Abstract
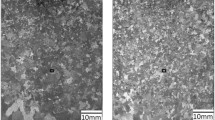
In the present study, molten Al 2024 alloy was subjected to two different electromagnetic flow directions, i.e., (1) irreversible clockwise (CW) and (2) reversible clockwise–anticlockwise (CW-ACW) direction rotational magnetic fields (RMF) at constant and varying intervals. The construction allows the aluminum melt to solidify in the TP-1 mold under a combination of directional solidification with a forced convection mechanism. With the help of computer-based simulation, secondary flow and variation in temperature profiles have been evaluated. The effect of the electromagnetic stirring current and pouring temperature on the microstructural morphology of the Al 2024 alloy has been analyzed by experimental work. It was found that at a low pouring temperature (913 K) with an increase in current value (6–9 A), when CW-ACW RMF is applied, the grain size of the sample was finer compared to the CW RMF. In contras, at higher pouring temperatures (943–993 K) and the same current value, better grain size refinement was observed in the case of the CW RMF samples. However, deviation in the grain refinement trend was observed at a current of 11 A at low and higher pouring temperature. The best grain refinement was achieved at a pouring temperature of 993 K with a 7.5-A current in an irreversible direction.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhang, W. Li, and J.P. Yao, J. Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.10.185 (2013).
Z. Huda and T. Zaharinie, J. Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.11.071 (2009).
J.C. Malas, S. Venugopal, and T. Seshacharyulu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.09.078 (2004).
B. Rahimi, H. Khosravi, and M. Haddad-Sabzevar, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1044-8 (2015).
A. Minagawa, K. Takahashi, and S. Shimasaki, Miner. Met. Mater. Ser. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05864-7-121 (2019).
K. Matsuda, T. Takehara, M. Yang, H. Uno, T. Kubo, G. Miyano, and M. Yoshida, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3377-y (2016).
H. Luo, W. Jie, Z. Gao, and Y. Zheng, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soci. China. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64738-7 (2018).
V. Metan and K. Eigenfeld, Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01803-6 (2013).
T.W. Kim, S.M. Lee, C.G. Kang, and B.M. Kim, Int J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1331-2 (2009).
P. Kaur, D.K. Dwivedi, and P.M. Pathak, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-3921-x (2012).
B.I. Jung, C.H. Jung, T.K. Han, and Y.H. Kim, J. Mater. Process. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)00514-3 (2001).
W.D. Griffiths and D.G. McCartney, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(96)10527-X (1997).
W.D. Griffiths and D.G. McCartney, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(96)10392-0 (1996).
I.G. Chung, A. Bolouri, and C.G. Kang, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3376-5 (2012).
H. Li, S. Liu, J. Jie, L. Guo, H. Chen, and T. Li, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0724-0 (2017).
C.G. Kang, J.W. Bae, and B.M. Kim, J. Mater. Process. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.11.181 (2007).
C.G. Kang and S.M. Lee, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1242-2 (2008).
E.J. Zoqui, M. Paes, and E.S. Sadiqi, J. Mater. Process. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01148-7 (2002).
T. Guan, Z. Zhang, Y. Bai, M. He, H. Zheng, H. Zhao, and X. Li, Mater. MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010022 (2018).
W. Mao, H. Lin, Y. Bai, and S. Gao, J .Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1005-8850(07)60012-7 (2007).
M. Paes, E.G. Santos, and E.J. Zoqui, Metall. Trans. B 19, 2 (1989).
C. Vives, Metall. Trans. B. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02655919 (1989).
S. Eckert, P.A. Nikrityuk, B. Willers, D. Rabiger, N. Shevchenko, H. Neumann-Heyme, V. Travnikov, S. Odenbach, A. Voigt, and K. Eckert, Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01802-7 (2013).
P.A. Nikrityuk, K. Eckert, and R.A. Grundmann, Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2005.08.035 (2006).
B. Willers, S. Eckert, P.A. Nikrityuk, and K. Eckert, Modeling of casting, in Welding, and Advanced Solidification Processes-XI. ed. by C.-A. Gandin, and M. Bellot (TMS, Warrendale PA, 2006), pp. 333–40.
S. Steinbach and L. Ratke, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2005.09.010 (2005).
S. Eckert, P.A. Nikrityuk, D. Rabiger, K. Eckert, and G. Gerbeth, Metall. Mater. Trans. B. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9126-x (2007).
M. Ungarish, J. Fluid Mech. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112097006605 (1997).
P.A. Nikrityuk, M. Ungarish, K. Eckert, and R. Grundmann, Phys. Fluid. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1897323 (2005).
P.A. Nikrityuk, S. Eckert, and K. Eckert, Eur. J. Mech. B Fluid. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2007.05.004 (2008).
M. Li, T. Tamura, N. Omura, Y. Murakami, and S. Tada, J. Mater. Proc. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.04.024 (2016).
B. Willers, S. Eckert, P.A. Nikrityuk, D. Rabiger, J. Dong, K. Eckert, and G. Gerbeth, Metall. Mater. Trans. B. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9126-x (2008).
H. Wei, F. Xia, S. Qian, and M. Wang, J. Mater. Process. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.10.012 (2017).
T.Y. Guan, Z.F. Zhang, Y.L. Bai, and P. Wang, Mater. Sci. Forum. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.898.24 (2017).
Y.B. Zuo, J.Z. Cui, M.O.U. Dan, Q.F. Zhu, X.J. Wang, and L.I. Lei, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63364-1 (2014).
A. Kundu, D. Patel, P. Biswas, S. Ranjan, A. Mallik, and S. Das, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02269-8 (2021).
ANSYS, Maxwell 2D User’s Guide (Ver. 14) (Ansys Inc, Canonsburg, 2010), p. 1–565.
ANSYS, Ansys Fluent Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Module Manual (Ver. 15) (Ansys Inc, Canonsburg, 2013), p. 1–35.
A. Maurya, R. Kumar, and P.K. Jha, J. Manuf. Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.11.003 (2020).
L.B. Trindade, J.E.A. Nadalon, A.C. Contini, and R.C. Barroso, Steel Res. Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201600319 (2017).
Z. Liu, W.M. Mao, and Z.D. Zhao, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(06)60013-7-76 (2006).
S. Tzamtzis, BCAST (WL) (Brunel University at West London, London, 2011).
A.F. Ferreira, W.B. Chrisostimo, R.C. Sales, W.J.L. Garcao, and N. de Paula-Sousa, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 104, 957 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03979-6 (2019).
J. Zou, H. Zhang, Z. Wu, J. Wang, B. Li, J. Cui, H. Nagaumi, and Y. Li, J. Mater. Res. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.039 (2021).
Y.L. Bai, J. Xu, Z.F. Zhang, and L.K. Shi, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(10)60103-3 (2009).
S. Nafisi, D. Emadi, M.T. Shehata, and R. Ghomashchi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.05.076 (2006).
T. Chandrashekar, M.K. Muralidhara, K.T. Kashyap, and P.R. Rao, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1336-x (2009).
M.C. Flemings, Metall. Mater. Trans. B. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02643923 (1974).
A. Hellawell, in Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Semi- Solid Processing of Alloys and Composites (Sheffield, England, 1996), p. 60
R.D. Doherty, H.I. Lee, and E.A. Feest, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5416(84)90211-8 (1984).
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to National institute of technology, Raipur for providing lab facilities to conduct the research experiment and very thankful to the technical assistant Mr. Santosh Nagwanshi from the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, NIT Raipur, for helping us during casting processes.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kundu, A., Biswas, P., Sahu, M. et al. Effect of Electromagnetic Flow Direction on Grain Refinement of Al 2024 Alloy. JOM 75, 2799–2817 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05907-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05907-2