Abstract
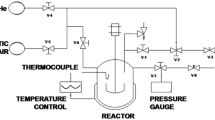
Catalytic wet air oxidation using heterogeneous catalysts is a promising technology for treatment of wastewaters. Wastewaters from olive oil mills are difficult to clean because effluents contain high levels of phenolic compounds that cannot be removed by biological treatment or incineration. Therefore, we tested the catalytic wet air oxidation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, as model molecule of olive oil mills wastewaters, over Ru-supported CeO2–TiO2 mixed oxides. We focussed on the Ce/Ti molar ratio because this ratio modifies the properties of the Ru catalysts. Supports were prepared by using the sol–gel method. The Ru catalysts were prepared by impregnation. Those products were characterized by N2 adsorption–desorption, X-ray diffraction, H2 chemisorption, transmission electron microscopy and inductively coupled plasma. Catalytic wet air oxidation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid was performed in a batch reactor at 140 °C and 50 bar of air. Our results show that the most efficient catalyst was Ru with a Ce/Ti ratio of 1/5, which converted totally p-hydroxybenzoic after 7 h of reaction without Ru leaching. We explain this finding by an enhanced dispersion of Ru due to better structural properties of the CeO2–TiO2 support.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhargava SK, Tardio J, Jani H, Akolekar DB, Foger K, Hoang M (2007) Catalytic wet air oxidation of industrial aqueous streams. Catal Surv Asia 11:70–86
Cybulski A (2007) Catalytic wet air oxidation: are monolithic catalysts and reactors feasible. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:4007–4033
Daghrir R, Drogui P (2013) Coupled electrocoagulation–electro-Fenton for efficient domestic wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 11:151–156
Epron F, Gauthard F, JrJ Barbier (2002) Catalytic reduction of nitrate in water on a monometallic Pd/CeO2 catalyst. J Catal 206:363–367
Gomez R, Lopez T, Ortiz-Islas E, Navrrete J, Sanchez E, Tzompantzi F, Bokhimi X (2003) Effect of sulfation on the photoactivity of TiO2 sol–gel derived catalysts. J Mol Catal A 193:217–226
Kanakaraju D, Glass BD, Oelgemoller M (2014) Titanium dioxide photocatalysis for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 12:27–47
Lopez T, Rojas F, Katz R, Galindo F, Balankin A, Buljan A (2004) Porosity, structural and fractal study of sol–gel TiO2–CeO2 mixed oxides. J Solid State Chem 177:1873–1885
Manole CC, Julcour-Lebigue C, Wilhelm AM, Delmas H (2007) Catalytic oxidation of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid on activated carbon in batch autoclave and fixed-bed reactors. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:8388–8396
Mikulová J, Rossignol S, JrJ Barbier, Mesnard D, Kappenstein C, Duprez D (2007) Ruthenium and platinum catalysts supported on Ce, Zr, Pr–O mixed oxides prepared by soft chemistry for acetic acid wet air oxidation. Appl Catal B 72:1–10
Mishra MK, Tyagi B, Jasra RV (2004) Synthesis and characterization of nano-crystalline sulfated zirconia by sol–gel method. J Mol Catal A 223:61–65
Okal J, Zawadzki M, Tylus W (2011) Microstructure characterization and propane oxidation over supported Ru nanoparticles synthesized by the microwave-polyol method. Appl Catal B 101:548–559
Oliviero L, Barbier J Jr, Duprez D, Wahyu H, Ponton JW, Metcalfe IS, Mantzavinos D (2001) Wet air oxidation of aqueous solutions of maleic acid over Ru/CeO2 catalysts. Appl Catal B 35:1–12
Pham MD, Aubert G, Gallezot P, Besson M (2007) Degradation of olive oil mill effluents by catalytic wet air oxidation: 2-oxidation of p-hydroxyphenylacetic and p-hydroxybenzoic acids over Pt and Ru supported catalysts. Appl Catal B 73:236–246
Pintar A, Berci G, Besson M, Gallezot P (2004) Catalytic wet air oxidation of industrial effluents: total mineralization of organics and lumped kinetic modeling. Appl Catal B 47:143–152
Renard B, Barbier J Jr, Duprez D, Durécu S (2005) Catalytic wet air oxidation of stearic acid on cerium oxide supported noble metal catalysts. Appl Catal B 55:1–10
Song A, Lu G (2015) Catalytic wet oxidation of aqueous methylamine: comparative study on the catalytic performance of platinum–ruthenium, platinum, and ruthenium catalysts supported on titania. Environ Technol 36:1160–1166
Triki M, Ksibi Z, Ghorbel A, Medina F (2009) Preparation and characterization of CeO2–TiO2 support for Ru catalysts: application in CWAO of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. Micro Meso Mater 117:431–435
Triki M, Ksibi Z, Ghorbel A, Medina F (2011) Preparation and characterization of CeO2–Al2O3 aerogels supported ruthenium for catalytic wet air oxidation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 59:1–6
Wang J, Zhu W, Yang S, Wang W, Zhou Y (2008) Catalytic wet air oxidation of phenol with pelletized ruthenium catalysts. Appl Catal B 78:30–37
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Spanish Government’s Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (project CTQ2012-35789). F. Medina and J. Llorca are grateful to the Generalitat de Catalunya for the Icrea Academia Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammedi, T., Triki, M., Alvarez, M.G. et al. Total degradation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid by Ru-catalysed wet air oxidation: a model for wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 13, 481–486 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0529-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0529-z