Abstract
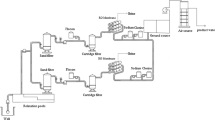
Reverse osmosis (RO) desalination, which produces multiple freshwater from seawater, has been studied in this work. An optimization method based on process synthesis has been applied to design the RO system. First, a simplified superstructure that contains all the feasible design for this desalination problem has been presented. In this structural representation, the stream split ratios and the logical expressions of stream mixing were employed, which can make the mathematical model easy to handle. Then, the membrane separation units employing the spiral wound reverse osmosis elements were described by using a pressure vessel model, which takes into account the pressure drop and the concentration changes in the membrane channel. The optimum design problem can be formulated as a mixedinteger non-linear programming (MINLP) problem, which minimizes the total annualized cost of the RO system. The cost equation relating the capital and operating cost to the design variables, as well as the structural variables, has been introduced in the objective function. The problem solution includes the optimal streams distribution, the optimal system structure and the operating conditions. The design method could also be used for the optimal selection of membrane element type in each stage and the optimal number of membrane elements in each pressure vessel. The effectiveness of this design methodology has been demonstrated by solving a desalination case. The comparisons with common industrial approach indicated that the integrative RO system proposed in this work is more economical, which can lead to significant capital cost and energy saving and provide an economically attractive desalination scheme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. El-Zanati and S. Eissa, Desalination, 165, 133 (2004).
A. Villafafila and I.M. Mujtaba, Desalination, 155, 1 (2003).
N. M. Wade, Desalination, 136, 3 (2001).
M. Wilf and C. Bartels, Desalination, 173, 1 (2005).
M. Wilf, Desalination, 113, 157 (1997).
M.G. Marcovecchio, P. A. Aguirre and N. J. Scenna, Desalination, 184, 259 (2005).
J. A. Redondo and A. Casanas, Desalination, 134, 83 (2001).
M. Busch and W. E. Mickols, Desalination, 165, 299 (2004).
Y. Y. Lu and Y. D. Hu, J. Membr. Sci., 282, 7 (2006).
Y. Y. Lu and Y. D. Hu, J. Membr. Sci., 287, 219 (2007).
I.M. El-Azizi, Desalination, 153, 273 (2002).
G. Al-Enezi and N. Fawzi, Desalination, 153, 281 (2002).
M.M. El-Halwagi, AIChE J., 38, 1185 (1992).
M. Zhu and M.M. El-Halwagi, J. Membr. Sci., 129, 161 (1997).
N.G. Voros and Z.B. Maroulis, Comp. Chem. Eng., 20, 345 (1996).
N. G. Voros and Z. B. Maroulis, J. Membr. Sci., 127, 47 (1997).
F. Maskan and D. E. Wiley, AIChE J., 46, 946 (2000).
J. E. Nemeth, Desalination, 118, 63 (1998).
W.G. J. Van der Meer and C.W. A. Averink, Desalination, 105, 25 (1996).
W.G. J. Van der Meer and M. Riemersma, Desalination, 119, 57 (1998).
L. P. Wessels and W. G. J. Van der Meer, Desalination, 119, 341 (1998).
A. Malek and M. N. A. Hawlader, Desalination, 105, 245 (1996).
N. M. Al-Bastaki and A. Abbas, Desalination, 132, 181 (2000).
N. M. Al-Bastaki and A. Abbas, Desalination, 126, 33 (1999).
Membrane Technical Information, http://www.dow.com/liquidseps/service/lm_techinfo.htm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Liao, A. & Hu, Y. Design of reverse osmosis networks for multiple freshwater production. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 30, 988–996 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0009-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0009-8