Abstract
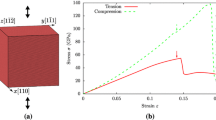
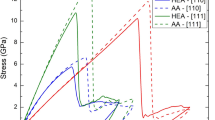
In this study, mechanical properties of cylindrical gold nanowires with diameters ranging from 5 nm to 17.5 nm were investigated using atomistic computer simulations. Displacement-controlled tensile tests were carried out to investigate the role of defects such as surface steps and twin boundaries commonly found in electrodeposited wires. The high surface-to-volume ratio of nanowires plays a critical role in the mechanical properties. Yield stress was found to be significantly affected by any disturbance in surface morphology. Twin boundaries were not more favorable as a source for dislocation nucleation but disturbed the surface in the neighborhood of the twin, resulting in lower yield strength. Twin boundaries are seen as obstacles for the propagation of dislocations leading to some hardening effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Kondo and K. Takayanagi, Physical Review Letters, 79 (18) (1997), pp. 3455–3458.
J.K. Diao, K. Gall, and M.L. Dunn, J. Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 52 (9) (2004), pp. 1935–1962.
Y. Kondo and K. Takayanagi, Science, 289 (5479) (2000), pp. 606–608.
O. Gulseren, F. Ercolessi, and E. Tosatti, Physical Review Letters, 80 (17) (1998), pp. 3775–3778.
P.E. Marszalek et al., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97 (12) (2000), pp. 6282–6286.
H. Koizumi et al., Ultramicroscopy, 88 (1) (2001), pp. 17–24.
M.L. Tian et al., Nano Letters, 3 (7) (2003), pp. 919–923.
S. Plimpton, J. Computational Physics, 117 (1) (1995), pp. 1–19.
S.M. Foiles, M.I. Baskes, and M.S. Daw, Physical Review B, 33 (12) (1986), pp. 7983–7991.
C.L. Kelchner, S.J. Plimpton, and J.C. Hamilton, Physical Review B, 58 (17) (1998), pp. 11085–11088.
Y. Zhu, N. Moldovan, and H.D. Espinosa, Applied Physics Letters, 86 (1) (2005), pp. 1–3.
Y. Zhu and H.D. Espinosa, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
For more information, contact Horacio D. Espinosa, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Northwestern University, 2145 Sheridan Rd., Evanston, IL 60208-3111 USA; (847) 467-5989; e-mail espinosa@northwestern.edu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyde, B., Espinosa, H.D. & Farkas, D. An atomistic investigation of elastic and plastic properties of Au nanowires. JOM 57, 62–66 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-005-0118-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-005-0118-x