Abstract
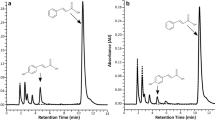
The moss Physcomitrella patens was engineered to produce the diterpenoid sclareol, an important precursor for the synthesis of ambergris substitutes for the perfume industry. The best total yield of sclareol was 2.84 mg/g dry weight (2.28 mg/l culture) obtained after 18 days of cultivation in liquid media (extracted from both media and cell pellet). The two active sclareol synthase genes were integrated in a random fashion, and linked with the ribosomal skip 2A under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. We conclude that moss can produce sclareol and utilize the ribosomal skip 2A. In addition, we observed growth impairment in all our sclareol-producing lines and moss lines knocked out in the endogenous diterpene synthase (copalyl/kaurene synthase—PpCPS/KS). A RT-PCR study, with ubiquitin as the best reference gene, showed that there was a down-regulation of the transcription of the terpenoid biosynthetic genes in the PpCPS/KS knock out moss. This down-regulation was recovered by the introduction of the two sclareol synthases, suggesting that the regulation of the general terpenoid biosynthesis is very flexible and can be amended in future biotechnological engineering.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharoni A, Giri AP, Deuerlein S, Griepink F, de Kogel WJ, Verstappen FW, Verhoeven HA, Jongsma MA, Schwab W, Bouwmeester HJ (2003) Terpenoid metabolism in wild-type and transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 15(12):2866–2884. doi:10.1105/tpc.016253
Anterola A, Shanle E, Perroud P-F, Quatrano R (2009) Production of taxa-4(5),11(12)-diene by transgenic Physcomitrella patens. Transgenic Res 18(4):655–660. doi:10.1007/s11248-009-9252-5
Bach SS, King BC, Zhan X, Simonsen HT, Hamberger B (2014) Heterologous stable expression of terpenoid biosynthetic genes using the moss Physcomitrella patens. In: Rodríguez-Concepción M (ed) Plant isoprenoids vol 1153. Methods in molecular biology. Springer, New York, pp 257–271. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-0606-2_19
Banerjee A, Wu Y, Banerjee R, Li Y, Yan HG, Sharkey TD (2013) Feedback inhibition of deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase regulates the methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway. J Biol Chem 288(23):16926–16936. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.464636
Barrero AF, Alvarez-Manzaneda EJ, Altarejos J, Salido S, Ramos JM (1993) Synthesis of Ambrox® from (−)-sclareol and (+)-cis-abienol. Tetrahedron 49(45):10405–10412. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)80567-6
Besumbes Ó, Sauret-Gueto S, Phillips MA, Imperial S, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Boronat A (2004) Metabolic engineering of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis for the production of taxadiene, the first committed precursor of Taxol. Biotechnol Bioeng 88(2):168–175. doi:10.1002/Bit.20237
Burén S, Ortega-Villasante C, Ötvös K, Samuelsson G, Bakó L, Villarejo A (2012) Use of the foot-and-mouth disease virus 2A peptide co-expression system to study intracellular protein trafficking in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 7(12):e51973. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051973
Caniard A, Zerbe P, Legrand S, Cohade A, Valot N, Magnard JL, Bohlmann J, Legendre L (2012) Discovery and functional characterization of two diterpene synthases for sclareol biosynthesis in Salvia sclarea (L.) and their relevance for perfume manufacture. BMC Plant Biol 12(1):119. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-12-119
Coman D, Altenhoff A, Zoller S, Gruissem W, Vranová E (2014) Distinct evolutionary strategies in the GGPPS family from plants. Front Plant Sci 5:230. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00230
Cove DJ, Perroud P-F, Charron AJ, McDaniel SF, Khandelwal A, Quatrano RS (2009) Transformation of the moss Physcomitrella patens using direct DNA uptake by protoplasts. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols 2009 (2):pdb.prot5143
Davidovich-Rikanati R, Sitrit Y, Tadmor Y, Iijima Y, Bilenko N, Bar E, Carmona B, Fallik E, Dudai N, Simon JE, Pichersky E, Lewinsohn E (2007) Enrichment of tomato flavor by diversion of the early plastidial terpenoid pathway. Nat Biotechnol 25(8):899–901. doi:10.1038/nbt1312
Drew DP, Rasmussen SK, Avato P, Simonsen HT (2012) A comparison of headspace solid-phase microextraction and classic hydrodistillation for the identification of volatile constituents from Thapsia spp. Provides insights into guaianolide biosynthesis in Apiaceae. Phytochem Anal 23(1):44–51. doi:10.1002/pca.1323
Dudareva N, Pichersky E (2008) Metabolic engineering of plant volatiles. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19(2):181–189. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2008.02.011
Dudareva N, Cseke L, Blanc VM, Pichersky E (1996) Evolution of floral scent in Clarkia: novel patterns of S-linalool synthase gene expression in the C. breweri flower. Plant Cell 8(7):1137–1148
Geu-Flores F, Nour-Eldin HH, Nielsen MT, Halkier BA (2007) USER fusion: a rapid and efficient method for simultaneous fusion and cloning of multiple PCR products. Nucleic Acids Res 35(7):e55
Hasan MM, Kim H-S, Jeon J-H, Kim S, Moon B, Song J-Y, Shim S, Baek K-H (2014) Metabolic engineering of Nicotiana benthamiana for the increased production of taxadiene. Plant Cell Rep 33(6):895–904. doi:10.1007/s00299-014-1568-9
Hayashi K, Kawaide H, Notomi M, Sakigi Y, Matsuo A, Nozaki H (2006) Identification and functional analysis of bifunctional ent-kaurene synthase from the moss Physcomitrella patens. FEBS Lett 580(26):6175–6181. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.10.018
Hayashi K, Horie K, Hiwatashi Y, Kawaide H, Yamaguchi S, Hanada A, Nakashima T, Nakajima M, Mander LN, Yamane H, Hasebe M, Nozaki H (2010) Endogenous diterpenes derived from ent-kaurene, a common gibberellin precursor, regulate protonema differentiation of the moss Physcomitrella patens. Plant Physiol 153(3):1085–1097
Ignea C, Trikka FA, Nikolaidis AK, Georgantea P, Ioannou E, Loupassaki S, Kefalas P, Kanellis AK, Roussis V, Makris AM, Kampranis SC (2015) Efficient diterpene production in yeast by engineering Erg20p into a geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. Metab Eng 27:65–75. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2014.10.008
Ikram NKBK, Zhan X, Pan X, King BC, Simonsen HT (2015) Stable heterologous expression of biologically active terpenoids in green plant cells. Front Plant Sci 6:1–10. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00129
Kawaide H, Hayashi K, Kawanabe R, Sakigi Y, Matsuo A, Natsume M, Nozaki H (2011) Identification of the single amino acid involved in quenching the ent-kauranyl cation by a water molecule in ent-kaurene synthase of Physcomitrella patens. FEBS J 278(1):123–133. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07938.x
Lange BM, Mahmoud SS, Wildung MR, Turner GW, Davis EM, Lange I, Baker RC, Boydston RA, Croteau RB (2011) Improving peppermint essential oil yield and composition by metabolic engineering. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(41):16944–16949. doi:10.1073/pnas.1111558108
Le Bail A, Scholz S, Kost B (2013) Evaluation of reference genes for RT qPCR analyses of structure-specific and hormone regulated gene expression in Physcomitrella patens gametophytes. PLoS One 8(8):e70998. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070998
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(−Delta Delta C) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lunde C, Baumann U, Shirley NJ, Drew DP, Fincher GB (2006) Gene structure and expression pattern analysis of three monodehydroascorbate reductase (Mdhar) genes in Physcomitrella patens: implications for the evolution of the MDHAR family in plants. Plant Mol Biol 60(2):259–275. doi:10.1007/s11103-005-3881-8
Moulines J, Lamidey AM, Desvergnes-Breuil V (2001) A practical synthesis of Ambrox (R) from sclareol using no metallic oxidant. Synthetic Commun 31(5):749–758. doi:10.1081/Scc-100103265
Nour-Eldin HH, Hansen BG, Norholm MH, Jensen JK, Halkier BA (2006) Advancing uracil-excision based cloning towards an ideal technique for cloning PCR fragments. Nucleic Acids Res 34(18):e122. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl635
Rodriguez-Concepcion M (2010) Supply of precursors for carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Arch Biochem Biophys 504(1):118–122. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2010.06.016
Schaefer DG (2001) Gene targeting in Physcomitrella patens. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:143–150. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00150-3
Schalk M, Pastore L, Mirata MA, Khim S, Schouwey M, Deguerry F, Pineda V, Rocci L, Daviet L (2012) Toward a biosynthetic route to sclareol and amber odorants. J Am Chem Soc 134(46):18900–18903. doi:10.1021/ja307404u
Simonsen HT, Drew DP, Lunde C (2009a) Perspectives on using Physcomitrella Patens as an alternative production platform for thapsigargin and other terpenoid drug candidates. Perspect Medicin Chem 3:1–6
Simonsen HT, Riedel C, Gade LB, Jebjerg CP, Guzman A, Mølgaard P (2009b) Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of the leaf essential oil of Baccharis magellanica (Lam.) Pers. and Baccharis elaeoides Remy from Chile. J Essent Oil Res 21(4):377–380
Sweetman C, Wong DC, Ford CM, Drew DP (2012) Transcriptome analysis at four developmental stages of grape berry (Vitis vinifera cv. Shiraz) provides insights into regulated and coordinated gene expression. BMC Genom 13:691. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-13-691
Tang W, Ehrlich I, Wolff SB, Michalski AM, Wolfl S, Hasan MT, Luthi A, Sprengel R (2009) Faithful expression of multiple proteins via 2A-peptide self-processing: a versatile and reliable method for manipulating brain circuits. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29(27):8621–8629. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0359-09.2009
Testone G, Condello E, Verde I, Nicolodi C, Caboni E, Dettori MT, Vendramin E, Bruno L, Bitonti MB, Mele G, Giannino D (2012) The peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch) genome harbours 10 KNOX genes, which are differentially expressed in stem development, and the class 1 KNOPE1 regulates elongation and lignification during primary growth. J Exp Bot 63(15):5417–5435. doi:10.1093/Jxb/Ers194
Von Schwartzenberg K, Schultze W, Kassner H (2004) The moss Physcomitrella patens releases a tetracyclic diterpene. Plant Cell Rep 22(10):780–786. doi:10.1007/s00299-004-0754-6
Weitzel C, Simonsen HT (2015) Cytochrome P450-enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of mono- and sesquiterpenes. Phytochem Rev 14(1):7–24. doi:10.1007/s11101-013-9280-x
Yang Z, Bennett EP, Jørgensen B, Drew DP, Arigi E, Mandel U, Ulvskov P, Levery SB, Clausen H, Petersen BL (2012a) Toward stable genetic engineering of human O-glycosylation in plants. Plant Physiol 160(1):450–463. doi:10.1104/pp.112.198200
Yang Z, Drew DP, Jørgensen B, Mandel U, Bach SS, Ulvskov P, Levery SB, Bennett EP, Clausen H, Petersen BL (2012b) Engineering mammalian mucin-type O-glycosylation in plants. J Biol Chem 287(15):11911–11923. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.312918
Zhan X (2014) Metabolic engineering of the moss Physcomitrella patens as a green cell factory to produce terpenoids. PhD thesis, University of Copenhagen, Frederiksberg, Denmark
Zhan X, Han LA, Zhang Y, Chen D, Simonsen HT (2014) Metabolic engineering of the moss Physcomitrella patens to produce the sesquiterpenoids patchoulol and α/β-santalene. Front Plant Sci 5:636. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00636
Zhao Y, Yang J, Qin B, Li Y, Sun Y, Su S, Xian M (2011) Biosynthesis of isoprene in Escherichia coli via methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(6):1915–1922. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3199-1
Zuo J, Niu QW, Chua NH (2000) Technical advance: an estrogen receptor-based transactivator XVE mediates highly inducible gene expression in transgenic plants. Plant J 24(2):265–273
Acknowledgments
The project was co-funded by the Danish Agency for Science, Technology and Innovation, and the Firmenich S. A with a PhD stipend to Xi-Wu Pan and the Danish Strategic Research Council Grant to H. T. Simonsen. The authors also wish thank Firmenich for providing the sclareol synthase genes and the authentic standards; Yong-Liang Tang and Dr. Lei Han are also thanked for the technical support on GC–MS and HPLC for metabolites analysis, and Dr. Brian C. King is thanked for the pBK3 vector for expression of terpene synthases under the PpCPS/KS promoter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, XW., Han, L., Zhang, YH. et al. Sclareol production in the moss Physcomitrella patens and observations on growth and terpenoid biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnol Rep 9, 149–159 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-015-0353-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-015-0353-8