Abstract
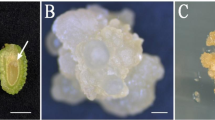
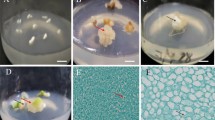
This study reports high-frequency plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryo cultures of Houttuynia cordata Thunb via somatic embryogenesis. Numerous green globular structures were directly formed on the surfaces of cotyledons and radicles from 2-week-old immature zygotic embryos at a frequency of 42.1 % when cultured on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with 2 mg l−1 of α-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) and 1 mg l−1 of 6-benzyladenine (BA). In comparison, white globular structures and pale-yellow calluses were formed simultaneously at a frequency of 28.3 % when cultured on MS medium supplemented with 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). The pale-yellow calluses were transferred to MS liquid medium supplemented with 2,4-D to establish embryogenic cell suspension cultures consisting of round, isodiametric cells that formed cell aggregates. Upon plating of these cell aggregates on half-strength MS medium without growth regulators under light conditions, cell aggregates gave rise to numerous globular embryos at a frequency of 56 %. Of the globular embryos, 15 % were successfully converted into cotyledonary embryos when cultured on half-strength MS medium under light conditions. The plant regeneration system of H. cordata established in this study will be useful for the selection, genetic transformation, and mass proliferation of elite clones with medicinal potential.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- BA:
-
6-Benzyladenine
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- NAA:
-
α-Naphthaleneacetic acid
References
Borthakur M, Singh RS, Bora P (1999) In vitro regeneration of Houttuynia cordata: a medicinal herb. Planta Med 65:677
Chakraborti S, Sinha S, Sinha RK (2006) High-frequency induction of multiple shoots and clonal propagation from rhizomatous nodal segments of Houttuynia cordata Thunb.—an ethnomedicinal herb of India. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:394–398
Chaudhury A, Qu R (2000) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of turf type bermudagrass: effect of 6-benzyladenine in callus induction medium. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 60:113–120
Cheong EJ, Pooler MR (2004) Factors affecting somatic embryogenesis in Prunus incisa cv. February Pink. Plant Cell Rep 22:810–815
Choi HJ, Song JH, Park KS, Kwon DH (2009) Inhibitory effects of quercetin 3-rhamnoside on influenza A virus replication. Eur J Pharm Sci 37(3–4):329–333
Chou SC, Su CR, Ku YC, Wu TS (2009) The constituents and their bioactivities of Houttuynia cordata. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 57:1227–1230
Croke JT, Cassells AC (1997) Dark induction and genetic stability of somatic embryos of zonal geraniums (Pelargonium × hortorum Baily). J Appl Bot 71:119–124
De-La-Peña C, Galaz-Ávalos RM, Loyola-Vargas VM (2008) Possible role of light and polyamines in the onset of somatic embryogenesis of Coffea canephora. Mol Biotechnol 39:215–224
Dong Y, Zhang Y, Yi L, Lai H, Zhang Y, Zhou L, Wang P (2010) Transformation of antimicrobial peptide fusion gene of cecropin B and rabbit NP-1 to Houttuynia cordata. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi 35:1660–1665
Han EH, Park JH, Kim JY, Jeong HG (2009) Houttuynia cordata water extract suppresses anaphylactic reaction and IgE-mediated allergic response by inhibiting multiple steps of FcepsilonRI signaling in mast cells. Food Chem Toxicol 47:1659–1666
Handique PJ, Bora P, Bora P (1999) In vitro regeneration of a medicinal plant—Houttuynia cordata Thunb. from nodal explants. Curr Sci 76:1245–1247
Holm LG, Pancho JV, Herberger JP, Plucknett DL (1979) A geographical atlas of world weeds. Wiley and Sons, New York
Hsia CN, Korban SS (1998) Effect of growth regulators, dark treatment and light intensity on shoot organogenesis from leaf tissues of evergreen azalea. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 73:53–60
Kim TJ (1996) Korean Resources Plants. Seoul National University press, Seoul
Kim SW, In DS, Tae KH, Liu JR (2005) High frequency plant regeneration from leaf-derived cell suspension cultures of Pinellia tripartita (Blume) Schott. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 80:267–270
Kim GS, Kim DH, Lim JJ, Lee JJ, Han DY, Lee WM, Jung WC, Min WG, Won CG, Rhee MH, Lee HJ, Kim S (2008) Biological and antibacterial activities of the natural herb Houttuynia cordata water extract against the intracellular bacterial pathogen salmonella within the RAW 264.7 macrophage. Biol Pharm Bull 31:2012–2017
Lin D, Sugimoto Y, Dong Y, Terao H, Matsuo M (2006) Natural herbicidal potential of saururaceae (Houttuynia cordata Thunb) dried powders on paddy weeds in transplanted rice. Crop Protect 25:1126–1129
Lu H, Wu X, Liang Y, Zhang J (2006) Variation in chemical composition and antibacterial activities of essential oils from two species of Houttuynia Thunb. Chem Pharm Bull 54:936–940
Min SR, Liu JR, Kim SW (2007) Plant regeneration from zygotic embryo-derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Ranunculus kazusensis. Plant Biotechnol Rep 1:57–60
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Oh MJ, Na HR, Choi HK, Liu JR, Kim SW (2008) High frequency plant regeneration from zygotic embryo derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures of watershield (Brasenia schreberi). Plant Biotechnol Rep 2:87–92
Oh MJ, Na HR, Choi HK, Liu JR, Kim SW (2010) Optimal plant regeneration system for Nymphoides coreana via somatic embryogenesis from zygotic embryo-derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures. Plant Biotechnol Rep 4:125–128
Pinto G, Park YS, Silva S, Neves L, Araújo C, Santos C (2008) Factors affecting maintenance, proliferation, and germination of secondary somatic embryos of Eucalyptus globulus Labill.: basal medium and anti-browning agents. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 95:69–78
Ren X, Sui X, Yin J (2011) The effect of Houttuynia cordata injection on pseudorabies herpesvirus (PrV) infection in vitro. Pharm Biol 49:161–166
Tang Y-J, Yang J-S, Lin C-F, Shyu W-C, Tsuzuki M, Lu C-C, Chen Y-F, Lai K-C (2009) Houttuynia cordata Thunb extract induces apoptosis through mitochondrial-dependent pathway in HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 22:1051–1056
Tauzuki K, Miyasita S, Kono N (1995) Report on the plant regeneration from the callus made of the leaf segments of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Bull Nip Vet Anim Sci Univ 44:65–68
Tian L, Zhao Y, Guo C, Yang X (2011) A comparative study on the antioxidant activities of an acidic polysaccharide and various solvent extracts derived from herbal Houttuynia cordata. Carbohydr Polym 83:537–544
Wangchauy C, Chanprasert S (2012) Effects of Houttuynia cordata Thunb extract, isoquercetin and rutin on cell growth inhibition and apoptotic induction in K562 human leukemic cells. J Chem Pharm Res 4:2590–2598
Wu W, Zheng Y, Liu F, Tan G, Ren H, Zhang W (2004) Construction of fast propagation system of Houttuynia cordata new line. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi 29:24–28
Zobayed SMA, Saxena PK (2003) In vitro regeneration of Echinacea purpurea L.: enhancement of somatic embryogenesis by indolebutyric acid and dark pre-incubation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:605–612
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant from the KRIBB Research Initiative Program. In addition, this work was supported by a grant provided to SWK from the BioGreen 21 Program (PJ00832901), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, M.J., Ahn, M.S., Jie, E.Y. et al. High-frequency plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryo cultures of Houttuynia cordata Thunb via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Biotechnol Rep 7, 527–534 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-013-0291-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-013-0291-2