Abstract
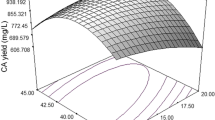
The experiments were based on multivariate statistical concepts, and response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to optimize the fermentation medium for the production of ribonucleic acid (RNA) by Candida tropicalis no. 121. The process involved the individual adjustment and optimization of various medium components at shake flask level. The two-level Plackett-Burman (PB) design was used to screen the medium components, which significantly influenced RNA production. Among seven variables, the concentrations of molasses, ZnSO4, and H3PO4 were found to be the important factors that significantly affected RNA production (confidence levels above 95%). These factors were further optimized using a central composite design (CCD) and RSM. The optimum values for the critical components were as follows: molasses 47.21 g/L: ZnSO4 0.048 g/L; H3PO4 1.19 g/L. Under optimal conditions, RNA production was 2.56 g/L, which was in excellent agreement with the predicted value (2.561 g/L), and led to a 2.1-fold increase compare with that using the original medium in RNA production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. H. Slobodianik, Nutrition, 19, 68 (2003).
Y. Kulshrestha and Q. Husain, Enzym. Microbial. Technol., 88, 470 (2006).
J. D. Carver, B. Pimentel and I. William, Pediatrics, 88, 359 (1991).
L. M. L. Masor and J. Lee, US Patent 5,700,590 (1997).
J. L. M. Herrick and J. A. S. Shecterle, Med. Hypoth., 72, 499 (2009).
L. P. Qiu, G. L. Zhao, H. Wu, L. Jiang, X. F. Li and J. J. Liu, Carbohyd. Polym., 80, 326 (2010).
Z. J. Xiao, P. H. Liu, J.Y. Qin and P. Xu, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 74, 61 (2007).
H. J. Ying, X. C. Chen, H. P. Cao and J. Xiong, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 84, 677 (2009).
S. Kar, T. K. Datta and R. C. Ray, Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol., 53, 301 (2010).
D. Granato, D. I. A. Castro, E. L. S. Neves and M. L. J. Food Sci., 75, 149 (2010).
Y.Y. Qu, W. Q. Pi, F. Ma, J. T. Zhou and X.W. Zhang, Bioresour. Technol., 101, 4527 (2010).
M. T. Küenzi, Biotechnol. Lett., 3, 127 (1979).
X. Li, J. Ouyang, Y. Xu, M. Chen, X.Y. Song, Q. Yong and S.Y. Yu, Bioresour. Technol., 100, 3613 (2009).
M. Kennedy and D. Krouse, J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 6, 456 (1999).
R. L. Plackett and J. P. Burman, Biometrika., 33, 305 (1946).
X. C. Chen, J. X. Bai, J. M. Cao, Z. J. Li, J. Xiong, L. Zhang, Y. Hong and H. J. Ying, Bioresour. Technol., 100, 919 (2009).
Y. P. Liu, P. Zheng, Z. H. Sun, Y. Ni, J. J. Dong and L. L. Zhu, Bioresour. Technol., 99, 1736 (2008).
Q. Ye, X. M. Li, M. Yan, H. Cao and L. Xu, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 87, 517 (2010).
R. Jain, J. Saxena and V. Sharma, Appl. Soil Ecol., 46, 90 (2010).
X. Wang, X.W. Wang, M. X. Yin, Z. J. Xiao, C. Q. Ma, Z. X. Lin, P. Wang and P. Xu, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 76, 321 (2007).
V. Kery, G. Kogan, K. Zajacova, L. Masler and J. Alfoldi, Enzyme. Microb. Technol., 13, 87 (1991).
K. M. O’Brien, R. Dirmeier and M. Engle, J. Biol. Chem., 279, 51817 (2004).
K. Shivam, C. P. M. Tripathi and S. K. Mishra, Electron. J. Biotechnol. (2009).
V. Siva and A. K. Mansoor, Int. J. Pharmaceut., 234, 179 (2002).
F. J. Cui, Z. Q. Liu, Y. Li, L. F. Ping, L.Y. Ping, Z. C. Zhang, L. Lin, Y. Dong and D. M. Huang, Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng., 15, 299 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These author equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, H., Chen, X., Cao, J. et al. Determination of optimal conditions for ribonucleic acid production by Candida tropicalis no. 121. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 28, 1721–1726 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0013-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0013-9