Abstract
Purpose of Review
The pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) is still unclear. The diagnosis of IC/BPS is made after ruling out bacterial cystitis. However, viral infection in the bladder might be a pathogenic factor for IC/BPS. The purpose of this review is to demonstrate the association between viral infection and IC/BPS.
Recent Findings
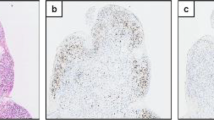
The presence of urinary tract viruses in patients with IC/BPS has been sporadically investigated since the 1970s. Early studies used viral culture to investigate urine and bladder tissue samples from patients with IC/BPS, but viruses were rarely detected. With polymerase chain reaction, several studies have reported increased papillomavirus, BK virus, and John Cunningham virus viral load in urine samples from patients with IC/BPS. The presence of urinary papillomavirus was associated with more severe IC/BPS symptoms. Recent studies have used transcriptomic RNA sequencing to investigate gene expression in bladder tissue samples from patients with IC/BPS. Enriched viral infection-associated gene pathways in patients with IC/BPS were noted in the studies, including cytomegalovirus infection, Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection, human papillomavirus infection, and Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection. Our recent studies reported the presence of EBV in IC/BPS bladders, especially in patients with IC/BPS with Hunner’s lesion (HIC). EBV latency and lytic infection were observed in HIC bladders, indicating EBV infection persistence and reactivation. EBV latency infection in B cells could induce brain-derived neurotrophic factor overexpression and might cause nerve hyperplasia in IC/BPS bladders.
Summary
The presence of urinary virus in the patients with IC/BPS suggested that viral infection might be a pathogenic factor in patients with IC/BPS. Molecular evidence from IC/BPS bladder tissue also showed that viral infection may involve the pathogenesis of IC/BPS. Further studies are needed to clarify the mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
Clemens JQ, Erickson DR, Varela NP, Lai HH. Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J Urol. 2022;208(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000002756.
Suskind AM, Berry SH, Ewing BA, Elliott MN, Suttorp MJ, Clemens JQ. The prevalence and overlap of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men: Results of the RAND Interstitial Cystitis Epidemiology male study. J Urol. 2013;189(1):141–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.088.
Akiyama Y, Hanno P. Phenotyping of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int J Urol. 2019;26(Suppl 1):17–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.13969.
Birder LA, Wolf-Johnston AS, Chib MK, Buffington CA, Roppolo JR, Hanna-Mitchell AT. Beyond neurons: Involvement of urothelial and glial cells in bladder function. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29(1):88–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.20747.
Hauser PJ, VanGordon SB, Seavey J, Sofinowski TM, Ramadan M, Abdullah S, et al. Abnormalities in expression of structural, barrier and differentiation related proteins, and chondroitin sulfate in feline and human interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 2015;194(2):571–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2015.01.090.
Hanno PM, Landis JR, Matthews-Cook Y, Kusek J, Nyberg L Jr. The diagnosis of interstitial cystitis revisited: Lessons learned from the National Institutes of Health Interstitial Cystitis Database study. J Urol. 1999;161(2):553–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(01)61948-7.
van de Merwe JP, Nordling J, Bouchelouche P, Bouchelouche K, Cervigni M, Daha LK, et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: An ESSIC proposal. Eur Urol. 2008;53(1):60–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2007.09.019.
Maeda D, Akiyama Y, Morikawa T, Kunita A, Ota Y, Katoh H, et al. Hunner-Type (Classic) interstitial cystitis: A distinct inflammatory disorder characterized by pancystitis, with frequent expansion of clonal b-cells and epithelial denudation. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0143316. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143316. This study showed the bladder histopathology features of IC/BPS is similar to virus infection in a mucosal tissue.
Pritt BS, Aubry MC. Histopathology of viral infections of the lung. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2017;34(6):510–7. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semdp.2017.06.005. This study firstly study investigate the presence of virus in human IC/BPS with viral culture.
Hanash KA, Pool TL. Interstitial and hemorrhagic cystitis: Viral, bacterial and fungal studies. J Urol. 1970;104(5):705–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61815-9.
Fall M, Johansson SL, Vahlne A. A clinicopathological and virological study of interstitial cystitis. J Urol. 1985;133(5):771–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)49221-4.
Keay S, Schwalbe RS, Trifillis AL, Lovchik JC, Jacobs S, Warren JW. A prospective study of microorganisms in urine and bladder biopsies from interstitial cystitis patients and controls. Urology. 1995;45(2):223–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-4295(95)80009-3.
Hukkanen V, Haarala M, Nurmi M, Klemi P, Kiilholma P. Viruses and interstitial cystitis: Adenovirus genomes cannot be demonstrated in urinary bladder biopsies. Urol Res. 1996;24(4):235–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295898. This study showed urinary polyomavirus was assocaited with IC/BPS.
Winter BJ, O’Connell HE, Bowden S, Carey M, Eisen DP. A case control study reveals that polyomaviruria is significantly associated with interstitial cystitis and vesical ulceration. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0137310. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137310.
Robles MTS, Cantalupo PG, Duray AM, Freeland M, Murkowski M, van Bokhoven A, et al. Analysis of viruses present in urine from patients with interstitial cystitis. Virus Genes. 2020;56(4):430–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-020-01767-z.
Jhang JF, Hsu YH, Peng CW, Jiang YH, Ho HC, Kuo HC. Epstein-Barr virus as a potential etiology of persistent bladder inflammation in human interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J Urol. 2018;200(3):590–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.133. This study first provide evidence to showed EBV presented in bladders of IC/BPS.
Jhang JF, Liu CD, Hsu YH, Chen CC, Chen HC, Jiang YH, et al. EBV infection mediated BDNF expression is associated with bladder inflammation in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome with Hunner’s lesion. J Pathol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.6040. This study first demonstrate the possible mechanisms that EBV infection may involve bladder nerve hyperplasia in IC/BPS.
Hematian A, Sadeghifard N, Mohebi R, Taherikalani M, Nasrolahi A, Amraei M, et al. Traditional and modern cell culture in virus diagnosis. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(2):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.11.011.
Hudu SA, Alshrari AS, Syahida A, Sekawi Z. Cell Culture, technology: Enhancing the culture of diagnosing human diseases. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(3):DE01-5. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2016/15837.7460.
Hodinka RL. Point: Is the era of viral culture over in the clinical microbiology laboratory? J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51(1):2–4. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02593-12.
Ryschkewitsch C, Jensen P, Hou J, Fahle G, Fischer S, Major EO. Comparison of PCR-southern hybridization and quantitative real-time PCR for the detection of JC and BK viral nucleotide sequences in urine and cerebrospinal fluid. J Virol Methods. 2004;121(2):217–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.06.021.
de Vries JJ, van der Eijk AA, Wolthers KC, Rusman LG, Pas SD, Molenkamp R, et al. Real-time PCR versus viral culture on urine as a gold standard in the diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Virol. 2012;53(2):167–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2011.11.006.
Al-Hadithi HN, Williams H, Hart CA, Frazer M, Adams EJ, Richmond DH, et al. Absence of bacterial and viral DNA in bladder biopsies from patients with interstitial cystitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol. 2005;174(1):151–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000161605.14804.a9.
Eisen DP, Fraser IR, Sung LM, Finlay M, Bowden S, O’Connell H. Decreased viral load and symptoms of polyomavirus-associated chronic interstitial cystitis after intravesical cidofovir treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(9):e86–8. https://doi.org/10.1086/597827. This case report first showed the clinical effecacy of anti-viral therapy in treating patients with IC/BPS.
Van der Aa F, Beckley I, de Ridder D. Polyomavirus BK—a potential new therapeutic target for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis? Med Hypotheses. 2014;83(3):317–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2014.06.004.
Sawinski D, Goral S. BK virus infection: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30(2):209–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfu023.
Jhang JF, Hsu YH, Jiang YH, Ho HC, Kuo HC. Clinical relevance of bladder histopathological findings and their impact on treatment outcomes among patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: An investigation of the European Society for the Study of Interstitial Cystitis Histopathological Classification. J Urol. 2021;205(1):226–35. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000001334.
Sant GR, Kempuraj D, Marchand JE, Theoharides TC. The mast cell in interstitial cystitis: Role in pathophysiology and pathogenesis. Urology. 2007;69(4 Suppl):34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2006.08.1109.
Logadottir Y, Delbro D, Lindholm C, Fall M, Peeker R. Inflammation characteristics in bladder pain syndrome ESSIC type 3C/classic interstitial cystitis. Int J Urol. 2014;21(Suppl 1):75–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.12370.
Akiyama Y, Maeda D, Katoh H, Morikawa T, Niimi A, Nomiya A, et al. Molecular taxonomy of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome based on whole transcriptome profiling by next-generation RNA sequencing of bladder mucosal biopsies. J Urol. 2019;202(2):290–300. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000000234. This study first investigated the whole transcriptome profiles in bladders of IC/BPS and showed several enriched virusassociated gene pathways in patients with IC/BPS.
Dienz O, Rincon M. The effects of IL-6 on CD4 T cell responses. Clin Immunol. 2009;130(1):27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2008.08.018.
Velazquez-Salinas L, Verdugo-Rodriguez A, Rodriguez LL, Borca MV. The role of interleukin 6 during viral infections. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:1057. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01057.
Saha SK, Jeon TI, Jang SB, Kim SJ, Lim KM, Choi YJ, et al. Bioinformatics approach for identifying novel biomarkers and their signaling pathways involved in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome with Hunner lesion. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061935.
Peng L, Jin X, Li BY, Zeng X, Liao BH, Jin T, et al. Integrating single-cell RNA sequencing with spatial transcriptomics reveals immune landscape for interstitial cystitis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):161. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-00962-8.
Jhang J-F, Hsu Y-H, Kuo H-C. Characteristics and electrocauterization of Hunner’s lesions associated with bladder pain syndrome. Urological Science. 2013;24(2):51–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urols.2013.04.001.
Wang H-J, Kuo H-C. Long-term satisfaction and complications in women with interstitial cystitis undergoing partial cystectomy and augmentation enterocystoplasty. Urological Science. 2018;29(2):81–5. https://doi.org/10.4103/uros.Uros_21_17.
Hirabayashi M, Traverse-Glehen A, Combes J-D, Clifford GM, de Martel C. Estimating the prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus in primary gastric lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Agents Cancer. 2023;18(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13027-023-00482-2.
Rea B, Liu YC, Maguire A, Soma LA, Bacon CM, Bayerl MG, et al. Genomic landscape of Epstein-Barr virus-positive extranodal marginal zone lymphomas of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Mod Pathol. 2022;35(7):938–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41379-021-01002-6.
Abe T, Shinohara N, Tada M, Harabayashi T, Sazawa A, Maruyama S, et al. Infiltration of Epstein-Barr virus-harboring lymphocytes occurs in a large subset of bladder cancers. Int J Urol. 2008;15(5):429–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2042.2008.02030.x.
Dere Y, Ekmekci S, Akarken I, Kucuk U. Can Epstein-Barr virus play a role in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas? Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2020;102(8):616–20. https://doi.org/10.1308/rcsann.2020.0138.
Takemori T, Kaji T, Takahashi Y, Shimoda M, Rajewsky K. Generation of memory B cells inside and outside germinal centers. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44(5):1258–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201343716.
Mohamed G, Vrzalikova K, Cader FZ, Vockerodt M, Nagy E, Flodr P, et al. Epstein-Barr virus, the germinal centre and the development of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Gen Virol. 2014;95(Pt 9):1861–9. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.066712-0.
Hatton OL, Harris-Arnold A, Schaffert S, Krams SM, Martinez OM. The interplay between Epstein-Barr virus and B lymphocytes: Implications for infection, immunity, and disease. Immunol Res. 2014;58(2–3):268–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-014-8496-1.
Jhang JF, Birder LA, Jiang YH, Hsu YH, Ho HC, Kuo HC. Dysregulation of bladder corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor in the pathogenesis of human interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):19169. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55584-y.
Regauer S, Gamper M, Fehr MK, Viereck V. Sensory hyperinnervation distinguishes bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis from overactive bladder syndrome. J Urol. 2017;197(1):159–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2016.06.089.
Ding H, Chen J, Su M, Lin Z, Zhan H, Yang F, et al. BDNF promotes activation of astrocytes and microglia contributing to neuroinflammation and mechanical allodynia in cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-1704-0.
Kashyap MP, Pore SK, de Groat WC, Chermansky CJ, Yoshimura N, Tyagi P. BDNF overexpression in the bladder induces neuronal changes to mediate bladder overactivity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018;315(1):F45–56. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00386.2017.
Yu YB, Zuo XL, Zhao QJ, Chen FX, Yang J, Dong YY, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 2012;61(5):685–94. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300265.
Chen J, Longnecker R. Epithelial cell infection by Epstein-Barr virus. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2019;43(6):674–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuz023.
Funding
Dr. Jia-Fong Jhang received funding from National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan R.O.C, 111-2314-B-303-033-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.F.J. collected the data and wrote the manuscript. H.C.K supervised, provided critical suggestions and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jhang, JF., Kuo, HC. The Role of Viral Infection in the Pathogenesis of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Curr Bladder Dysfunct Rep 18, 374–380 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11884-023-00713-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11884-023-00713-7