Abstract
One of the hallmarks of dyslexia is the failure to automatise written patterns despite repeated exposure to print. Although many explanations have been proposed to explain this problem, researchers have recently begun to explore the possibility that an underlying implicit learning deficit may play a role in dyslexia. This hypothesis has been investigated through non-linguistic tasks exploring implicit learning in a general domain. In this study, we examined the abilities of children with dyslexia to implicitly acquire positional regularities embedded in both non-linguistic and linguistic stimuli. In experiment 1, 42 children (21 with dyslexia and 21 typically developing) were exposed to rule-governed shape sequences; whereas in experiment 2, a new group of 42 children were exposed to rule-governed letter strings. Implicit learning was assessed in both experiments via a forced-choice task. Experiments 1 and 2 showed a similar pattern of results. ANOVA analyses revealed no significant differences between the dyslexic and the typically developing group, indicating that children with dyslexia are not impaired in the acquisition of simple positional regularities, regardless of the nature of the stimuli. However, within group t-tests suggested that children from the dyslexic group could not transfer the underlying positional rules to novel instances as efficiently as typically developing children.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
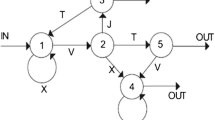
Shapes were sequentially added as a previous pilot study with a sample of TD third graders showed that participants could only learn the visual regularities when each shape was added to the display one-at-a-time (instead of presenting all four shapes at once).
References
Arciuli, J., & Simpson, I. C. (2012). Statistical learning is related to reading ability in children and adults. Cognitive Science, 36(2), 286–304. doi:10.1111/j.1551-6709.2011.01200.x.
Defior, S., Fonseca, L., Gottheil, B., Aldrey, A., Jiménez-Fernández, G., Pujals, M., … Serrano, F. (2006). LEE. Test de Lectura y Escritura en Español. Buenos Aires: Paidós.
Du, W., & Kelly, S. W. (2013). Implicit sequence learning in dyslexia: a within-sequence comparison of first- and higher-order information. Annals of Dyslexia, 63(2), 154–170. doi:10.1007/s11881-012-0077-1.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A.-G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175–191. doi:10.3758/BF03193146.
Fiser, J., & Aslin, R. N. (2001). Unsupervised statistical learning of higher-order spatial structures from visual scenes. Psychological Science, 12(6), 499–504. doi:10.1111/1467-9280.00392.
Folia, V., Uddén, J., Forkstam, C., Ingvar, M., Hagoort, P., & Petersson, K. M. (2008). Implicit learning and dyslexia. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1145(1), 132–150.
Gabay, Y., Schiff, R., & Vakil, E. (2012). Dissociation between the procedural learning of letter names and motor sequences in developmental dyslexia. Neuropsychologia, 50(10), 2435–2441. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.06.014.
Gombert, J. (2003). Implicit and explicit learning to read: implication as for subtypes of dyslexia. Current Psychology Letters, 10(1), 25–40.
Goschke, T. (1998). Implicit learning of perceptual and motor sequences: Evidence for independent learning systems. In M. A. Stadler & P. A. Frensch (Eds.), Handbook of implicit learning (pp. 401–444). Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications, Inc.
Grabe, W. (2010). Fluency in reading—thirty-five years later. Reading in a Foreign Language, 22(1), 71–83.
Howard, J. H., Jr., Howard, D. V., Japikse, K. C., & Eden, G. F. (2006). Dyslexics are impaired on implicit higher-order sequence learning, but not on implicit spatial context learning. Neuropsychologia, 44(7), 1131–1144. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.10.015.
Ise, E., Arnoldi, C. J., Bartling, J., & Schulte-Körne, G. (2012). Implicit learning in children with spelling disability: evidence from artificial grammar learning. Journal of Neural Transmission, 119(9), 999–1010. doi:10.1007/s00702-012-0830-y.
Jiménez-Fernández, G., Vaquero, J. M. M., Jiménez, L., & Defior, S. (2011). Dyslexic children show deficits in implicit sequence learning, but not in explicit sequence learning or contextual cueing. Annals of Dyslexia, 61(1), 85–110. doi:10.1007/s11881-010-0048-3.
Kelly, S. W., Griffiths, S., & Frith, U. (2002). Evidence for implicit sequence learning in dyslexia. Dyslexia, 8(1), 43–52. doi:10.1002/dys.208.
Lum, J. A. G., Ullman, M. T., & Conti-Ramsden, G. (2013). Procedural learning is impaired in dyslexia: evidence from a meta-analysis of serial reaction time studies. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(10), 3460–3476. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2013.07.017.
Menghini, D., Finzi, A., Benassi, M., Bolzani, R., Facoetti, A., Giovagnoli, S., … Vicari, S. (2010). Different underlying neurocognitive deficits in developmental dyslexia: a comparative study. Neuropsychologia, 48(4), 863–872. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.11.003.
Nigro, L., Jiménez-Fernández, G., Simpson, I. C., & Defior, S. (2015). Implicit learning of written regularities and its relationship to literacy acquisition in a shallow orthography. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 44(5), 571–585. doi:10.1007/s10936-014-9303-9.
Nissen, M. J., & Bullemer, P. (1987). Attentional requirements of learning: evidence from performance measures. Cognitive Psychology, 19(1), 1–32. doi:10.1016/0010-0285(87)90002-8.
Pacton, S., Fayol, M., & Perruchet, P. (2005). Children’s implicit learning of graphotactic and morphological regularities. Child Development, 76(2), 324–339. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2005.00848_a.x.
Pacton, S., Perruchet, P., Fayol, M., & Cleeremans, A. (2001). Implicit learning out of the lab: the case of orthographic regularities. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 130(3), 401–426. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.130.3.401.
Pavlidou, E. V., Kelly, M. L., & Williams, J. M. (2010). Do children with developmental dyslexia have impairments in implicit learning? Dyslexia, 16(2), 143–161. doi:10.1002/dys.400.
Pavlidou, E. V., & Williams, J. M. (2014). Implicit learning and reading: Insights from typical children and children with developmental dyslexia using the artificial grammar learning (AGL) paradigm. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 35(7), 1457–1472. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2014.03.040.
Pavlidou, E. V., Williams, J. M., & Kelly, L. M. (2009). Artificial grammar learning in primary school children with and without developmental dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 59(1), 55–77. doi:10.1007/s11881-009-0023-z.
Pothos, E. M. (2007). Theories of artificial grammar learning. Psychological Bulletin, 133(2), 227–244. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.133.2.227.
Pothos, E. M., & Kirk, J. (2004). Investigating learning deficits associated with dyslexia. Dyslexia, 10(1), 61–76. doi:10.1002/dys.266.
Raven, J. C., Court, J. H., & Raven, J. (1996). Raven matrices progresivas, escalas color (CPM), general (SPM), superior (APM): Manual. Madrid: Tea.
Reber, A. S. (1967). Implicit learning of artificial grammars. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 6, 855–863.
Reber, A. S. (1993). Implicit learning and tacit knowledge: an essay on the cognitive unconscious. New York: Oxford University Press.
Roodenrys, S., & Dunn, N. (2008). Unimpaired implicit learning in children with developmental dyslexia. Dyslexia, 14(1), 1–15. doi:10.1002/dys.340.
Rüsseler, J., Gerth, I., & Münte, T. F. (2006). Implicit learning is intact in adult developmental dyslexic readers: evidence from the serial reaction time task and artificial grammar learning. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 28(5), 808–827. doi:10.1080/13803390591001007.
Schneider, W., Eschman, A., & Zuccolotto, A. (2002). E-Prime 2.0 software. Pittsburgh: Psychology Software Tools Inc.
Snowling, M. J., & Stackhouse, J. (Eds.). (2006). Dyslexia, speech and language: a practitioner’s handbook (2nd ed.). London: Wiley.
Sperling, A. J., Lu, Z. L., & Manis, F. R. (2004). Slower implicit categorical learning in adult poor readers. Annals of Dyslexia, 54(2), 281–303. doi:10.1007/s11881-004-0014-z.
Stoodley, C. J., Harrison, E. P. D., & Stein, J. F. (2006). Implicit motor learning deficits in dyslexic adults. Neuropsychologia, 44(5), 795–798. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.07.009.
Stoodley, C. J., Ray, N. J., Jack, A., & Stein, J. F. (2008). Implicit learning in control, dyslexic, and garden-variety poor readers. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1145(1), 173–183. doi:10.1196/annals.1416.003.
Vicari, S., Marotta, L., Menghini, D., Molinari, M., & Petrosini, L. (2003). Implicit learning deficit in children with developmental dyslexia. Neuropsychologia, 41(1), 108–114. doi:10.1016/S0028-3932(02)00082-9.
Acknowledgments
This research has been partially supported by PITN-215961-ELDEL project of the FP7 Marie Curie programme and HUM-820 research group of the Junta de Andalucía.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nigro, L., Jiménez-Fernández, G., Simpson, I.C. et al. Implicit learning of non-linguistic and linguistic regularities in children with dyslexia. Ann. of Dyslexia 66, 202–218 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-015-0116-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-015-0116-9