Abstract
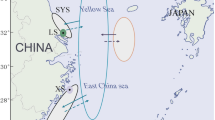
This study investigates the migration and distribution of the warm-temperate fish Nibea albiflora. Their spawning migration and wintering migratory routes within in the Yellow Sea are described in detail. Considering the main physical features and environment of the Yellow Sea, it appears to be have one wintering ground and three migratory routes from the wintering ground to the spawning grounds. The fish begin to migrate from the wintering ground to the spawning grounds in the northwest region of the Yellow Sea in late March. The Yellow Sea has three spawning grounds. The first is located near the Yalu River on the Liaodong Peninsula and the second one is located in Rushan Bay of Shandong Peninsula. The third spawning ground is located in Haizhou Bay in the southern region of the Yellow Sea. This study found that the temperature of the Yellow Sea influences the migration of N. albiflora, and that the migratory routes coincide with the thermal fronts in the sea. Nutrients for juvenile fish are taken from the coastal upwelling area. Chlorophyll is a good environmental indicator of phytoplankton biomass and thereby provides the status of biological resources. Different types of sediment in near-shore zones are also of practical significance for the growth of fish. The study of the effects of marine environments on the migration of various fishes is not only significant to the fishing industry, but can also provide a scientific basis for the understanding of the ecological implications of the relevant physical processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao, X. W., Wan, X. Q., Gao, G. P., and Wu, D. X., 2002. The characteristics of the seasonal variability of the sea surface temperature field in the Bohai Sea, the Huanghai Sea and the East China Sea from AVHRR data. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 24 (5): 125–133.
Bertignac, M., and Lehodey, P., 1998. A spatial population dynamics simulation model of tropical tunas using a habitat index based on environmental parameters. Fisheries Oceanography, 7 (3-4): 326–334.
Bourque, M.-C., LeBlond, P. H., and Cummins, P. F., 1999. Effects of tidal current on Pacific salmon migration: Results from a fine-resolution coastal model. Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences, 56 (5): 839–846.
Chen, D. G., 1991. Fisheries Ecology of Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. China Ocean Press, Beijing, 113pp.
Hu, C. J., and Zhang, J., 2005. Probe into the relationship between the migration routes of endemic branch tribles of Larimichthys polyactis in the Southern Yellow Sea and the environment. Marine Fisheries, 27 (2): 109–112.
Hu, D., 1984. Upwelling and sedimentation dynamics. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2: 12–19.
Humston, R., Ault, J. S., Lutcavage, M., and Olson, D. B., 2000. Schooling and migration of large pelagic fishes relative to environmental cues. Fisheries Oceanography, 9 (2): 136–146.
Li, Y., Zhao, X. Y., Zhang, T., Li, X. S., and Wei, H., 2007. Wintering migration and distribution of anchovy in the Yellow Sea and its relation to physical environment. Marine Fisheries Research, 28 (2): 104–112.
Niu, M. X., 2012. Spatiotemporal dynamics of anchovy population and its response to environmental factors in the Yellow Sea based on ocean RS and GIS. PhD thesis. Shandong Agricultural University.
Song, D. H., Bao, X. W., Wang, X. H., Xu, L. L., Lin, X. P., and Wu, D. X., 2009. The inter-annual variability of the Yellow Sea Warm Current surface axis and its influencing factors. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 27 (3): 607–613.
Tang, Q. S., and Su, J. L., 2000. Study of China Ocean Ecosystem Dynamics. I Key Scientific Problem and Development Strategies. Science Press, Beijing, 252pp.
Tang, Q. S., and Su, J. L., 2001. Study on marine ecosystem dynamics and living resources sustainable utilization. Advance in Earth Sciences, 16 (1): 5–11.
Wei, Q. S., Lv, X. G., Wang, Z. X., Wang, S. Q., and Zang, J. Y., 2010. A preliminary analysis of the characteristics of the continental shelf front and its ecological effects in the Yellow Sea. Advances in Earth Science, 25 (4): 435–443.
Xu, D. D., Li, S. L., Lou, B., Cheng, L. N., and Xin, J., 2010. Research status of biological characteristics and cultured ecology of Nibea albiflora (Richardson) and its culture prospect. Modern Fisheries Information, 25 (10): 23–26.
Xu, Z. L., and Chen, J. J., 2011. Analysis of migratory route of Larimichthys crocea in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Journal of Fisheries of China, 35 (3): 429–437.
Yuan, Y. Y., 2009. Fishery oceanography and spatial-temporal distribution variation of Scomberomorus niphonius and Pampus argenteus in spring in southern Yellow Sea. Master thesis. Ocean University of China.
Zhang, J. Q., 2012. Evolution and provenance of sedimentation on the off-shore shelf of the western Yellow Sea since the late Pleistocene. PhD thesis. Ocean University of China.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Ocean Public Welfare Scientific Research Project (No. 201405029-4). We would like to thank Prof. Maochong Shi for his unselfish help with the guidance and improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Wu, K. & Wu, L. Influence of the physical environment on the migration and distribution of Nibea albiflora in the Yellow Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 16, 87–92 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3036-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3036-y