Abstract
Purpose of Review
This review provides the most recent update of metformin, a biguanide oral antihyperglycemic drug used as a first-line treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Recent Findings
Metformin continues to dominate in the world of antidiabetics, and its use will continue to rise because of its high efficiency and easy availability. Apart from type 2 diabetes, research is exploring its potential in other conditions such as cancer, memory loss, bone disorders, immunological diseases, and aging.
Summary
Metformin is the most prescribed oral antidiabetic worldwide. It has been in practical use for the last six decades and continues to be the preferred drug for newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. It reduces glucose levels by decreasing hepatic glucose production, reducing intestinal glucose absorption, and increasing insulin sensitivity. It can be used as monotherapy or combined with other antidiabetics like sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT-2 inhibitors, or insulin, improving its efficacy. Metformin can be used once or twice daily, depending on requirements. Prolonged usage of metformin may lead to abdominal discomfort, deficiency of Vitamin B12, or lactic acidosis. It should be used carefully in patients with renal impairment. Recent studies have explored additional benefits of metformin in polycystic ovarian disease, gestational diabetes mellitus, cognitive disorders, and immunological diseases. However, more extensive studies are needed to confirm these additional benefits.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Bailey CJ, Day C. Metformin: its botanical background. Pract Diabetes Int. 2004;21(3):115–7.
Sterne J. Innovations in antidiabetics. NN dimethylamine guanyl guanidine [NNDG]. Maroc Med. 1957;36:1295–6.
Ra D. Efficacy of metformin in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:541–9.
Campbell IW. Metformin: a 60-year odyssey with the journey still continuing–a personal commentary from Professor Ian Campbell. Curr Med Res Opin. 2022;38(1):55–8.
Petrie JR, Rossing PR, Campbell IW. Metformin and cardiorenal outcomes in diabetes: a reappraisal. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22(6):904–15.
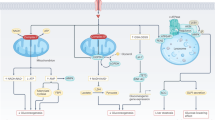
LaMoia TE, Shulman GI. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin action. Endocr Rev. 2021;42(1):77–96.
Rena G, Pearson ER, Sakamoto K. Molecular mechanism of action of metformin: old or new insights? Diabetologia. 2013;56:1898–906.
Misra P, Chakrabarti R. The role of AMP kinase in diabetes. Indian J Med Res. 2007;125(3):389–98.
Foretz M, Guigas B, Viollet B. Understanding the glucoregulatory mechanisms of metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(10):569–89.
Gerstein HC, Pare G, Hess S, Ford RJ, Sjaarda J, Raman K, McQueen M, Lee S, Haenel H, Steinberg GR. Growth differentiation factor 15 as a novel biomarker for metformin. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(2):280–3.
Proctor WR, Ming X, Bourdet D, Han TK, Everett RS, Thakker DR. Why does the intestine lack basolateral efflux transporters for cationic compounds? A provocative hypothesis. J Pharm Sci. 2016;105(2):484–96.
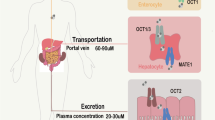
•• Tobar N, Rocha GZ, Santos A, Guadagnini D, Assalin HB, Camargo JA, Gonçalves AE, Pallis FR, Oliveira AG, Rocco SA, Neto RM. Metformin acts in the gut and induces gut-liver crosstalk. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2023;120(4):e2211933120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2211933120. This study indicate that the first site of metformin action is the gut, and through gut-portal vein-liver crosstalk, it may have a role in the control of HGP, integrating the sites and the mechanisms of metformin action.
Chang HS, Kim SJ, Kim YH. Association between colonic 18 F-FDG uptake and glycemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020;54:168–74.
Breining P, Jensen JB, Sundelin EI, Gormsen LC, Jakobsen S, Busk M, Rolighed L, Bross P, Fernandez-Guerra P, Markussen LK, Rasmussen NE. Metformin targets brown adipose tissue in vivo and reduces oxygen consumption in vitro. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(9):2264–73.
Bridges HR, Blaza JN, Yin Z, Chung I, Pollak MN, Hirst J. Structural basis of mammalian respiratory complex I inhibition by medicinal biguanides. Science. 2023;379(6630):351–7.
Zhang CS, Li M, Ma T, Zong Y, Cui J, Feng JW, Wu YQ, Lin SY, Lin SC. Metformin activates AMPK through the lysosomal pathway. Cell Metab. 2016;24(4):521–2.
Miller RA, Chu Q, Xie J, Foretz M, Viollet B, Birnbaum MJ. Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signaling by decreasing the production of cyclic AMP. Nature. 2013;494(7436):256–60.
•• Foretz M, Guigas B, Viollet B. Metformin: update on mechanisms of action and repurposing potential. Nat Rev Endocrinolo. 2023;19(8):460–76. This Review highlights the latest advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of action of metformin and discuss potential emerging novel therapeutic uses like treatment of cancer, age-related diseases, inflammatory diseases and COVID-19.
Garber AJ, Duncan TG, Goodman AM, Mills DJ, Rohlf JL. Efficacy of metformin in type II diabetes: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response trial. Am J Med. 1997;103(6):491–7.
Bennett WL, Maruthur NM, Singh S, Segal JB, Wilson LM, Chatterjee R, Marinopoulos SS, Puhan MA, Ranasinghe P, Block L, Nicholson WK. Comparative effectiveness and safety of medications for type 2 diabetes: an update including new drugs and 2-drug combinations. Ann Intern Med. 2011;154(9):602–13.
Davidson MB, Peters AL. An overview of metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1997;102(1):99–110.
Fujita Y, Inagaki N. Metformin: new preparations and nonglycemic benefits. Curr DiabRep. 2017;17:1.
Schwartz S, Fonseca V, Berner B, Cramer M, Chiang YK, Lewin A. Efficacy, tolerability, and safety of a novel once-daily extended-release metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(4):759–64.
McCreight LJ, Bailey CJ, Pearson ER. Metformin and the gastrointestinal tract. Diabetologia. 2016;59(3):426–35.
De Jager J, Kooy A, Lehert P, Wulffelé MG, Van der Kolk J, Bets D, Verburg J, Donker AJ, Stehouwer CD. Long-term treatment with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes and risk of vitamin B-12 deficiency: randomized placebo-controlled trial. BMJ. 2010;20:340.
Aroda VR, Edelstein SL, Goldberg RB, Knowler WC, Marcovina SM, Orchard TJ, Bray GA, Schade DS, Temprosa MG, White NH, Crandall JP. Long-term metformin use and vitamin B12 deficiency in the diabetes prevention program outcomes study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(4):1754–61.
Richy FF, Sabidó-Espin M, Guedes S, Corvino FA, Gottwald-Hostalek U. Incidence of lactic acidosis in patients with type 2 diabetes with and without renal impairment treated with metformin: a retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(8):2291–5.
Inzucchi SE, Lipska KJ, Mayo H, Bailey CJ, McGuire DK. Metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes and kidney disease: a systematic review. Jama. 2014;312(24):2668–75.
Nadeau KJ, Chow K, Alam S, Lindquist K, Campbell S, McFann K, Klingensmith G, Walravens P. Effects of low dose metformin in adolescents with type I diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blinded placebo-controlled study. Pediatr Diabetes. 2015;16(3):196–203.
National Institute of Clinical Excellence. In: Type 1 diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes. 2016. p. 29 Available from www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng17?unlid=43059219201639184149. Accessed 22 May 2017.
Vella S, Buetow L, Royle P, Livingstone S, Colhoun HM, Petrie JR. The use of metformin in type 1 diabetes: a systematic review of efficacy. Diabetologia. 2010;53:809–20.
Lorenz MW, Polak JF, Kavousi M, Mathiesen EB, Völzke H, Tuomainen TP, Sander D, Plichart M, Catapano AL, Robertson CM, Kiechl S. Carotid intima-media thickness progression to predict cardiovascular events in the general population (the PROG-IMT collaborative project): a meta-analysis of individual participant data. Lancet. 2012;379(9831):2053–62.
Libman IM, Miller KM, DiMeglio LA, Bethin KE, Katz ML, Shah A, Simmons JH, Haller MJ, Raman S, Tamborlane WV, Coffey JK. Effect of metformin added to insulin on glycemic control among overweight/obese adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314(21):2241–50.
Petrie JR, Chaturvedi N, Ford I, Brouwers MC, Greenlaw N, Tillin T, Hramiak I, Hughes AD, Jenkins AJ, Klein BE, Klein R. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of metformin in patients with type 1 diabetes (REMOVAL): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(8):597–609.
Polak JF, Szklo M, Kronmal RA, Burke GL, Shea S, Zavodni AE, O’Leary DH. The value of carotid artery plaque and intima-media thickness for incident cardiovascular disease: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2(2):e000087.
Jablonski KA, McAteer JB, de Bakker PI, Franks PW, Pollin TI, Hanson RL, Saxena R, Fowler S, Shuldiner AR, Knowler WC, Altshuler D. Common variants in 40 genes assessed for diabetes incidence and response to metformin and lifestyle intervention in the diabetes prevention program. Diabetes. 2010;59(10):2672–81.
Pau CT, Cheang KI, Modi BP, Kasippillai T, Keefe CC, Shulleeta M, Evans WS, Pal L, Strauss JF III, Nestler JE, Welt CK. The role of variants regulating metformin transport and action in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Pharmacogenomics. 2016;17(16):1765–73.
Legro RS, Barnhart HX, Schlaff WD, Carr BR, Diamond MP, Carson SA, Steinkampf MP, Coutifaris C, McGovern PG, Cataldo NA, Gosman GG. Ovulatory response to treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome is associated with a polymorphism in the STK11 gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(3):792–800.
Schweighofer N, Lerchbaum E, Trummer O, Schwetz V, Pieber T, Obermayer-Pietsch B. Metformin resistance alleles in polycystic ovary syndrome: pattern and association with glucose metabolism. Pharmacogenomics. 2014;15(3):305–17.
McCartney CR, Marshall JC. Polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(1):54–64.
Nestler JE, Powers LP, Matt DW, Steingold KA, Plymate SR, Rittmaster RS, Clore JN, Blackard WG. A direct effect of hyperinsulinemia on serum sex hormone-binding globulin levels in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991;72(1):83–9.
Hirsch A, Hahn D, Kempna P, Hofer G, Nuoffer JM, Mullis PE, Flück CE. Metformin inhibits human androgen production by regulating steroidogenic enzymes HSD3B2 and CYP17A1 and complex I activity of the respiratory chain. Endocrinology. 2012;153(9):4354–66.
Morley LC, Tang T, Yasmin E, Norman RJ, Balen AH. Insulin‐sensitising drugs (metformin, rosiglitazone, pioglitazone, D‐chiro‐inositol) for women with polycystic ovary syndrome, oligo amenorrhoea and subfertility. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;11(11):CD003053.
Balen AH, Morley LC, Misso M, Franks S, Legro RS, Wijeyaratne CN, Stener-Victorin E, Fauser BC, Norman RJ, Teede H. The management of anovulatory infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: an analysis of the evidence to support the development of global WHO guidance. Hum Reprod Update. 2016;22(6):687–708.
Palomba S, Falbo A, Russo T, Manguso F, Tolino A, Zullo F, De Feo P, Orio F Jr. Insulin sensitivity after metformin suspension in normal-weight women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(8):3128–35.
Pau CT, Keefe C, Duran J, Welt CK. Metformin improves glucose effectiveness, not insulin sensitivity: predicting treatment response in women with polycystic ovary syndrome in an open-label, interventional study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(5):1870–8.
Naderpoor N, Shorakae S, de Courten B, Misso ML, Moran LJ, Teede HJ. Metformin and lifestyle modification in polycystic ovary syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2015;21(5):560–74.
Rowan JA, Hague WM, Gao W, Battin MR, Moore MP. Metformin versus insulin for the treatment of gestational diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(19):2003–15.
Rowan JA, Rush EC, Obolonkin V, Battin M, Wouldes T, Hague WM. Metformin in gestational diabetes: the offspring follow-up (MiG TOFU) body composition at 2 years of age. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(10):2279–84.
Balsells M, García-Patterson A, Solà I, Roqué M, Gich I, Corcoy R. Glibenclamide, metformin, and insulin for the treatment of gestational diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2015;21:350.
• Tarry-Adkins JL, Aiken CE, Ozanne SE. Neonatal, infant, and childhood growth following metformin versus insulin treatment for gestational diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2019;16(8):e1002848. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002848. This study analysed the impact of maternal metformin treatment on the trajectory of fetal, infant, and childhood growth. When it is used as a alternative to insulin for treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Dodd JM, Louise J, Deussen AR, Grivell RM, Dekker G, McPhee AJ. Effect of metformin in addition to dietary and lifestyle advice for pregnant women who are overweight or obese: the GRoW randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(1):15–24.
Chiswick C, Reynolds RM, Denison F, Drake AJ, Forbes S, Newby DE, Walker BR, Quenby S, Wray S, Weeks A, Lashen H. Effect of metformin on maternal and fetal outcomes in obese pregnant women (EMPOWaR): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3(10):778–86.
Syngelaki A, Nicolaides KH, Balani J, Hyer S, Akolekar R, Kotecha R, Pastides A, Shehata H. Metformin versus placebo in obese pregnant women without diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(5):434–43.
Gardiner SJ, Kirkpatrick CM, Begg EJ, Zhang M, Moore MP, Saville DJ. Transfer of metformin into human milk. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003;73(1):71–7.
Zhang K, Yang W, Dai H, Deng Z. Cardiovascular risk following metformin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;1(160):108001.
Han Y, Xie H, Liu Y, Gao P, Yang X, Shen Z. Effect of metformin on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with coronary artery diseases: a systematic review and an updated meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):1–6.
Dutta S, Shah RB, Singhal S, Dutta SB, Bansal S, Sinha S, Haque M. Metformin: a review of potential mechanisms and therapeutic utility beyond diabetes. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2023;31:1907–32.
• Kheniser KG, Kashyap SR, Kasumov T. A systematic review: the appraisal of the effects of metformin on lipoprotein modification and function. Obes Sci Pract. 2019;5(1):36–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/osp4.309. It is the first review on the effects of metformin on lipoprotein metabolism (high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL).)
Matsuki K, Tamasawa N, Yamashita M, Tanabe J, Murakami H, Matsui J, Imaizumi T, Satoh K, Suda T. Metformin restores impaired HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux due to glycation. Atherosclerosis. 2009;206(2):434–8.
Dziubak A, Wójcicka G, Wojtak A, Bełtowski J. Metabolic effects of metformin in the failing heart. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):2869.
Wang XF, Zhang JY, Li L, Zhao XY, Tao HL, Zhang L. Metformin improves cardiac function in rats via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011;38(2):94–101.
Mohan M, Al-Talabany S, McKinnie A, Mordi IR, Singh JS, Gandy SJ, Baig F, Hussain MS, Bhalraam U, Khan F, Choy AM. A randomized controlled trial of metformin on left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with coronary artery disease without diabetes: the MET-REMODEL trial. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(41):3409–17.
Su C, Li X, Yang Y, Du Y, Zhang X, Wang L, Hong B. Metformin alleviates choline diet-induced TMAO elevation in C57BL/6J mice by influencing gut-microbiota composition and functionality. Nutr Diabetes. 2021;11(1):27.
Wu H, Esteve E, Tremaroli V, Khan MT, Caesar R, Mannerås-Holm L, Ståhlman M, Olsson LM, Serino M, Planas-Fèlix M, Xifra G. Metformin alters the gut microbiome of individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nat Med. 2017;23(7):850–8.
• Mueller NT, Differding MK, Zhang M, Maruthur NM, Juraschek SP, Miller ER III, Appel LJ, Yeh HC. Metformin affects gut microbiome composition and function and circulating short-chain fatty acids: a randomized trial. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(7):1462–71. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-2257. It is a 3-parallel-arm, randomized control trial to determine the longer-term effects of metformin treatment and behavioral weight loss on gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
De La Cuesta-Zuluaga J, Mueller NT, Corrales-Agudelo V, Velásquez-Mejía EP, Carmona JA, Abad JM, Escobar JS. Metformin is associated with higher relative abundance of mucin-degrading Akkermansia muciniphila and several short-chain fatty acid–producing microbiota in the gut. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):54–62.
Zhou ZY, Ren LW, Zhan P, Yang HY, Chai DD, Yu ZW. Metformin exerts glucose-lowering action in high-fat-fed mice via attenuating endotoxemia and enhancing insulin signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016;37(8):1063–75.
Ahmadi S, Razazan A, Nagpal R, Jain S, Wang BO, Mishra SP, Wang S, Justice J, Ding J, McClain DA, Kritchevsky SB. Metformin reduces aging-related leaky gut and improves cognitive function by beneficially modulating gut microbiome/goblet cell/mucin axis. J Gerontol: Series A. 2020;75(7):e9-21.
Isoda K, Young JL, Zirlik A, MacFarlane LA, Tsuboi N, Gerdes N, Schonbeck U, Libby P. Metformin inhibits pro-inflammatory responses and nuclear factor-κB in human vascular wall cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(3):611–7.
Glossmann HH, Lutz O. Metformin and aging: a review. Gerontology. 2019;65(6):581–90.
•• Mohammed I, Hollenberg MD, Ding H, Triggle CR. A critical review of the evidence that metformin is a putative anti-aging drug that enhances healthspan and extends lifespan. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:718942. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.718942. This review summarizes till date published evidence that argues for, or against, an anti-aging effect of metformin.
Kulkarni AS, Gubbi S, Barzilai N. Benefits of metformin in attenuating the hallmarks of aging. Cell Metab. 2020;32(1):15–30.
Eikawa S, Nishida M, Mizukami S, Yamazaki C, Nakayama E, Udono H. Immune-mediated anti-tumor effect by type 2 diabetes drug, metformin. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112(6):1809–14.
Cameron AR, Morrison VL, Levin D, Mohan M, Forteath C, Beall C, McNeilly AD, Balfour DJ, Savinko T, Wong AK, Viollet B. Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status. Circ Res. 2016;119(5):652–65.
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Struhl K. Metformin inhibits the inflammatory response associated with cellular transformation and cancer stem cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2013;110(3):972–7.
Reis G, Silva EA, Silva DC, Thabane L, Milagres AC, Ferreira TS, Dos Santos CV, Campos VH, Nogueira AM, de Almeida AP, Callegari ED. Effect of early treatment with ivermectin among patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(18):1721–31.
•• Bramante CT, Huling JD, Tignanelli CJ, Buse JB, Liebovitz DM, Nicklas JM, Cohen K, Puskarich MA, Belani HK, Proper JL, Siegel LK. Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19. New England J Med. 2022;387(7):599–610. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2201662. This is a phase 3, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, to test the effectiveness of metformin in preventing serious SARS-CoV-2 infection in nonhospitalized adults after a confirmed diagnosis of infection.
Ben Sahra I, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti JF, Bost F. Metformin in cancer therapy: a new perspective for an old antidiabetic drug? Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(5):1092–9.
Whitaker-Menezes D, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Flomenberg N, Birbe R, Witkiewicz AK, Howell A, Pavlides S, Tsirigos A, Ertel A, Pestell RG, Broda P. Hyperactivation of oxidative mitochondrial metabolism in epithelial cancer cells in situ: visualizing the therapeutic effects of metformin in tumor tissue. Cell Cycle. 2011;10(23):4047–64.
Pierotti MA, Berrino F, Gariboldi M, Melani C, Mogavero A, Negri T, Pasanisi P, Pilotti S. Targeting metabolism for cancer treatment and prevention: metformin, an old drug with multi-faceted effects. Oncogene. 2013;32(12):1475–87.
Wang S, Lin Y, Xiong X, Wang L, Guo Y, Chen Y, Chen S, Wang G, Lin P, Chen H, Yeung SC. Low-dose metformin reprograms the tumor immune microenvironment in human esophageal cancer: results of a phase II clinical trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(18):4921–32.
Hardie DG, Ashford ML. AMPK: regulating energy balance at the cellular and whole body levels. Physiology. 2014;29(2):99–107.
Cusi K, Consoli A, Defronzo RA. Metabolic effects of metformin on glucose and lactate metabolism in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(11):4059–67.
Gonda TA, Tu S, Wang TC. Chronic inflammation, the tumor microenvironment and carcinogenesis. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(13):2005–13.
•• Aung M, Amin S, Gulraiz A, Gandhi FR, Escobar JA, Malik BH, Gandhi F. The future of metformin in the prevention of diabetes-related osteoporosis. Cureus. 2020;12(9):e10412. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.10412. This article demonstrates that metformin influences the bone homeostasis by its stimulatory effect on the AMPK pathway leading to reduction in the occurrence of Osteoporosis.
Gong J, Kelekar G, Shen J, Shen J, Kaur S, Mita M. The expanding role of metformin in cancer: an update on anti-tumor mechanisms and clinical development. Target Oncol. 2016;11:447–67.
Chevalier B, Pasquier D, Lartigau EF, Chargari C, Schernberg A, Jannin A, Mirabel X, Vantyghem MC, Escande A. Metformin:(future) best friend of the radiation oncologist? Radiother Oncol. 2020;1(151):95–105.
Onken B, Driscoll M. Metformin induces a dietary restriction–like state and the oxidative stress response to extend C. elegans healthspan via AMPK, LKB1, and SKN-1. PloS one. 2010;5(1):e8758.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sandeep Chaudhary conducted literature review and manuscript writing, while Amitabh Kulkarni contributed to the mechanism of action and future of Metformin. Additionally, Kulkarni prepared Fig. 1.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, S., Kulkarni, A. Metformin: Past, Present, and Future. Curr Diab Rep (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-024-01539-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-024-01539-1