Abstract
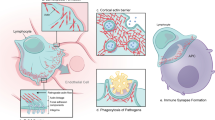
Since the first discovery of coronin in the amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum, remarkable insights have been gained regarding the structure and function of coronins, highly conserved from yeast to humans. It has been speculated that coronins have evolved from actin-binding molecules in lower eukaryotes to regulators of various cellular processes in mammals. Indeed, coronins are not only involved in cytokinesis, cell motility, and other actin-related processes but they are also implicated in immune homeostasis and calcium–calcineurin signaling. Most strikingly, coronin 1 deficiencies give rise to immune deficiencies in mice and humans that are characterized by severe T lymphocytopenia. Whereas complete absence of coronin 1A is associated with severe combined immunodeficiency in humans, hypomorphic mutations lead to a profound defect in naïve T cells, expansion of oligoclonal memory T cells, and exquisite susceptibility to EBV-associated B cell lymphoproliferation. Recent publications show that coronin 1A also plays a role in natural killer cell cytotoxic function and in neurobehavioral processes. It can be expected that future identification of coronin 1A-deficient patients will further extend the phenotypic spectrum thereby increasing our knowledge of this fascinating molecule.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
de Hostos EL, Bradtke B, Lottspeich F, Guggenheim R, Gerisch G. Coronin, an actin binding protein of Dictyostelium discoideum localized to cell surface projections, has sequence similarities to G protein beta subunits. EMBO J. 1991;10(13):4097–104.
Chan KT, Creed SJ, Bear JE. Unraveling the enigma: progress towards understanding the coronin family of actin regulators. Trends Cell Biol. 2011;21(8):481–8.
de Hostos EL, Rehfuess C, Bradtke B, et al. Dictyostelium mutants lacking the cytoskeletal protein coronin are defective in cytokinesis and cell motility. J Cell Biol. 1993;120(1):163–73.
Eckert C, Hammesfahr B, Kollmar M. A holistic phylogeny of the coronin gene family reveals an ancient origin of the tandem-coronin, defines a new subfamily, and predicts protein function. BMC Evol Biol. 2011;11:268.
Xavier CP, Eichinger L, Fernandez MP, Morgan RO, Clemen CS. Evolutionary and functional diversity of coronin proteins. Sub-cellular Biochem. 2008;48:98–109.
de Hostos EL. The coronin family of actin-associated proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 1999;9(9):345–50.
Gatfield J, Albrecht I, Zanolari B, Steinmetz MO, Pieters J. Association of the leukocyte plasma membrane with the actin cytoskeleton through coiled coil-mediated trimeric coronin 1 molecules. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(6):2786–98.
Kammerer RA, Kostrewa D, Progias P, et al. A conserved trimerization motif controls the topology of short coiled coils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(39):13891–6.
Appleton BA, Wu P, Wiesmann C. The crystal structure of murine coronin-1: a regulator of actin cytoskeletal dynamics in lymphocytes. Structure. 2006;14(1):87–96.
Rybakin V, Stumpf M, Schulze A, Majoul IV, Noegel AA, Hasse A. Coronin 7, the mammalian POD-1 homologue, localizes to the Golgi apparatus. FEBS Lett. 2004;573(1–3):161–7.
Suzuki K, Nishihata J, Arai Y, et al. Molecular cloning of a novel actin-binding protein, p57, with a WD repeat and a leucine zipper motif. FEBS Lett. 1995;364(3):283–8.
Oku T, Itoh S, Okano M, et al. Two regions responsible for the actin binding of p57, a mammalian coronin family actin-binding protein. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26(4):409–16.
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403–10.
Rybakin V, Clemen CS. Coronin proteins as multifunctional regulators of the cytoskeleton and membrane trafficking. BioEssays News Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol. 2005;27(6):625–32.
Foger N, Rangell L, Danilenko DM, Chan AC. Requirement for coronin 1 in T lymphocyte trafficking and cellular homeostasis. Science. 2006;313(5788):839–42.
Huang W, Ghisletti S, Saijo K, et al. Coronin 2A mediates actin-dependent de-repression of inflammatory response genes. Nature. 2011;470(7334):414–8.
Cai L, Makhov AM, Bear JE. F-actin binding is essential for coronin 1B function in vivo. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(Pt 10):1779–90.
Cai L, Marshall TW, Uetrecht AC, Schafer DA, Bear JE. Coronin 1B coordinates Arp2/3 complex and cofilin activities at the leading edge. Cell. 2007;128(5):915–29.
Pieters J, Muller P, Jayachandran R. On guard: coronin proteins in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;13(7):510–8. A very recent and comprehensive review on the coronin proteins and the many facettes of their functions.
Ferrari G, Langen H, Naito M, Pieters J. A coat protein on phagosomes involved in the intracellular survival of mycobacteria. Cell. 1999;97(4):435–47.
Jayachandran R, Sundaramurthy V, Combaluzier B, et al. Survival of mycobacteria in macrophages is mediated by coronin 1-dependent activation of calcineurin. Cell. 2007;130(1):37–50.
Suzuki K, Takeshita F, Nakata N, Ishii N, Makino M. Localization of CORO1A in the macrophages containing Mycobacterium leprae. Acta Histochem Cytochemica. 2006;39(4):107–12.
Zheng PY, Jones NL. Helicobacter pylori strains expressing the vacuolating cytotoxin interrupt phagosome maturation in macrophages by recruiting and retaining TACO (coronin 1) protein. Cell Microbiol. 2003;5(1):25–40.
Combaluzier B, Pieters J. Chemotaxis and phagocytosis in neutrophils is independent of coronin 1. J Immunol. 2009;182(5):2745–52.
Westritschnig K, BoseDasgupta S, Tchang V, Siegmund K, Pieters J. Antigen processing and presentation by dendritic cells is independent of coronin 1. Mol Immunol. 2013;53(4):379–86. First report on the role of coronin 1 in dendritic cells.
Haraldsson MK, Louis-Dit-Sully CA, Lawson BR, et al. The lupus-related Lmb3 locus contains a disease-suppressing Coronin-1A gene mutation. Immunity. 2008;28(1):40–51.
Mueller P, Massner J, Jayachandran R, et al. Regulation of T cell survival through coronin-1-mediated generation of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate and calcium mobilization after T cell receptor triggering. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(4):424–31.
Mugnier B, Nal B, Verthuy C, et al. Coronin-1A links cytoskeleton dynamics to TCR alpha beta-induced cell signaling. PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3467.
Shiow LR, Roadcap DW, Paris K, et al. The actin regulator coronin 1A is mutant in a thymic egress-deficient mouse strain and in a patient with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(11):1307–15.
Mueller P, Liu X, Pieters J. Migration and homeostasis of naive T cells depends on coronin 1-mediated prosurvival signals and not on coronin 1-dependent filamentous actin modulation. J Immunol. 2011;186(7):4039–50.
Shiow LR, Paris K, Akana MC, Cyster JG, Sorensen RU, Puck JM. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) associated with a Coronin-1A mutation and a chromosome 16p11.2 deletion. Clin Immunol. 2009;131(1):24–30.
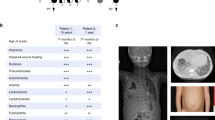
Moshous D, Martin E, Carpentier W, et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies Coronin-1A deficiency in 3 siblings with immunodeficiency and EBV-associated B-cell lymphoproliferation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131(6):1594–603. In this study, the second kindred with CORO1A deficiency is described. The patients, three siblings, presented a hypomorphic mutation in Coro1a leading to a combined immunodeficiency and particular predisposition to develop EBV-associated B-cell lymphoproliferation at an very early age.
Hogquist KA. Immunodeficiency: when T cells are stuck at home. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(11):1207–8.
Yagi H, Matsumoto M, Nakamura M, et al. Defect of thymocyte emigration in a T cell deficiency strain (CTS) of the mouse. J Immunol. 1996;157(8):3412–9.
Engelhardt KR, McGhee S, Winkler S, et al. Large deletions and point mutations involving the dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) in the autosomal-recessive form of hyper-IgE syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124(6):1289–302 e4.
Nehme NT, Pachlopnik Schmid J, Debeurme F, et al. MST1 mutations in autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency characterized by defective naive T-cell survival. Blood. 2012;119(15):3458–68.
Abdollahpour H, Appaswamy G, Kotlarz D, et al. The phenotype of human STK4 deficiency. Blood. 2012;119(15):3450–7.
Mou F, Praskova M, Xia F, et al. The Mst1 and Mst2 kinases control activation of rho family GTPases and thymic egress of mature thymocytes. J Exp Med. 2012;209(4):741–59.
Mace EM, Orange JS. Lytic immune synapse function requires filamentous actin deconstruction by Coronin 1A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(18):6708–13. This is the first report on the role of Coronin 1A for NK cell function.
Jayachandran R, Liu X, Bosedasgupta S, et al. Coronin 1 regulates cognition and behavior through modulation of cAMP/protein kinase A signaling. PLoS Biol. 2014;12(3):e1001820. Important work showing the critical role for coronin 1 in neurobehavior in mice and humans through regulating the transmission of signals within cells. It is shown that coronin 1 modulates the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and protein kinase A (PKA) signaling.
Weiss LA, Shen Y, Korn JM, et al. Association between microdeletion and microduplication at 16p11.2 and autism. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(7):667–75.
Rosenfeld JA, Coppinger J, Bejjani BA, Girirajan S, Eichler EE. Speech delays and behavioral problems are the predominant features in individuals with developmental delays and 16p11.2 microdeletions and microduplications. J Neurodev Disord. 2010;2:26–38.
Kumar RA, KaraMohamed S, Sudi J, et al. Recurrent 16p11.2 microdeletions in autism. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17(4):628–38.
Shinawi M, Liu P, Kang SH, et al. Recurrent reciprocal 16p11.2 rearrangements associated with global developmental delay, behavioural problems, dysmorphism, epilepsy, and abnormal head size. J Med Genet. 2010;47(5):332–41.
Shen Z, Zhang X, Chai Y, et al. Conditional knockouts generated by engineered crispr-cas9 endonuclease reveal the roles of coronin in C. elegans neural development. Dev Cell. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2014.07.017. A very recent study showing very elegantly through a conditional knockout strategy that Coronin is implicated in regulation of actin organization and cell morphology during postembryonic neuroblast migration and neuritogenesis in C. elegans.
Shiow LR, Paris K, Puck JM. Severe combined immunodeficiency due to absent coronin-1a. Primary immunodeficiency diseases a molecular and genetic approach 2014; 3rd ed. In: Ochs HD, Smith E, and Puck, JM, editors. 295.
Okumura M, Kung C, Wong S, Rodgers M, Thomas ML. Definition of family of coronin-related proteins conserved between humans and mice: close genetic linkage between coronin-2 and CD45-associated protein. DNA Cell Biol. 1998;17(9):779–87.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by institutional grants from INSERM, Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (Equipe Labellisée La Ligue), INCa, Institut Imagine, and the European Research Council (PIDIMMUN grant no. 249816).
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Despina Moshous and Jean-Pierre de Villartay report no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Immune Deficiency and Dysregulation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moshous, D., de Villartay, JP. The Expanding Spectrum of Human coronin 1A deficiency. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 14, 481 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-014-0481-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-014-0481-1
Keywords
- Coronin 1A
- Coronin
- Actin-binding molecules
- Actin-related protein 2/3 (ARP2/3) complex
- F-actin
- Immune homeostasis
- Calcium–calcineurin signaling
- Primary immunodeficiency
- T cell immunodeficiency
- Severe combined immune deficiency
- EBV-associated B cell lymphoproliferation
- Thymus
- Invariant natural killer T cell
- Mucosal-associated invariant T cell