Abstract
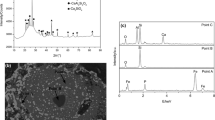
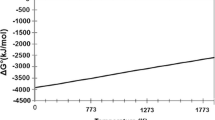
Unlike previous dephosphorization studies, the present work complies with a concept to recover phosphorus within the utilization of high-phosphorus oolitic iron ores to prepare Fe-P alloy for high-phosphorus steel production. Simultaneous enrichment of iron and phosphorus can be achieved by directly alloying the high-phosphorus oolitic iron ore at high reduction temperatures (≥1623 K). Neither fluxes nor other special additives need to be used. Consequently, the phosphorus element migrates from original apatite to the slag phase with the elevating temperature from 1323 K to 1473 K, and it further moves into metallic iron and forms Fe3P at 1623 K. A metalized iron-phosphorus alloy with assaying of 96.51% iron and 2.03% phosphorus content was obtained at 1623 K for 10 min at corresponding iron and phosphorus recovery rates of 97.50% and 64.51%, respectively. This process exhibits high economic efficiency and is practicable as a stepping-stone for the efficient and direct utilization of high-phosphorus iron ore resources.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.R. Arvidson, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 66, 467 (2013).
S.X. Song, E.F. Campos-Toro, Y.M. Zhang, and A. Lopez-Valdivieso, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 20, 113 (2013).
J.T. Yu, Z.C. Guo, and H.Q. Tang, J. Univ. Sci. Tech. Beijing 35, 986 (2013).
C.Q. Xiao, X.Y. Wu, and R. Chi, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 176, 518 (2015).
J.C. Wang, S.B. Shen, J.H. Kang, H.X. Li, and Z.C. Guo, Process. Biochem. 45, 1624 (2010).
Y.F. Yu and C.Y. Qi, J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Mater. Sci. Ed.) 26, 176 (2011).
D. Zhu, Y. Xiao, T. Chun, B. Chen, and J. Pan, XXV International Mineral Processing Congress (IMPC) 2010 Proceedings (Brisbane, QLD, Australia: Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2010), p. 1667.
D.Q. Zhu, H. Wang, J. Pan, and C.C. Yang, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 23, 661 (2016).
K. Ionkov, S. Gaydardzhiev, A.C. Araujo, D. Bastin, and M. Lacoste, Miner. Eng. 46, 119 (2013).
G.H. Li, S.H. Zhang, M.J. Rao, Y.B. Zhang, and J. Tao, Int. J. Miner. Process. 124, 26 (2013).
J.T. Gao, L. Guo, and Z.C. Guo, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46, 2180 (2015).
W. Yu, T.C. Sun, J. Kou, Y.X. Wei, C.Y. Xu, and Z.Z. Liu, ISIJ Int. 53, 427 (2013).
H.L. Han, D.P. Duan, X. Wang, and S.M. Chen, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 1634 (2014).
D.Q. Zhu, Z.Q. Guo, J. Pan, and F. Zhang, Metals-Basel 6, 123 (2016).
H.Q. Tang, W.D. Liu, H.Y. Zhang, and Z.C. Guo, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 1683 (2014).
H.Q. Tang, T.F. Qi, and Y.Q. Qin, JOM 67, 1956 (2015).
S. Takeuchi, N. Sano, and Y. Matsushita, Tetsu-to-Hagané 66, 2050 (1980).
K. Morita, M. Guo, N. Oka, and N. Sano, J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 4, 93 (2002).
T. Kim and J. Lee, Metall. Mater. Trans. 52, 2233 (2011).
Y.B. Kang, T. Kim, and J. Lee, Ironmaker Steelmak. 39, 498 (2012).
G.P. Zhou, S.C. Yu, Z.Y. Liu, J. Chen, Y.Q. Qiu, and G.D. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. 23, 36 (2011).
R.A. Howell and D.C.V. Aken, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46, 3309 (2015).
S. Hong, J. Lee, K.S. Park, and S. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 589, 165 (2014).
D.W. Yang, T.C. Sun, and C.Y. Xu, Min. Metall. Eng. 30, 29 (2010).
J.T. Gao, Y.W. Zhong, L. Guo, and Z.C. Guo, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 1080 (2016).
H.Q. Tang, Z.C. Guo, and Z.L. Zhao, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 17, 1 (2010).
C. Cheng, Q.G. Xue, G. Wang, Y.Y. Zhang, and J.S. Wang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 154 (2016).
G.H. Li, M.J. Rao, C.Z. Ouyang, S.H. Zhang, Z.W. Peng, and T. Jiang, ISIJ Int. 55, 2304 (2015).
J. Cha, D. Kim, and S. Jung, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46, 2165 (2015).
W. Yu, T.C. Sun, and Q. Cui, Int. J. Miner. Process. 133, 119 (2014).
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the National Torch Program Project of China (Grant 2011GH561685), China Scholarship Council (CSC) Ph.D. scholarship program, and Hunan Provincial Co-innovation Center for Clean and Efficient Utilization of Strategic Metal Mineral Resources are sincerely appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Zhu, D., Pan, J. et al. Simultaneous Recovery of Iron and Phosphorus from a High-Phosphorus Oolitic Iron Ore to Prepare Fe-P Alloy for High-Phosphorus Steel Production. JOM 69, 1663–1668 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2385-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2385-8