Abstract
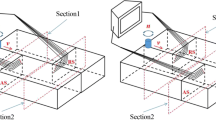
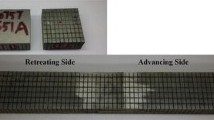
The purpose of this investigation was to evaluate the microstructural change, lap shear tensile load, and fatigue resistance of ultrasonic spot welded joints of aluminum 5754 alloy for automotive applications. A unique “necklace”-type structure with very fine equiaxed grains was observed to form along the weld line due to the mechanical interlocking coupled with the occurrence of dynamic recrystallization. The maximum lap shear tensile strength of 85 MPa and the fatigue limit of about 0.5 kN (at 1 × 107 cycles) were achieved. The tensile fracture occurred at the Al/Al interface in the case of lower energy inputs, and at the edge of nugget zone in the case of higher energy inputs. The maximum cyclic stress for the transition of fatigue fracture mode from the transverse through-thickness crack growth to the interfacial failure increased with increasing energy input. Fatigue crack propagation was mainly characterized by the formation of fatigue striations, which usually appeared perpendicular to the fatigue crack propagation.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
According to Science News entitled “Air pollution kills 7 million people a year” on March 25, 2014 at http://news.sciencemag.org/signal–noise/2014/03/air-pollution-kills-7-million-people-year: “Air pollution isn’t just harming Earth; it’s hurting us, too. Startling new numbers released by the World Health Organization today reveal that one in eight deaths are a result of exposure to air pollution. The data reveal a strong link between the tiny particles that we breathe into our lungs and the illnesses they can lead to, including stroke, heart attack, lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.”
References
S. Chu and A. Majumdar, Nature 488, 294 (2012).
M. McNutt, Science 341, 435 (2013).
V.K. Patel, S.D. Bhole, and D.L. Chen, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45, 2055 (2014).
G. Wagner, F. Balle, and D. Eifler, JOM 64, 401 (2012).
P.B. Prangnell, F. Haddadi, and Y.C. Chen, Mater. Sci. Technol. 27, 617 (2011).
L. Xiao, L. Liu, Y. Zhou, and S. Esmaeili, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41–6, 1511 (2010).
D. Bakavos and P.B. Prangnell, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 14, 443 (2009).
T. Liyanage, J. Kilbourne, A.P. Gerlich, and T.H. North, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 14, 500 (2009).
P.B. Prangnell and D. Bakavos, Mat. Sci. Forum. 638–642, 1237 (2010).
C.Y. Zhang, D.L. Chen, and A.A. Luo, Weld. J. 93, 131s (2014).
V.K. Patel, S.D. Bhole, and D.L. Chen, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 17, 202 (2012).
L.E. Murr, G. Liu, and J.C. McClure, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 16, 1801 (1997).
R. Jahn, R. Cooper, and D. Wilkosz, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38, 570 (2007).
S.H. Chowdhury, D.L. Chen, S.D. Bhole, X. Cao, and P. Wanjara, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 556, 500 (2012).
S. Elangovan, S. Semeer, and K. Prakasan, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 1143 (2009).
D. Bakavos and P.B. Prangnell, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 6320 (2010).
A. Macwan, X.Q. Jiang, and D.L. Chen, JOM 67, 1468 (2015).
A. Macwan and D.L. Chen, Mater. Des. 84, 261 (2015).
J. Schneider and R. Radzilowski, JOM 66, 2123 (2014).
S.M. Allameh, C. Mercer, D. Popoola, and W.O. Soboyejo, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 127, 65 (2005).
N. Pathak, K. Bandyopadhyay, M. Sarangi, and S.P. Kumar, JMEPEG 22, 131 (2013).
A. Panteli, Y.C. Chen, D. Strong, X. Zhang, and P.B. Prangnell, JOM 64, 414 (2012).
F. Khodabakhshi, M. Haghshenas, S. Sahraeinejad, J. Chen, B. Shalchi, J. Li, and A.P. Gerlich, Mater. Charact. 98, 73 (2014).
L. Ying, L.E. Murr, and J.C. McClure, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 271, 213 (1999).
Z. Zhang, B.L. Xiao, and Z.Y. Ma, Mater. Charact. 106, 255 (2015).
H.E. Hu, L. Zhen, B.Y. Zhang, L. Yang, and J.Z. Chen, Mater. Charact. 59, 1185 (2008).
Y.C. Chen, D. Bakavos, A. Gholinia, and P.B. Prangnel, Acta Mater. 60, 2816 (2012).
F. Haddadi, D. Strong, and P.B. Pragnell, JOM 64, 407 (2012).
H.P.C. Daniels, Ultrasonics 3, 190 (1965).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and AUTO21 Network of Centres of Excellence for providing financial support. The authors thank Dr. A.A. Luo, Ohio State University (formerly General Motors Research and Development Center) for the supply of test materials. One of the authors (D.L. Chen) is grateful for the financial support by the Premier’s Research Excellence Award (PREA), NSERC-Discovery Accelerator Supplement (DAS) Award, Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI), and Ryerson Research Chair (RRC) program. The authors would also like to thank Messrs. A. Machin, Q. Li, J. Amankrah and R. Churaman for easy access to the laboratory facilities of Ryerson University and their assistance in the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirza, F.A., Macwan, A., Bhole, S.D. et al. Microstructure and Fatigue Properties of Ultrasonic Spot Welded Joints of Aluminum 5754 Alloy. JOM 68, 1465–1475 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1796-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1796-7