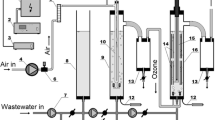
Abstract
Wet air oxidation (WAO) and catalytic wet air oxidation (CWAO) are efficient processes to degrade organic pollutants in water. In this paper, we especially reviewed the WAO and CWAO processes for phenolic compounds degradation. It provides a comprehensive introduction to the CWAO processes that could be beneficial to the scientists entering this field of research. The influence of different reaction parameters, such as temperature, oxygen pressure, pH, stirring speed are analyzed in detail; Homogenous catalysts and heterogeneous catalysts including carbon materials, transitional metal oxides and noble metals are extensively discussed, among which Cu based catalysts and Ru catalysts were shown to be the most active. Three different kinds of the reactor implemented for the CWAO (autoclave, packed bed and membrane reactors) are illustrated and compared. To enhance the degradation efficiency and reduce the cost of the CWAO process, biological degradation can be combined to develop an integrated technology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Autenrieth R L, Bonner J S, Akgerman A, Okaygun M, McCreary E M. Biodegradation of phenolic watstes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1991, 28(1–2): 29–53
Stich H F. The beneficial and hazardous effects of simple phenoliccompounds. Mutation Research, 1991, 259(3–4): 307–324
Mohammadi S, Kargari A, Sanaeepur H, Abbassian K, Najafi A, Mofarrah E. Phenol removal from industrial wastewaters: a short review. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2014, 53(8): 2215–2234
Rappoport Z. The Chemistry of Phenols. New York: JohnWiley & Sons, 2004
Veeresh G S, Kumar P, Mehrotra I. Treatment of phenol and cresols in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) process: a review. Water Research, 2005, 39(1): 154–170
Ribeiro A R, Nunes O C, Pereira M F, Silva A M. An overview on the advanced oxidation processes applied for the treatment of water pollutants defined in the recently launched directive 2013/39/EU. Environment International, 2015, 75: 33–51
Andreozzi R, Caprio V, Insola A, Marotta R. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery. Catalysis Today, 1999, 53(1): 51–59
Debellefontaine H, Chakchouk M, Foussard J N, Tissot D, Striolo P. Treatment of organic aqueous wastes: wet air oxidation and wet peroxide oxidation(R). Environmental Pollution, 1996, 92(2): 155–164
Dietrich M J, Rall T L, Canney P J. Wet air oxidation of hazardous organics in wastewater. Environment and Progress, 1985, 4(3): 171–177
Freeman H. Standard Handbook of Hazardous Waste Treatment and Disposal. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1989
Kim K H, Ihm S K. Heterogeneous catalytic wet air oxidation of refractory organic pollutants in industrial wastewaters: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1): 16–34
Kolaczkowski S T, Plucinski P, Beltran F J, Rivas F J, McLurgh D B. Wet air oxidation: a review of process technologies and aspects in reactor design. Chemical Engineering Journal, 1999, 73(2): 143–160
Levec J, Pintar A. Catalytic wet-air oxidation processes: a review. Catalysis Today, 2007, 124(3–4): 172–184
Guo J, Al-Dahhan M. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol in concurrent downflow and upflow packed-bed reactors over pillared clay catalyst. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(3): 735–746
Imamura S. Catalytic and noncatalytic wet oxidation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1999, 38(5): 1743–1753
Bhargava S K, Tardio J, Prasad J, Foger K, Akolekar D B, Grocott S C. Wet oxidation and catalytic wet oxidation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2006, 45(4): 1221–1258
Devlin H R, Harris I J. Mechanism of the oxidation of aqueous phenol of aqueous phenol with dissolved oxygen. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1984, 23(4): 387–392
Kolaczkowski S T, Beltran F J, McLurgh D B, Rivas F J. Wet air oxidation of phenol: factors that may influence global kinetics. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 1997, 75(4 B4): 257–265
Pintar A, Levec J. Catalytic-oxidation of aqueous p-chlorophenol and p-nitrophenol solutions. Chemical Engineering Science, 1994, 49(24): 4391–4407
Joglekar H S, Samant S D, Joshi J B. Kinetics of wet air oxidation of phenol and substitued phenols. Water Research, 1991, 25(2): 135–145
Rivas F J, Kolaczkowski S T, Beltran F J, McLurgh D B. Development of a model for the wet air oxidation of phenol based on a free radical mechanism. Chemical Engineering Science, 1998, 53(14): 2575–2586
Lin S H, Chuang T S. Combined treatment of phenol of phenolic wastewater by wet air oxidation and activated sludge. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 1994, 44(3–4): 243–258
Shibaeva L V. Oxidation of phenol with molecular oxygen in aqueous solutions I. The kinetics of the oxidation of phenol with oxygen. Kinetics and Catalysis, 1969, 10: 832–836
Willms R S, Balinsky AM, Reible D D,Wetzel DM, Harrison D P. Aqueous phase oxidation: the intrinsic kinetics of single organic compounds. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1987, 26(1): 148–154
Vicente J, Rosal R, Diaz M. Noncatalytic oxidation of phenol in aqueous solutions. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(1): 46–51
Pruden B, Le H. Wet air oxidation of soluble components in waste water. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1976, 54(4): 319–325
Jaulin L, Chornet E. High shear jet-mixers as two-phase reactors: an application to the oxidation of phenol in aqueous media. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1987, 65(1): 64–70
Mundale V D, Joglekar H S, Kalam A, Joshi J B. Regeneration of spent acitivated carbon by wet air oxidation. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1991, 69(5): 1149–1159
Vaidya P D, Mahajani V V. Insight into subcritical wet oxidation of phenol. Advances in Environmental Research, 2002, 6(4): 429–439
Arena F, Italiano C, Raneri A, Saja C. Mechanistic and kinetic insights into the wet air oxidation of phenol with oxygen (CWAO) by homogeneous and heterogeneous transition-metal catalysts. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2010, 99(1–2): 321–328
Tufano V. A multi-step kinetic model for phenol oxidation in highpressure water. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 1993, 16(3): 186–190
Gopalan S, Savage P E. A reaction network model for phenol oxidation in supercritical water. AIChE Journal, 1995, 41(8): 1864–1873
Gopalan S, Savage P E. Reaction mechanism for phenol oxidation in supercritical water. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1994, 98(48): 12646–12652
Suárez-Ojeda M E, Carrera J, Metcalfe I S, Font J. Wet air oxidation (WAO) as a precursor to biological treatment of substituted phenols: refractory nature of the WAO intermediates. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 144(2): 205–212
Arena F, Di Chio R, Gumina B, Spadaro L, Trunfio G. Recent advances on wet air oxidation catalysts for treatment of industrial wastewaters. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 2015, 431: 101–109
Fu D M, Zhang F F, Wang L Z, Yang F, Liang X M. Simultaneous removal of nitrobenzene and phenol by homogenous catalytic wet air oxidation. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 36(7): 952–956
Priyanka S V, Srivastava V C, Mall I D. Catalytic oxidation of nitrobenzene by copper loaded activated carbon. Separation and Purification Technology, 2014, 125: 284–290
Messele S A, Soares O S G P, Órfão J J M, Stüber F, Bengoa C, Fortuny A, Fabregat A, Font J. Zero-valent iron supported on nitrogen-containing activated carbon for catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 154–155: 329–338
Ayusheev A B, Taran O P, Seryak I A, Podyacheva O Y, Descorme C, Besson M, Kibis L S, Boronin A I, Romanenko A I, Ismagilov Z R, Parmon V. Ruthenium nanoparticles supported on nitrogendoped carbon nanofibers for the catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 146: 177–185
Podyacheva O Y, Ismagilov Z R, Boronin A I, Kibis L S, Slavinskaya E M, Noskov A S, Shikina N V, Ushakov V A, Ischenko A V. Platinum nanoparticles supported on nitrogencontaining carbon nanofibers. Catalysis Today, 2012, 186(1): 42–47
Barroso-Bogeat A, Alexandre-Franco M, Fernández-González C, Gómez-Serrano V. Preparation of activated carbon-metal oxide hybrid catalysts: textural characterization. Fuel Processing Technology, 2014, 126: 95–103
Akyurtlu J F, Akyurtlu A, Kovenklioglu S. Catalytic oxidation of phenol in aqueous solutions. Catalysis Today, 1998, 40(4): 343–352
Fortuny A, Bengoa C, Font J, Fabregat A. Bimetallic catalysts for continuous catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1999, 64(2): 181–193
Yang S, Zhu W, Wang J, Chen Z. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol over CeO2-TiO2 catalyst in the batch reactor and the packed-bed reactor. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 153(3): 1248–1253
Espinosa de los Monteros A, Lafaye G, Cervantes A, Del Angel G, Barbier J, Torres G. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol over metal catalyst (Ru, Pt) supported on TiO2-CeO2 oxides. Catalysis Today, 2015, 258: 564–569
Messele S A. Homogenous and heterogenous aqueous phase oxidation of phenol with fenton like process. Doctoral Thesis universitat Rovira I Virgili 2014
Shalagina A E, Ismagilov Z R, Podyacheva O Y, Kvon R I, Ushakov V A. Synthesis of nitrogen-containing carbon nanofibers by catalytic decomposition of ethylene/ammonia mixture. Carbon, 2007, 45(9): 1808–1820
Ribeiro R S, Silva A M T, Figueiredo J L, Faria J L, Gomes H T. Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation: a route towards the application of hybrid magnetic carbon nanocomposites for the degradation of organic pollutants: a review. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 187: 428–460
Baricot M, Dastgheib S A, Fortuny A, Stüber F, Bengoa Ch, Fabregat A. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol by surface modified activated carbons. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2004, 69(1): 1–6
Janecki D, Szczotka A, Burghardt A, Bartelmus G. Modelling wetair oxidation of phenol in a trickle-bed reactor using active carbon as a catalyst. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology (Oxford, Oxfordshire), 2016, 91(3): 596–607
Fortuny A, Font J, Fabregat A. Wet air oxidation of phenol using active carbon as catalyst. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 1998, 19(3–4): 165–173
Soares O S G P, Rocha R P, Gonçalves A G, Figueiredo J L, Órfão J J M, Pereira M F R. Highly active N-doped carbon nanotubes prepared by an easy ball milling method for advanced oxidation processes. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 192: 296–303
Yang S, Li X, Zhu W, Wang J, Descorme C. Catalytic activity, stability and structure of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in the wet air oxidation of phenol. Carbon, 2008, 46(3): 445–452
Rocha R P, Sousa J P S, Silva A M T, Pereira M F R, Figueiredo J L. Catalytic activity and stability of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in catalytic wet air oxidation of oxalic acid: The role of the basic nature induced by the surface chemistry. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2011, 104(3–4): 330–336
Yang S X, Sun Y, Yang H W, Wan J F. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol, nitrobenzene and aniline over the multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) as catalysts. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2014, 9(3): 436–443
Wang J, Fu W, He X, Yang S, Zhu W. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol with functionalized carbon materials as catalysts: reaction mechanism and pathway. Joural of Enviromental Sciences, 2014, 26(8): 1741–1749
Quintanilla A, Menéndez N, Tornero J, Casas J A, Rodríguez J J. Surface modification of carbon-supported iron catalyst during the wet air oxidation of phenol: Influence on activity, selectivity and stability. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2008, 81(1–2): 105–114
Oliviero L, Barbier-Jr J, Duprez D, Guerrero-Ruiz A, Bachiller- Baeza B, Rodriguez-Ramos I. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol and acrylic acid over Ru/C and Ru-CeO2/C catalysts. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2000, 25(4): 267–275
Stuber F, Polaert I, Delmas H, Font J, Fortuny A, Fabregat A. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol using active carbon: performance of discontinuous and continuous reactors. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology (Oxford, Oxfordshire), 2001, 76(7): 743–751
Carriazo J, Guelou E, Barrault J, Tatibouet J M, Molina R, Moreno S. Synthesis of pillared clays containing Al, Al-Fe or Al-Ce-Fe from a bentonite: characterization and catalytic activity. Catalysis Today, 2005, 107–08: 126–132
Pires C A, dos Santos A C C, Jordao E. Oxidation of phenol in aqueous solution with copper oxide catalysts supported on g- Al2O3, pillared clay and TiO2: comparsion of the performance and costs associated with each catalyst. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2015, 32(4): 837–848
Ksontini N, Najjar W, Ghorbel A. Al-Fe pillared clays: synthesis, characterization and catalytic wet air oxidation activity. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2008, 69(5–6): 1112–1115
Kloprogge J T. Synthesis of smectites and porous pillared clay catalysts: a review. Journal of Porous Materials, 1998, 5(1): 5–41
Guo J, Al-Dahhan M. Activity and stability of iron-containing pillared clay catalysts for wet air oxidation of phenol. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2006, 299: 175–184
Wu Q, Hu X, Yue P L, Zhao X S, Lu G Q. Copper/MCM-41 as catalyst for the wet oxidation of phenol. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2001, 32(3): 151–156
Lin S S Y, Chang D J, Wang C H, Chen C C. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol by CeO2 catalyst—effect of reaction conditions. Water Research, 2003, 37(4): 793–800
Chen I P, Lin S S, Wang C H, Chang S H. CWAO of phenol using CeO2/g-Al2O3 with promoter effectiveness of promoter addition and catalyst regeneration. Chemosphere, 2007, 66(1): 172–178
Chang L Z, Chen I P, Lin S S. An assessment of the suitable operating conditions for the CeO2/g-Al2O3 catalyzed wet air oxidation of phenol. Chemosphere, 2005, 58(4): 485–492
Hocevar S, Krasovec U O, Orel B, Arico A S, Kim H. CWO of phenol on two differently prepared CuO-CeO2 catalysts. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2000, 28(2): 113–125
Delgado J J, Chen X, Pérez-Omil J A, Rodríguez-Izquierdo J M, Cauqui M A. The effect of reaction conditions on the apparent deactivation of Ce-Zr mixed oxides for the catalytic wet oxidation of phenol. Catalysis Today, 2012, 180(1): 25–33
Parvas M, Haghighi M, Allahyari S. Degradation of phenol via wet air oxidation over CuO/CeO2-ZrO2 nanocatalyst synthesized employing ultrasound energy: physicochemical characterization and catalytic performance. Environmental Technology, 2014, 35 (9–12): 1140–1149
Parvas M, Haghighi M, Allahyari S. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol over ultrasound-assisted synthesized Ni/CeO2-ZrO2 nanocatalyst used in wastewater treatment. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2014
Arena F, Italiano C, Drago Ferrante G, Trunfio G, Spadaro L. A mechanistic assessment of the wet air oxidation activity of MnCeOx catalyst toward toxic and refractory organic pollutants. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 144: 292–299
Chen H, Sayari A, Adnot A, Larachi F. Composition-activity effects of Mn-Ce-O composites on phenol catalytic wet oxidation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2001, 32(3): 195–204
Gutiérrez M, Pina P, Torres M, Cauqui M A, Herguido J. Catalytic wet oxidation of phenol using membrane reactors: a comparative study with slurry-type reactors. Catalysis Today, 2010, 149(3–4): 326–333
Aihua X, Chenglin S. Catalytic behaviour and copper leaching of Cu0.10Zn0.90Al1.90Fe0.10O4 spinel for catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol. Environmental Technology, 2012, 33(10–12): 1339–1344
Toledo J A, Valenzuela M A, Bosch P, Armendariz H, Montoya A, Nava N, Vazquez A. Effect of Al3+ introduction into hydrothermally prepared ZnFe2O4. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2000, 198(1–2): 235–245
Xu A, Yang M, Qiao R, Du H, Sun C. Activity and leaching features of zinc-aluminum ferrites in catalytic wet oxidation of phenol. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 147(1–2): 449–456
Alejandre A, Medina F, Rodriguez X, Salagre P, Cesteros Y, Sueiras J E. Cu/Ni/Al layered double hydroxides as precursors of catalysts for the wet air oxidation of phenol aqueous solutions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2001, 30(1–2): 195–207
Li N, Descorme C, Besson M. Application of Ce0.33Zr0.63Pr0.04O2- supported noble metal catalysts in the catalytic wet air oxidation of 2-chlorophenol: influence of the reaction conditions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2008, 80(3–4): 237–247
Lafaye G, Barbier J Jr, Duprez D. Impact of cerium-based support oxides in catalytic wet air oxidation: conflicting role of redox and acid-base properties. Catalysis Today, 2015, 253: 89–98
Chen I P, Lin S S, Wang C H, Chang L, Chang J S. Preparing and characterizing an optimal supported ceria catalyst for the catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2004, 50(1): 49–58
Yamaguchi T, Ikeda N, Hattori H, Tanabe K. Surface and catalytic propeties of cerium oxide. Journal of Catalysis, 1981, 67(2): 324–330
Jampaiah D, Venkataswamy P, Tur K M, Ippolito S J, Bhargava S K, Reddy B M. Effect of MnOx loading on structural, surface, and catalytic properties of CeO2-MnOx mixed oxides prepared by Sol-Gel method. Zeitschrift fur Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie, 2015, 641(6): 1141–1149
Wu X D, Liang Q, Weng D, Fan J, Ran R. Synthesis of CeO2- MnOx mixed oxides and catalytic performance under oxygen-rich condition. Catalysis Today, 2007, 126(3–4): 430–435
Khachatryan L, Lomnicki S, Dellinger B. An expanded reaction kinetic model of the CuO surface-mediated formation of PCDD/F from pyrolysis of 2-chlorophenol. Chemosphere, 2007, 68(9): 1741–1750
Rocha M A L, Del Ángel G, Torres-Torres G, Cervantes A, Vázquez A, Arrieta A, Beltramini J N. Effect of the Pt oxidation state and Ce3+/Ce4+ ratio on the Pt/TiO2-CeO2 catalysts in the phenol degradation by catalytic wet air oxidation (CWAO). Catalysis Today, 2015, 250: 145–154
Imamura S, Fukuda I, Ishida S. Wet oxidatrion catalyzed by ruthenium supported on cerium(IV) oxides. Industria & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1988, 27(4): 718–721
Keav S, Espinosa de los Monteros A, Barbier J, Duprez D. Wet air oxidation of phenol over Pt and Ru catalysts supported on ceriumbased oxides: resistance to fouling and kinetic modelling. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 150–151: 402–410
Wei H, Yan X, He S, Sun C. Catalytic wet air oxidation of pentachlorophenol over Ru/ZrO2 and Ru/ZrSiO2 catalysts. Catalysis Today, 2013, 201: 49–56
Wang J, Zhu W, Yang S, Wang W, Zhou Y. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol with pelletized ruthenium catalysts. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2008, 78(1–2): 30–37
Martín-Hernández M, Carrera J, Suárez-Ojeda M E, Besson M, Descorme C. Catalytic wet air oxidation of a high strength pnitrophenol wastewater over Ru and Pt catalysts: influence of the reaction conditions on biodegradability enhancement. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2012, 123–124: 141–150
Hamoudi S, Sayari A, Belkacemi K, Bonneviot L, Larachi F. Catalytic wet oxidation of phenol over PtxAg1–x MnO2/CeO2 catalysts. Catalysis Today, 2000, 62(4): 379–388
Massa P, Ivorra F, Haure P, Cabello F M, Fenoglio R. Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol aqueous solutions by 1% Ru/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts prepared by different methods. Catalysis Communications, 2007, 8(3): 424–428
Yu C, Meng X, Chen G, Zhao P. Catalytic wet air oxidation of high-concentration organic pollutants by upflow packed-bed reactor using a Ru-Ce catalyst derived from a Ru3(CO)12 precursor. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(27): 22633–22638
Sang-Kyung K, Son-Ki I. Effects of Ce addition and Pt precursor on the activity of Pt/Al2O3 catalysts for wet oxidation of phenol, 2002: 1967–1972
Li N, Descorme C, Besson M. Catalytic wet air oxidation of 2- chlorophenol over Ru loaded CexZr1–x O2 solid solutions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2007, 76(1–2): 92–100
Manole C C, Julcour-Lebigue C, Wilhelm A M, Delmas H. Catalytic oxidation of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid on activated carbon in batch autoclave and fixed-bed reactors. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2007, 46(25): 8388–8396
Iojoiu E E, Walmsley J C, Raeder H, Miachon S, Dalmon J A. Catalytic membrane structure influence on the pressure effects in an interfacial contactor catalytic membrane reactor applied to wet air oxidation. Catalysis Today, 2005, 104(2–4): 329–335
Mantzavinos D, Psillakis E. Enhancement of biodegradability of industrial wastewaters by chemical oxidation pre-treatment. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology (Oxford, Oxfordshire), 2004, 79(5): 431–454
Guisasola A, Baeza J A, Carrera J, Casas C, Lafuente J. An off-line respirometric procedure to determine inhibition and toxicity of biodegradable compounds in biomass from an industrial WWTP. Water Science and Technology, 2003, 48(11–12): 267–275
Mantzavinos D, Sahibzada M, Livingston A G, Metcalfe I S, Hellgardt K. Wastewater treatment: wet air oxidation as a precursor to biological treatment. Catalysis Today, 1999, 53(1): 93–106
Mantzavinos D, Hellenbrand R, Livingston A G, Metcalfe I S. Beneficial combination of wet oxidation, membrane separation and biodegradation processes for treatment of polymer processing wastewaters. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2000, 78 (2): 418–422
Hellenbrand R, Mantzavinos D, Metcalfe I S, Livingston A G. Integration of wet oxidation and nanofiltration for treatment of recalcitrant organics in wastewater. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1997, 36(12): 5054–5062
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 51425405), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 8172043) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (ZDRW-ZS-2016-5-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Cao, H., Descorme, C. et al. Phenolic compounds removal by wet air oxidation based processes. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 12, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0970-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-017-0970-2