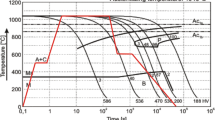
Abstract
We describe the effect of varying tension leveling parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of steel strips. We found that, when the tension leveling elongation was constant, an increase in the screw-down value resulted in an initial decrease in the cross-sectional grain size of the strip, which was followed by an increase. However, the longitudinal grain size remained constant, and the yield strength and tensile strength increased gradually. In addition, with a constant screw-down value, an increase in tension leveling elongation resulted in refining of the cross-sectional grain size, elongation of the longitudinal grain size, and small increases in both yield and tensile strength. This study therefore provides an insight into the optimal configuration of tension leveling parameters to improve steel strip properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Meyer and H. Zhao, Optimization of Material Properties During Strip Rolling (Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 1996), p. 1.
T.P. Wang and K.M. Qi, Metal Plastic Processing—Rolling Theory and Process, 3rd ed. (Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2013), p. 215.
J.X. Zou, Rolling Machinery, 3rd ed. (Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2013), p. 390.
H. Huh, H.W. Lee, S.R. Park, G.Y. Kim, and S.H. Nam, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 113, 714 (2001).
F. Hibino, Sci. Mach. 56, 366 (2004).
F. Hibino, Sci. Mach. 62, 19 (2010).
H. Hamasaki, M. Shigaki, F. Yoshida, and V. Toropov, J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 14, 740 (2009).
Y.Y. Fu, G.L. Li, and F. Liu, Mod. Manuf. Eng. 7, 61 (2006).
Q.D. Zhang, T.H. Liu, W.G. Wang, and J.R. Zhu, Iron Steel 42, 44 (2007).
Q.D. Zhang, T.Z. Chang, H. Huang, Z.L. Jiang, and B. Wu, Iron Steel 42, 47 (2007).
Q.D. Zhang, T.H. Liu, and J.R. Zhu, Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 44, 236 (2008).
E. Ishimaru, H. Hamasaki, and F. Yoshida, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 223, 34 (2015).
M.H. Korayem, M.K. Jain, and R.K. Mishra, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 648, 371 (2015).
E.J. Hoggan, R.I. Scott, M.R. Barnett, and P.D. Hodgson, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 125–126, 155 (2002).
S. Huang, C.F. He, and Y.X. Zhao, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25, 966 (2016).
M.L. Wang, Z.W. Zheng, and L. Xiao, Mater. Mech. Eng. 36, 42 (2012).
H.B. Huang and F. Li, Phys. Test. Chem. Anal. A: Phys. Test 42, 15 (2006).
Q. Zhao, G.C. Zhou, and J.C. Zhao, Phys. Test. Chem. Anal. A: Phys. Test 41, 283 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shanxi Province Natural Science Fund of China (201601D011052) and the Taiyuan Talent special project of Shanxi Province, China (12024706).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhou, C.L., Li, H.B. et al. Influence of Tension Leveling Parameters on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Steel Strip. JOM 69, 937–941 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2272-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2272-3