Abstract
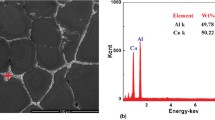
This article reports the effects of stirring speed and T6 heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-2024 alloy synthesized by a rheocasting process. There was a decrease in grain size of α-Al particles corresponding to an increase in stirring speed. By increasing the stirring speed, however, the globularity of matrix particles first increased and then declined. It was also found that the hardness, compressive strength, and compressive strain increased with the increase of stirring speed. Microstructural studies revealed the presence of nonsoluble Al15(CuFeMn)3Si2 phase in the vicinity of CuAl2 in the rheocast samples. The required time for the solution treatment stage was also influenced by stirring speed; the solution treatment time decreased with the increase in stirring speed. Furthermore, the rheocast samples required a longer homogenization period compared to conventionally wrought alloys. Improvements in hardness and compressive properties were observed after T6 heat treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.B. Spencer, R. Mehrabian, and M.C. Flemings, Rheological behavior of Sn-15 pct Pb in the crystallization range, Metall. Trans., 3(1972), No. 7, p. 1925.
H.M. Guo, X.B. Liu, X.J. Yang, A.S. Zhang, and Y. Liu, Microstructure evolution behavior of AlSi9Cu3 alloy during rheocasting, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 20(2010), p. 815.
H. Mirzadeh and B. Niroumand, Effects of rheocasting parameters on the microstructure of rheo-centrifuged cast Al-7.1wt%Si alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 474(2009), No. 1–2, p. 257.
P. Falak and B. Niroumand, Rheocasting of an Al-Si alloy, Scripta Mater., 53(2005), No. 1, p. 53.
H. Nakato, M. Oka, S. Itoyama, M. Urata, T. Kawasaki, K. Hashiguchi, and S. Okano, Continuous semi-solid casting process for aluminum alloy billets, Mater. Trans., 43(2002), No. 1, p. 24.
Z. Fan, X. Fang, and S. Ji, Microstructure and mechanical properties of rheo-diecast (RDC) aluminium alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 412(2005), No. 1–2, p. 298.
P.A. Joly and R. Mehrabian, The rheology of a partially solid alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 11(1976), p. 1393.
M. Reisi and B. Niroumand, Effects of stirring parameters on rheocast structure of Al-7.1wt.%Si alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 470(2009), p. 413.
B. Niroumand and K. Xia, 3D study of the structure of primary crystals in a rheocast Al-Cu alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 283(2000), No. 1–2, p. 70.
Z. Fan, Semisolid metal processing, Int. Mater. Rev., 47(2002), No. 2, p. 49.
T. Haga and P. Kapranos, Thixoforming of laminate made from semisolid cast strips, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 157–158(2004), p. 508.
A. Hekmat-Ardakan and F. Ajersch, Effect of conventional and rheocasting processes on microstructural characteristics of hypereutectic Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloy with variable Mg content, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 210(2010), No. 5, p. 767.
P.K. Seo, D.U. Kim, and C.G. Kang, The characteristics of grain size controlled microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Si alloy by thixocasting and rheocasting process, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 162–163(2005), p. 570.
T. Haga and P. Kapranos, Simple rheocasting processes, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 130–131(2002), p. 594.
Z.H. Bai, F. Qiu, X.X. Wu, Y.Y. Liu, and Q.C. Jiang, Age hardening and creep resistance of cast Al-Cu alloy modified by praseodymium, Mater. Charact., 86(2013), p. 185.
A.K. Dey, P. Poddar, K.K. Singh, and K.L. Sahoo, Mechanical and wear properties of rheocast and conventional gravity die cast A356 alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 435–436(2006), p. 521.
U.A. Curle, Semi-solid near-net shape rheocasting of heat treatable wrought aluminum alloys, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 20(2010), No. 9, p. 1719.
N. Mahathaninwong, T. Plookphol, J. Wannasin, and S. Wisutmethangoon, T6 heat treatment of rheocasting 7075 Al alloy, Mater Sci Eng A, 532(2012), p. 91–99.
S.L. Lü, S.S. Wu, L. Wan, and P. An, Microstructure and tensile properties of wrought Al alloy 5052 produced by rheo-squeeze casting, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 44(2013), No. 6, p. 2735.
ASM International Handbook Committee, ASM Metals Handbook, Vol. 15, Casting, ASM International, The Materials Information Company, 1991.
J.D. Seidt and A. Gilat, Plastic deformation of 2024-T351 aluminum plate over a wide range of loading conditions, Int. J. Solids Struct., 50(2013), No. 10, p. 1781.
J.C. Malas, S. Venugopal, and T. Seshacharyulu, Effect of microstructural complexity on the hot deformation behavior of aluminum alloy 2024, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 368(2004), No. 1–2, p. 41.
A.K. Gupta, B.K. Prasad, R.K. Pajnoo, and S. Das, Effects of T6 heat treatment on mechanical, abrasive and erosive-corrosive wear properties of eutectic Al-Si alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 22(2012), No. 5, p. 1041.
I. Aguilera Luna, H. Mancha Molinar, M.J. Castro Román, J.C. Escobedo Bocardo, and M. Herrera Trejo, Improvement of the tensile properties of an Al-Si-Cu-Mg aluminum industrial alloy by using multi stage solution heat treatments, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 561(2013), p. 1.
Y. Birol, Response to artificial ageing of dendritic and globular Al-7Si-Mg alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 484(2009), No. 1–2, p. 164.
P.K. Seo and C.G. Kang, The effect of raw material fabrication process on microstructural characteristics in reheating process for semi-solid forming, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 162–163(2005), p. 402.
R.A. Martinez and M.C. Flemings, Evolution of particle morphology in semisolid processing, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 36(2005), No. 8, p. 2205.
ASM International Handbook Committee, ASM Metals Handbook, Vol. 4, Heat Treating, ASM International, The Materials Information Company, 1991.
E.J. Zoqui and M.H. Robert, Structural modifications in rheocast Al-Cu alloys by heat treatment and implications on mechanical properties, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 78(1998), No. 1–3, p. 198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahimi, B., Khosravi, H. & Haddad-Sabzevar, M. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of Al-2024 alloy processed via a rheocasting route. Int J Miner Metall Mater 22, 59–67 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1044-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1044-8