Abstract
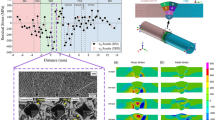
Residual stress distribution and its magnitude varies across the weldment, contributing to many catastrophic failures. Moreover, it is challenging to reliably measure residual stresses, considering a particular technique. Therefore, the present investigation aims to examine residual stresses in similar (T91-T91) and dissimilar (T91-Super304H) welds before and after post-weld heat treatments (PWHT), using non-destructive methods (sin2ψ and cos α) and SYSWELDS simulations. For a similar weld, the peak tensile residual stresses near to fusion line reached ~ 238 MPa (as per sin2ψ method) and ~ 258 MPa (as per cos α method), which is ~ 48% of yield stress (520 MPa) of T91 steel. Alternatively, for the case of dissimilar welds, peak tensile residual stresses of ~ 518 MPa and peak compressive residual stresses of ~ 290 MPa were observed at the fusion line of the T91 side and Super304H side, respectively. Dissimilar welds show relatively high residual stresses with significant deviation across weldment due to varying thermal coefficients of expansion/contraction resulting from dissimilar metal joints. Hence, PWHTs were performed to decrease the magnitude of peak residual stresses and their deviation across weldment to enhance the life of welded joints. For instance, the peak tensile residual stresses decreased from ~ 258 to ~ 120 MPa after 775 °C—30 min PWHT condition in similar welds. Similarly, for dissimilar welds, post-weld normalizing and tempering (PWNT) at 1050 °C—30 min followed by 760 °C—60 min condition was found to decrease the residual stresses from ~ 518 to ~ 70 MPa, which is a significant reduction achieved due to austenitizing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. Klueh, Elevated Temperature Ferritic and Martensitic Steels and Their Application to Future Nuclear Reactors, Int. Mater. Rev., 2005, 50, p 287–310. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328005X41140
A. Sauraw, A.K. Sharma, D. Fydrych, S. Sirohi, A. Gupta, A. Świerczyńska, C. Pandey, and G. Rogalski, Study on Microstructural Characterization, Mechanical Properties and Residual Stress of Gtaw Dissimilar Joints of p91 and p22 Steels, Materials (Basel)., 2021 https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14216591
J. Shen, P. Agrawal, T.A. Rodrigues, J.G. Lopes, N. Schell, Z. Zeng, R.S. Mishra, and J.P. Oliveira, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of As-cast AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Des., 2022, 223, p 111176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2022.111176
J. Shen, P. Agrawal, T.A. Rodrigues, J.G. Lopes, N. Schell, J. He, Z. Zeng, R.S. Mishra, and J.P. Oliveira, Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties in a Gas Tungsten Arc Welded Fe42Mn28Co10Cr15Si5 Metastable High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2023, 867, p 144722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2023.144722
J.G. Lopes, P. Rocha, D.A. Santana, J. Shen, E. Maawad, N. Schell, J.P. Oliveira, Impact of Arc‐Based Welding on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties in Newly Developed Cr29. 7Co29. 7Ni35. 4Al4Ti1. 2 Multi‐principal Element alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. (2023)
H.T. Kang, Y.L. Lee, and X.J. Sun, Effects of Residual Stress and Heat Treatment on Fatigue Strength of Weldments, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2008, 497, p 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.06.011
Y.C. Lin and S.C. Chen, Effect of Residual Stress on Thermal Fatigue in a Type 420 Martensitic Stainless Steel Weldment, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, 138, p 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00043-8
D. Deng, Y. Zhou, T. Bi, and X. Liu, Experimental and Numerical Investigations of Welding Distortion Induced by CO2 Gas Arc Welding in Thin-plate Bead-on Joints, Mater. Des., 2013, 52, p 720–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.06.013
J.B. Ju, J.S. Lee, J.I. Jang, W.S. Kim, and D. Kwon, Determination of Welding Residual Stress Distribution in API X65 Pipeline Using a Modified Magnetic Barkhausen Noise Method, Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip., 2003, 80, p 641–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-0161(03)00131-5
S. Paddea, J.A. Francis, A.M. Paradowska, P.J. Bouchard, and I.A. Shibli, Residual Stress Distribution in a P91 Steel-pipe Girth Weld Before and After Post Weld Heat Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2012, 534, p 663–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.12.024
V.I. Monin, T. Gurova, X. Castello, and S.F. Estefen, Analysis of Residual Stress State in Welded Steel Plates by X-ray Diffraction Method, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci., 2009, 20, p 172–175.
A. Yaghi, T.H. Hyde, A.A. Becker, W. Sun, and J.A. Williams, Residual Stress Simulation in Thin and Thick-walled Stainless Steel Pipe Welds Including Pipe Diameter Effects, Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip., 2006, 83, p 864–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2006.08.014
J.A. Francis, M. Turski, and P.J. Withers, Measured Residual Stress Distributions for Low and High Heat Input Single Weld Beads Deposited on to SA508 Steel, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2009, 25, p 325–334. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328408X372074
J. Shen, R. Gonçalves, Y.T. Choi, J.G. Lopes, J. Yang, N. Schell, H.S. Kim, and J.P. Oliveira, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Gas Metal Arc Welded CoCrFeMnNi Joints Using a 308 Stainless Steel Filler Metal, Scr. Mater., 2023, 222, p 115053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2022.115053
J. Shen, R. Gonçalves, Y.T. Choi, J.G. Lopes, J. Yang, N. Schell, H.S. Kim, and J.P. Oliveira, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Gas Metal Arc Welded CoCrFeMnNi Joints Using a 410 Stainless Steel Filler Metal, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2022, 857, p 144025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.144025
D. Akbari and I. Sattari-Far, Effect of the Welding Heat Input on Residual Stresses in Butt-welds of Dissimilar Pipe Joints, Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip., 2009, 86, p 769–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2009.07.005
K. Tanaka, K. Suzuki, Y. Akiniwa, Evaluation of Residual Stresses by X-ray Diffraction, Yokendo (in Japanese) (2006)
Y. Maruyama, T. Miyazaki, and T. Sasaki, Development and Validation of an X-ray Stress Measurement Device Using an Imaging Plate Suitaible for the cosα Method, J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Japan., 2015, 64, p 560–566. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171813Y.0000000132
S. Kumar, R. Awasthi, C.S. Viswanadham, K. Bhanumurthy, and G.K. Dey, Thermo-metallurgical and Thermo-mechanical Computations for Laser Welded Joint in 9Cr-1Mo(V, Nb) Ferritic/Martensitic Steel, Mater. Des., 2014, 59, p 211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.046
R.P. Mahto, R. Kumar, and S.K. Pal, Characterizations of Weld Defects, Intermetallic Compounds and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Lap Welded Dissimilar Alloys, Mater. Charact., 2020, 160, p 110115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.110115
C. Pandey, M. Mohan Mahapatra, P. Kumar, J.G. Thakre, and N. Saini, Role of Evolving Microstructure on the Mechanical Behaviour of P92 Steel Welded Joint in As-welded and Post Weld Heat Treated State, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, 263, p 241–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.08.032
R. Kumar, A. Varma, Y.R. Kumar, H. Vashishtha, J. Jain, and S. Neelakantan, Optimization of Post-weld Heat Treatment Condition of Arc-welded T91 Steel Tubes, Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip., 2020, 188, p 104213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2020.104213
Z. Liang, Y. Gui, and Q. Zhao, Investigation of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of T92 Martensitic Steel/Super304 Austenitic Steel Weld Joints Made with Three Welding Consumables, Arch. Metall. Mater., 2018, 63, p 1249–1256. https://doi.org/10.24425/123798
R. Kumar, A. Varma, Y.R. Kumar, S. Neelakantan, and J. Jain, Enhancement of Mechanical Properties Through Modified Post-weld Heat Treatment Processes of T91 and Super304H Dissimilar Welded Joint, J. Manuf. Process., 2022, 78, p 59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.04.008
ESI Group, SYSWELD 2010 reference manual. Digital Version, 4 (2010)
C. Pandey, M.M. Mahapatra, P. Kumar, and N. Saini, Effect of Normalization and Tempering on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of V-groove and Narrow-groove P91 Pipe Weldments, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2017, 685, p 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.12.079
M.Y. Kim, S.C. Kwak, I.S. Choi, Y.K. Lee, J.Y. Suh, E. Fleury, W.S. Jung, and T.H. Son, High-temperature Tensile and Creep Deformation of Cross-Weld Specimens of Weld Joint between T92 Martensitic and Super304H Austenitic Steels, Mater. Charact., 2014, 97, p 161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2014.09.011
R. Kumar, A. Varma, Y.R. Kumar, J. Jain, and S. Neelakantan, Microstructure Anomaly Upon High Temperature Exposure and Its Influence on the Mechanical Properties of a Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel Weld, Mater. Charact., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2022.111937
R. Kumar, A. Gokhale, A. Varma, Y.R. Kumar, S. Neelakantan, and J. Jain, Role of Nb (C, N) and Cr Carbides on the Fracture Behaviour of Super304H Steel Using In-situ Tensile Studies, Mater. Lett., 2023, 351, p 135107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2023.135107
L. Lars-Erik, Computational Welding Mechanics: Thermomechanical and Microstructural Simulation, Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, 2007.
J. Goldak, A. Chakravati, and M. Bibly, A New Finite Element Model for Welding Heat Sources, Metall. Trans. B., 1984, 15, p 299–305. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60352a844
J. Moravec, Influence of Welding Parameters on Weld Pool’s Geometry in Shielding Gas Welding. Pollypress, Lib. (2011)
D. Kollár, B. Kövesdi, and J. Néző, Numerical Simulation of Welding Process: Application in Buckling Analysis, Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng., 2017, 61, p 98–109. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPci.9257
S.H. Kim, J.B. Kim, and W.J. Lee, Numerical Prediction and Neutron Diffraction Measurement of the Residual Stresses for a Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel Weld, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209, p 3905–3913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.09.012
H.H. Lai and W. Wu, Practical Examination of the Welding Residual Stress in View of Low-carbon Steel Welds, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9, p 2717–2726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.004
N.S. Rossini, M. Dassisti, K.Y. Benyounis, and A.G. Olabi, Methods of Measuring Residual Stresses in Components, Mater. Des., 2012, 35, p 572–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.08.022
K.A. Venkata, S. Kumar, H.C. Dey, D.J. Smith, P.J. Bouchard, and C.E. Truman, Study on the Effect of Post Weld Heat Treatment Parameters on the Relaxation of Welding Residual Stresses in Electron Beam Welded P91 Steel Plates, Procedia Eng., 2014, 86, p 223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.032
M. Belassel, J. Pineault, N. Caratanasov, M. Brauss, Comparison of Residual Stress Measurement Techniques and Implementation Using x-ray diffraction., Eur. Conf. Residual Stress. 43 (2016)
M.E. Fitzpatrick, A.T. Fry, P. Holdway, F.A. Kandil, J. Shaackleton, L. Suominen, Determination of Residual Stresses by X-ray Diffraction - Issue 2, (2005) 31.
Acknowledgments
This project has been sponsored by NTPC NETRA. The authors also acknowledge the research infrastructure support of the department of materials science and engineering and central research facilities of IIT Delhi. The valuable discussion and support of Prof. S. Aravindan (Mechanical department, IIT Delhi) is duly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This invited article is part of a special topical issue of the Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance on Residual Stress Analysis: Measurement, Effects, and Control. The issue was organized by Rajan Bhambroo, Tenneco, Inc.; Lesley Frame, University of Connecticut; Andrew Payzant, Oak Ridge National Laboratory; and James Pineault, Proto Manufacturing on behalf of the ASM Residual Stress Technical Committee.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Halder, P., Amrithalingam, M. et al. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Residual Stresses in Similar and Dissimilar Welds of T91 and Super304H Steel Tubes. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 33, 3722–3730 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08703-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08703-w