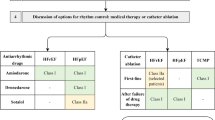
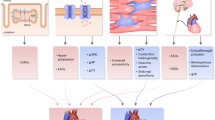
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation and heart failure are both associated with increased morbidity as well as mortality, and there is a complex interaction between the two conditions. The increasing prevalence and incidence rates of AF and CHF, as well as emerging novel but relatively expensive treatments and interventions, have compounded the significant public health impact at a global level. Ongoing investigative efforts continue to advance the knowledge of the complex interplay between these two conditions. This review critically assesses the current evidence in the field regarding prognostication metrics, drug therapy, and interventions for AF in CHF. We will summarize the important new findings published over the last year, with a focus on the latest advances that are of clinical relevance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Braunwald E. Shattuck lecture–cardiovascular medicine at the turn of the millennium: triumphs, concerns, and opportunities. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(19):1360–9. doi:10.1056/NEJM199711063371906.
Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, et al. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001;285(18):2370–5.
Majeed A, Moser K, Carroll K. Trends in the prevalence and management of atrial fibrillation in general practice in England and Wales, 1994-1998: analysis of data from the general practice research database. Heart. 2001;86(3):284–8.
Benjamin EJ, Levy D, Vaziri SM, D'Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, Wolf PA. Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA. 1994;271(11):840–4.
Miyasaka Y, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Cha SS, Bailey KR, Abhayaratna WP, et al. Secular trends in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future prevalence. Circulation. 2006;114(2):119–25. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.595140.
Savelieva I, Camm AJ. Clinical relevance of silent atrial fibrillation: prevalence, prognosis, quality of life, and management. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2000;4(2):369–82.
Stewart S, Murphy NF, Walker A, McGuire A, McMurray JJ. Cost of an emerging epidemic: an economic analysis of atrial fibrillation in the UK. Heart. 2004;90(3):286–92.
Coyne KS, Paramore C, Grandy S, Mercader M, Reynolds M, Zimetbaum P. Assessing the direct costs of treating nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in the United States. Value Health. 2006;9(5):348–56. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2006.00124.x.
Middlekauff HR, Stevenson WG, Stevenson LW. Prognostic significance of atrial fibrillation in advanced heart failure. A study of 390 patients. Circulation. 1991;84(1):40–8.
Senni M, Tribouilloy CM, Rodeheffer RJ, Jacobsen SJ, Evans JM, Bailey KR, et al. Congestive heart failure in the community: a study of all incident cases in Olmsted County, Minnesota, in 1991. Circulation. 1998;98(21):2282–9.
Kannel WB, Abbott RD, Savage DD, McNamara PM. Epidemiologic features of chronic atrial fibrillation: the Framingham study. N Engl J Med. 1982;306(17):1018–22. doi:10.1056/NEJM198204293061703.
Maisel WH, Stevenson LW. Atrial fibrillation in heart failure: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and rationale for therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2003;91(6A):2D–8D.
Ehrlich JR, Nattel S, Hohnloser SH. Atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure: specific considerations at the intersection of two common and important cardiac disease sets. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002;13(4):399–405.
Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1998;98(10):946–52.
Dries DL, Exner DV, Gersh BJ, Domanski MJ, Waclawiw MA, Stevenson LW. Atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk for mortality and heart failure progression in patients with asymptomatic and symptomatic left ventricular systolic dysfunction: a retrospective analysis of the SOLVD trials. Studies of Left Ventricular Dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;32(3):695–703.
Carson PE, Johnson GR, Dunkman WB, Fletcher RD, Farrell L, Cohn JN. The influence of atrial fibrillation on prognosis in mild to moderate heart failure. The V-HeFT Studies. The V-HeFT VA Cooperative Studies Group. Circulation. 1993;87(6 Suppl):VI102–10.
Swedberg K, Olsson LG, Charlesworth A, Cleland J, Hanrath P, Komajda M, et al. Prognostic relevance of atrial fibrillation in patients with chronic heart failure on long-term treatment with beta-blockers: results from COMET. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(13):1303–8. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi166.
Mamas MA, Caldwell JC, Chacko S, Garratt CJ, Fath-Ordoubadi F, Neyses L. A meta-analysis of the prognostic significance of atrial fibrillation in chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2009;11(7):676–83. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfp085.
Jons C, Jacobsen UG, Joergensen RM, Olsen NT, Dixen U, Johannessen A, et al. The incidence and prognostic significance of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with acute myocardial infarction and left ventricular systolic dysfunction: a CARISMA substudy. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(3):342–8. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.09.090.
Tveit A, Flonaes B, Aaser E, Korneliussen K, Froland G, Gullestad L, et al. No impact of atrial fibrillation on mortality risk in optimally treated heart failure patients. Clin Cardiol. 2011;34(9):537–42. doi:10.1002/clc.20939.
• Mitchell JE, Tam SW, Trivedi K, Taylor AL, O'Neal W, Cohn JN, et al. Atrial fibrillation and mortality in African American patients with heart failure: results from the African American Heart Failure Trial (A-HeFT). Am Heart J. 2011;162(1):154–9. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2011.04.022. This study by Mitchell et al addresses the knowledge gap regarding AF and HF in African Americans and showed that.
Olsson LG, Swedberg K, Ducharme A, Granger CB, Michelson EL, McMurray JJ, et al. Atrial fibrillation and risk of clinical events in chronic heart failure with and without left ventricular systolic dysfunction: results from the Candesartan in Heart failure-Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) program. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(10):1997–2004. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.01.060.
• Linssen GC, Rienstra M, Jaarsma T, Voors AA, van Gelder IC, Hillege HL, et al. Clinical and prognostic effects of atrial fibrillation in heart failure patients with reduced and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2011;13(10):1111–20. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfr066. This study underlines that AF is equally common in HF patients with preserved or impaired EF.
Badheka AO, Rathod A, Kizilbash MA, Bhardwaj A, Ali O, Afonso L, et al. Comparison of mortality and morbidity in patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure with preserved versus decreased left ventricular ejection fraction. Am J Cardiol. 2011;108(9):1283–8. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.06.045.
Banerjee A, Taillandier S, Olesen JB, Lane DA, Lallemand B, Lip GY, et al. Ejection fraction and outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure: the Loire Valley Atrial Fibrillation Project. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14(3):295–301. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfs005.
Armstrong PW, Stopps TP, Ford SE, de Bold AJ. Rapid ventricular pacing in the dog: pathophysiologic studies of heart failure. Circulation. 1986;74(5):1075–84.
Wilson JR, Douglas P, Hickey WF, Lanoce V, Ferraro N, Muhammad A, et al. Experimental congestive heart failure produced by rapid ventricular pacing in the dog: cardiac effects. Circulation. 1987;75(4):857–67.
Goette A, Lendeckel U, Klein HU. Signal transduction systems and atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 2002;54(2):247–58.
Redfield MM, Kay GN, Jenkins LS, Mianulli M, Jensen DN, Ellenbogen KA. Tachycardia-related cardiomyopathy: a common cause of ventricular dysfunction in patients with atrial fibrillation referred for atrioventricular ablation. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000;75(8):790–5. doi:10.4065/75.8.790.
Fujino T, Yamashita T, Suzuki S, Sugiyma H, Sagara K, Sawada H, et al. Characteristics of congestive heart failure accompanied by atrial fibrillation with special reference to tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 2007;71(6):936–40.
Nattel S, Shiroshita-Takeshita A, Brundel BJ, Rivard L. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: lessons from animal models. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2005;48(1):9–28. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2005.06.002.
• Ikeda T, Murai H, Kaneko S, Usui S, Kobayashi D, Nakano M, et al. Augmented single-unit muscle sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure with chronic atrial fibrillation. J Physiol. 2012;590(Pt 3):509–18. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.223842. This study procides further evidence regarding the importance of sympathetic tone in the interplay between AF and HF.
Chang SL, Chen YC, Yeh YH, Lin YK, Wu TJ, Lin CI, et al. Heart failure enhanced pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis and dysregulated sodium and calcium homeostasis with increased calcium sparks. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2011;22(12):1378–86. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8167.2011.02126.x.
Chang SL, Chen YC, Yeh YH, Lai YJ, Yeh HI, Lin CI, et al. Heart failure enhances arrhythmogenesis in pulmonary veins. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011;38(10):666–74. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05553.x.
•• Nishijima Y, Sridhar A, Bonilla I, Velayutham M, Khan M, Terentyeva R, et al. Tetrahydrobiopterin depletion and NOS2 uncoupling contribute to heart failure-induced alterations in atrial electrophysiology. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(1):71–9. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr087. The results from this experimental study by Nishijima et al suggest that oxidative stress is an important modulator of AF in HF and that the administration of nitric oxide synthase co-factor tetrahydrobiopterin appeares to attenuate the frequency of atrial arrhythmias during HF. The findings may provide a novel potential target for treating AF in HF patients.
Crijns HJ, Schotten U, Moens AL. Is NOS uncoupling the missing link between atrial fibrillation and chronic non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy? Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(3):556. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr176. author reply 7-8.
Wijffels MC, Kirchhof CJ, Dorland R, Allessie MA. Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation. A study in awake chronically instrumented goats. Circulation. 1995;92(7):1954–68.
Holm M, Pehrson S, Ingemansson M, Sornmo L, Johansson R, Sandhall L, et al. Non-invasive assessment of the atrial cycle length during atrial fibrillation in man: introducing, validating and illustrating a new ECG method. Cardiovasc Res. 1998;38(1):69–81.
Platonov PG, Cygankiewicz I, Stridh M, Holmqvist F, Vazquez R, Bayes-Genis A, et al. Low atrial fibrillatory rate is associated with poor outcome in patients with mild to moderate heart failure. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012;5(1):77–83. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.111.964395.
Fuster V, Ryden LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS focused updates incorporated into the ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2011;123(10):e269–367. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e318214876d.
Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, Feldman AM, Francis GS, Ganiats TG, et al. 2009 Focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2005 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure in Adults A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines Developed in Collaboration with the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(15):e1–e90. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.11.013.
Authors/Task Force M, McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Bohm M, et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2012. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehs104.
Adams Jr KF, Fonarow GC, Emerman CL, LeJemtel TH, Costanzo MR, Abraham WT, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for heart failure in the United States: rationale, design, and preliminary observations from the first 100,000 cases in the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry (ADHERE). Am Heart J. 2005;149(2):209–16. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2004.08.005.
Klein AL, Grimm RA, Murray RD, Apperson-Hansen C, Asinger RW, Black IW, et al. Use of transesophageal echocardiography to guide cardioversion in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(19):1411–20. doi:10.1056/NEJM200105103441901.
Wyse DG, Waldo AL, DiMarco JP, Domanski MJ, Rosenberg Y, Schron EB, et al. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(23):1825–33. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa021328.
Hohnloser SH, Kuck KH, Lilienthal J. Rhythm or rate control in atrial fibrillation–Pharmacological Intervention in Atrial Fibrillation (PIAF): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;356(9244):1789–94.
Van Gelder IC, Hagens VE, Bosker HA, Kingma JH, Kamp O, Kingma T, et al. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with recurrent persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(23):1834–40. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa021375.
Carlsson J, Miketic S, Windeler J, Cuneo A, Haun S, Micus S, et al. Randomized trial of rate-control versus rhythm-control in persistent atrial fibrillation: the Strategies of Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (STAF) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(10):1690–6.
Roy D, Talajic M, Nattel S, Wyse DG, Dorian P, Lee KL, et al. Rhythm control versus rate control for atrial fibrillation and heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(25):2667–77. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708789.
Cain ME, Curtis AB. Rhythm control in atrial fibrillation–one setback after another. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(25):2725–7. doi:10.1056/NEJMe0803289.
Pedersen OD, Brendorp B, Elming H, Pehrson S, Kober L, Torp-Pedersen C. Does conversion and prevention of atrial fibrillation enhance survival in patients with left ventricular dysfunction? Evidence from the Danish Investigations of Arrhythmia and Mortality ON Dofetilide/(DIAMOND) study. Card Electrophysiol Rev. 2003;7(3):220–4. doi:10.1023/B:CEPR.0000012386.82055.81.
Corley SD, Epstein AE, DiMarco JP, Domanski MJ, Geller N, Greene HL, et al. Relationships between sinus rhythm, treatment, and survival in the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) Study. Circulation. 2004;109(12):1509–13. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000121736.16643.11.
Henrard V, Ducharme A, Khairy P, Gisbert A, Roy D, Levesque S, et al. Cardiac remodeling with rhythm versus rate control strategies for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure: Insights from the AF-CHF echocardiographic sub-study. Int J Cardiol. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.08.077.
Talajic M, Khairy P, Levesque S, Connolly SJ, Dorian P, Dubuc M, et al. Maintenance of sinus rhythm and survival in patients with heart failure and atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(17):1796–802. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.01.023.
Olshansky B, Rosenfeld LE, Warner AL, Solomon AJ, O'Neill G, Sharma A, et al. The Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) study: approaches to control rate in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(7):1201–8. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.11.032.
Fuster V, Ryden LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2001 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation): developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2006;114(7):e257–354. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.177292.
Van Gelder IC, Groenveld HF, Crijns HJ, Tuininga YS, Tijssen JG, Alings AM, et al. Lenient versus strict rate control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(15):1363–73. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1001337.
Roy D, Talajic M, Dorian P, Connolly S, Eisenberg MJ, Green M, et al. Amiodarone to prevent recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Canadian Trial of Atrial Fibrillation Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(13):913–20. doi:10.1056/NEJM200003303421302.
Investigators AFADS. Maintenance of sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation: an AFFIRM substudy of the first antiarrhythmic drug. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42(1):20–9.
Santangeli P, Di Biase L, Burkhardt JD, Bai R, Mohanty P, Pump A, et al. Examining the safety of amiodarone. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2012;11(2):191–214. doi:10.1517/14740338.2012.660915.
Connolly SJ, Camm AJ, Halperin JL, Joyner C, Alings M, Amerena J, et al. Dronedarone in high-risk permanent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(24):2268–76. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1109867.
Kober L, Torp-Pedersen C, McMurray JJ, Gotzsche O, Levy S, Crijns H, et al. Increased mortality after dronedarone therapy for severe heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(25):2678–87. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0800456.
Schmiegelow MD, Pedersen OD, Kober L, Seibaek M, Abildstrom SZ, Torp-Pedersen C. Incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with either heart failure or acute myocardial infarction and left ventricular dysfunction: a cohort study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2011;11:19. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-11-19.
Lau DH, Psaltis PJ, Carbone A, Kelly DJ, Mackenzie L, Worthington M, et al. Atrial protective effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: a long-term study in ovine chronic heart failure. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(4):575–82. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.12.009.
Mozaffarian D, Psaty BM, Rimm EB, Lemaitre RN, Burke GL, Lyles MF, et al. Fish intake and risk of incident atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2004;110(4):368–73. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000138154.00779.A5.
Frost L, Vestergaard P. n-3 Fatty acids consumed from fish and risk of atrial fibrillation or flutter: the Danish Diet, Cancer, and Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81(1):50–4.
Brouwer IA, Heeringa J, Geleijnse JM, Zock PL, Witteman JC. Intake of very long-chain n-3 fatty acids from fish and incidence of atrial fibrillation. The Rotterdam Study. Am Heart J. 2006;151(4):857–62. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2005.07.029.
Cleland JG, Coletta AP, Castiello T, Clark AL. Clinical trials update from the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure meeting 2011: TEHAF, WHICH, CARVIVA, and atrial fibrillation in GISSI-HF and EMPHASIS-HF. Eur J Heart Fail. 2011;13(10):1147–51. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfr119.
Schneider MP, Hua TA, Bohm M, Wachtell K, Kjeldsen SE, Schmieder RE. Prevention of atrial fibrillation by Renin-Angiotensin system inhibition a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(21):2299–307. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.01.043.
Huang G, Xu JB, Liu JX, He Y, Nie XL, Li Q, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers decrease the incidence of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest. 2011;41(7):719–33. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2010.02460.x.
Li D, Shinagawa K, Pang L, Leung TK, Cardin S, Wang Z, et al. Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on the development of the atrial fibrillation substrate in dogs with ventricular tachypacing-induced congestive heart failure. Circulation. 2001;104(21):2608–14.
Investigators AI, Yusuf S, Healey JS, Pogue J, Chrolavicius S, Flather M, et al. Irbesartan in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(10):928–38. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1008816.
Tsai CF, Chen YC, Lin YK, Chen SA, Chen YJ. Electromechanical effects of the direct renin inhibitor (aliskiren) on the pulmonary vein and atrium. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(6):979–93. doi:10.1007/s00395-011-0206-8.
Fauchier L, Pierre B, de Labriolle A, Grimard C, Zannad N, Babuty D. Antiarrhythmic effect of statin therapy and atrial fibrillation a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51(8):828–35. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.09.063.
Kitamura K, Shibata R, Tsuji Y, Shimano M, Inden Y, Murohara T. Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents atrial fibrillation associated with heart failure in a rabbit model. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300(5):H1814–21. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00771.2010.
Wood MA, Brown-Mahoney C, Kay GN, Ellenbogen KA. Clinical outcomes after ablation and pacing therapy for atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Circulation. 2000;101(10):1138–44.
Sweeney MO, Hellkamp AS, Ellenbogen KA, Greenspon AJ, Freedman RA, Lee KL, et al. Adverse effect of ventricular pacing on heart failure and atrial fibrillation among patients with normal baseline QRS duration in a clinical trial of pacemaker therapy for sinus node dysfunction. Circulation. 2003;107(23):2932–7. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000072769.17295.B1.
Chen L, Hodge D, Jahangir A, Ozcan C, Trusty J, Friedman P, et al. Preserved left ventricular ejection fraction following atrioventricular junction ablation and pacing for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2008;19(1):19–27. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8167.2007.00994.x.
Proclemer A, Allocca G, Gregori D, Bonanno C, Ometto R, Fontanelli A, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of drug-refractory atrial fibrillation: an observational study comparing 'ablate and pace' with pulmonary vein isolation. Europace. 2008;10(9):1085–90. doi:10.1093/europace/eun197.
Molhoek SG, Bax JJ, Bleeker GB, Boersma E, van Erven L, Steendijk P, et al. Comparison of response to cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with sinus rhythm versus chronic atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2004;94(12):1506–9. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.08.028.
Adelstein EC, Saba S. Burden of atrial fibrillation after cardiac resynchronization therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2007;100(2):268–72. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.02.100.
Fung JW, Yip GW, Zhang Q, Fang F, Chan JY, Li CM, et al. Improvement of left atrial function is associated with lower incidence of atrial fibrillation and mortality after cardiac resynchronization therapy. Heart Rhythm. 2008;5(6):780–6. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2008.02.043.
Hoppe UC, Casares JM, Eiskjaer H, Hagemann A, Cleland JG, Freemantle N, et al. Effect of cardiac resynchronization on the incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with severe heart failure. Circulation. 2006;114(1):18–25. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.614560.
Brenyo A, Link MS, Barsheshet A, Moss AJ, Zareba W, Wang PJ, et al. Cardiac resynchronization therapy reduces left atrial volume and the risk of atrial tachyarrhythmias in MADIT-CRT (Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial with Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(16):1682–9. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.07.020.
Gasparini M, Auricchio A, Metra M, Regoli F, Fantoni C, Lamp B, et al. Long-term survival in patients undergoing cardiac resynchronization therapy: the importance of performing atrio-ventricular junction ablation in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(13):1644–52. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehn133.
Khadjooi K, Foley PW, Chalil S, Anthony J, Smith RE, Frenneaux MP, et al. Long-term effects of cardiac resynchronisation therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart. 2008;94(7):879–83. doi:10.1136/hrt.2007.129429.
van Rees JB, Borleffs CJ, de Bie MK, Stijnen T, van Erven L, Bax JJ, et al. Inappropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks: incidence, predictors, and impact on mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(5):556–62. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.06.059.
Mishkin JD, Saxonhouse SJ, Woo GW, Burkart TA, Miles WM, Conti JB, et al. Appropriate evaluation and treatment of heart failure patients after implantable cardioverter-defibrillator discharge: time to go beyond the initial shock. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(22):1993–2000. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.07.039.
Hsu LF, Jais P, Sanders P, Garrigue S, Hocini M, Sacher F, et al. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(23):2373–83. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa041018.
Efremidis M, Sideris A, Xydonas S, Letsas KP, Alexanian IP, Manolatos D, et al. Ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure: reversal of atrial and ventricular remodelling. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2008;49(1):19–25.
• MacDonald MR, Connelly DT, Hawkins NM, Steedman T, Payne J, Shaw M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with advanced heart failure and severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction: a randomised controlled trial. Heart. 2011;97(9):740–7. doi:10.1136/hrt.2010.207340. This randomized controlled trial did not find any improved sinus rhythm maintenance with catheter ablation over medical therapy in patients with AF and relatively advanced HF. This undersores the need for careful judgement in the treatment of this rpidly growing group of patients.
Dagres N, Varounis C, Gaspar T, Piorkowski C, Eitel C, Iliodromitis EK, et al. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Card Fail. 2011;17(11):964–70. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2011.07.009.
Khan MN, Jais P, Cummings J, Di Biase L, Sanders P, Martin DO, et al. Pulmonary-vein isolation for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(17):1778–85. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708234.
Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, Brugada J, Camm AJ, Chen SA, et al. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert Consensus Statement on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. Europace. 2012;14(4):528–606. doi:10.1093/europace/eus027.
Hart RG, Benavente O, McBride R, Pearce LA. Antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131(7):492–501.
Lip GY, Edwards SJ. Stroke prevention with aspirin, warfarin and ximelagatran in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res. 2006;118(3):321–33. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2005.08.007.
Rietbrock S, Heeley E, Plumb J, van Staa T. Chronic atrial fibrillation: Incidence, prevalence, and prediction of stroke using the Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age >75, Diabetes mellitus, and prior Stroke or transient ischemic attack (CHADS2) risk stratification scheme. Am Heart J. 2008;156(1):57–64. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2008.03.010.
Cleland JG, Coletta AP, Yassin A, Buga L, Torabi A, Clark AL. Clinical trials update from the European Society of Cardiology Meeting 2009: AAA, RELY, PROTECT, ACTIVE-I, European CRT survey, German pre-SCD II registry, and MADIT-CRT. Eur J Heart Fail. 2009;11(12):1214–9. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfp162.
•• Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, Eikelboom J, Oldgren J, Parekh A, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139–51. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0905561. The findings of this study underscore the on-going pardigm shift in thromboembolic prevention and suggest that dabigatran is an option to warfarin in patients with AF.
•• Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek EM, Hanna M, et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(11):981–92. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1107039. The findings of this study underscors the on-going pardigm shift in thromboembolic prevention and suggest that apixaban is an option to warfarin in patients with AF.
Disclosure
R. Havmöller: supported by a grant from the Swedish Research Council (#2011-1071); S.S. Chugh: holder of the Pauline and Harold Price Chair in Electrophysiology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Havmöller, R., Chugh, S.S. Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep 9, 309–318 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11897-012-0108-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11897-012-0108-6