Abstract
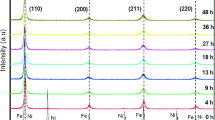
Nanocrystalline FeCoNi and FeCoNiSi powdered alloys were prepared by mechanical milling process (MA). Using X-ray diffraction patterns, we experimentally proved that when MA reached a time of 50 h, it led to a decrease of the crystallite size down to 20 nm and 32 nm for FeCoNiSi and FeCoNi, respectively. However, the dislocation density increased, reaching the highest value for the alloy associated with silicon. Nevertheless, this high energy ball-milling process is not used only for the refining of microstructure, but also to induce either a chemical reaction between the powdered chemical elements or a phase transformation, such as the allotropic transformation of HCP-Co to FCC-Co and the formation of highly disordered Fe-based solid solutions. Thermal stability of the milled mixtures was investigated by DSC from 25 up to 700 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min. Various milled samples were first annealed at specific temperatures and then analyzed using X-ray diffraction, which demonstrated the stability of the evolved phases during subsequent heating and the formation of some metallic oxides, such as Fe3O4 Fe2O3 and FeO, particularly for the elevated annealing temperatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. K. Prasad and V. Kumar, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elect., 26, 10109 (2015).
H. Raanaei, H. Eskandari and H. V. Mohammad, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 398, 190 (2016).
A. Zeleńáková, D. Olekšáková, J. Degmová, J. Kováč, P. Kollár, M. Kusý and P. Sovák, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 316, e519 (2007).
C. Suryanarayana, Prog. Mater. Sci., 46, 1 (2001).
E. Jartych, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 323, 209 (2011).
T. Pikula, D. Oleszak, M. Pękała and E. Jartych, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 320, 413 (2008).
G. M. Mocolvin and M. J. Shaw, Mater. Sci. Forum, 88, 235 (1992).
G. B. Schaffer and P. G. McCormick, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1, 45 (1988).
B. Avar and S. Ozcan, J. Alloys Compd., 650, 53 (2015).
C. Suryanarayana, Int. Mater. Rev., 40, 41 (1995).
C. Suryanarayana, Prog. Mater. Sci., 46, 1 (2001).
M. R. Kasaai, J. Nanotechnol., 4, 1 (2015).
C. A. Poland, P. B. Larsen, S. A. K. Read, J. Varet, S. M. Hankin and H. R. Lam, D.E.P.A: Copenhagen, Denmark, 23 (2016).
A. C. Santos, F. Morais, A. Simóes, I. Pereira, J. A. D. Sequeira, M. Pereira-Silva, F. Veiga and A. Ribeiro, Expert Opin. Drug Deliv., 16, 313 (2019).
D. Jiles, Introduction to magnetism and magnetic materials, Chapman and Hall/CRC Press: New York, NY, USA (1998).
H. Raanaei, H. Eskandari and V. Mohammad-Hosseini, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 398, 190 (2016).
X. Li and S. Takahashi, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 214, 195 (2000).
Q. I. Tianlong, L. I. Yanhui, A. Takeuchi, X. Guoqiang, H. Miao and W. Zhang, Intermetallics, 66, 8 (2015).
Y. Li, W. Zhang and T. Qi, J. Alloys Compd., 693, 25 (2017).
R. Wei, H. Sun, C. Chen, Z. Han and F. Li, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 435, 184 (2017).
V. Petrisek and D. M. Jana, The Crystallographic Computing System (Institute of Physics), Prague (2000).
E. A. Owen and D. Madoc Jones, University College of North Wales, Bangor MS (1954).
P. Novák, M. Zelinková, J. Šerák, A. Michalcová, M. Novák and D. Vojtĕch, Intermetallics, 19, 1306 (2011).
G. K Williamson and W. H. Hall, Acta Metall., 1, 22 (1953).
Y. Zhao, H. Sheng and K. Lu, Acta Mater., 49, 365 (2001).
L. D. Rafailović and D. M. Minić, Chem. Ind., 63, 557 (2009).
B. N. Mondal, A. Basumallick, D. N. Nath and P. P. Chattopadhyay, Mater. Chem. Phys., 116, 358 (2009).
D. Bruce and P. Hancock, Br. Corros. J., 4, 221 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daly, R., Sunol, J.J. & Khitouni, M. Structural and thermal properties of the Fe-based alloys prepared by mechanical milling. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 39, 1614–1623 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-021-1025-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-021-1025-8