-mediated PPARalpha poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation suppresses fatty acid oxidation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2017;66:962–77.
Gariani K, Ryu D, Menzies KJ, Yi HS, Stein S, Zhang H, et al. Inhibiting poly ADP-ribosylation increases fatty acid oxidation and protects against fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2017;66:132–41.
Cao Y, Xue Y, Xue L, Jiang X, Wang X, Zhang Z, et al. Hepatic menin recruits SIRT1 to control liver steatosis through histone deacetylation. J Hepatol. 2013;59:1299–306.
Tough DF, Tak PP, Tarakhovsky A, Prinjha RK. Epigenetic drug discovery: breaking through the immune barrier. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15:835–53.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Ferreira DM, Simao AL, Rodrigues CM, Castro RE. Revisiting the metabolic syndrome and paving the way for microRNAs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. FEBS J. 2014;281:2503–24.
Gallego-Duran R, Romero-Gomez M. Epigenetic mechanisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an emerging field. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:2497–502.
Krutzfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M, et al. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs. Nature. 2005;438:685–9.
Miyaaki H, Ichikawa T, Kamo Y, Taura N, Honda T, Shibata H, et al. Significance of serum and hepatic microRNA-122 levels in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2014;34:e302–7.
Loyer X, Paradis V, Henique C, Vion AC, Colnot N, Guerin CL, et al. Liver microRNA-21 is overexpressed in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and contributes to the disease in experimental models by inhibiting PPARalpha expression. Gut. 2016;65:1882–94.
Baffy G. MicroRNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Med. 2015;4:1977–88.
Atanasovska B, Rensen SS, van der Sijde MR, Marsman G, Kumar V, Jonkers I, et al. A liver-specific long noncoding RNA with a role in cell viability is elevated in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2017;66(3):794–808.
Eslam M, George J. Genome-wide association studies and hepatitis C: harvesting the benefits of the genomic revolution. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35:402–20.
Eslam M, Hashem AM, Romero-Gomez M, Berg T, Dore GJ, Mangia A, et al. FibroGENE: a gene-based model for staging liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 2016;64:390–8.
Funding
Mohammed Eslam and Jacob George are supported by the Robert W. Storr Bequest to the Sydney Medical Foundation, University of Sydney; a National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) Program Grant (1053206) and Project grants (APP1107178 and APP1108422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of this article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Mayada Metwally and Mohammed Eslam each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Jacob George is a section editor for Current Hepatology Reports.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Fatty Liver Disease
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metwally, M., Eslam, M. & George, J. Genetic and Epigenetic Associations of NAFLD: Focus on Clinical Decision Making. Curr Hepatology Rep 16, 335–345 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-017-0372-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-017-0372-8