Abstract
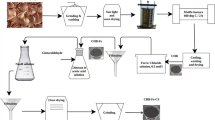
A hydroxyl-functionalized magnetic fungus nanocomposite (MFH@GO) was prepared by a simple one-pot method for the removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater. The adsorption behavior of MFH@GO to Cr(VI) in wastewater was discussed in detail. At pH of 5.0 and temperature of 323.15 K, MFH@GO had higher adsorption capacity to Cr(VI) (58.4 mg/g) than the unmodified fungus and GO. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetry and differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA), scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-Ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) were employed to determine the characteristics of MFH@GO. Results showed that magnetic graphene oxide nanoparticles significantly enhanced the physiochemical properties of the fungi. In addition, the adsorption mechanisms analyses show that Cr(VI) could be reduced and mineralized into ferric chromate in residues. These results suggested that MFH@GO could be used as an promising and alternative biosorbent for removal of Cr(VI) from industrial wastewater.
摘要
本文采用一种简单、 温和的方法制备了富含功能基团的磁性菌丝复合材料 MFH@GO, 并用于处理废水中的 Cr(VI). 详细地研究了 MFH@GO 对 Cr(VI) 的吸附性能. 结果表明, 在 pH 值为 5.0, 温度为 323.15 K 的条件下, MFH@GO 对 Cr(VI) 的最大吸附量达到 58.4 mg/g, 远高于未改性的菌丝粉和氧化石墨烯. 通过 FTIR, XRD, TG-DTA, SEM 和 EDX 等分析 MFH@GO 的特性及对 Cr(VI)的吸附机理, 结果表明, 铁及氧化石墨烯纳米颗粒显著改善了菌丝的理化特性, MFH@GO 能够将 Cr(VI) 还原成无毒的铬酸铁化合物存在于残留物中. 该研究结果表明 MFH@GO 在处理Cr(VI)废水中具有较大的潜力和应用价值.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Yang-yang, LIU Yi-dan, ZHAN Wen-hao, NIU Liu-min, ZOU Xue-yan, ZHANG Chao-sheng, RUAN Xin-ling. A field experiment on stabilization of Cd in contaminated soils by surface-modified nano-silica (SMNS) and its phyto-availability to corn and wheat [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20: 91–98. DOI: 10.1007/ sll368-019-02416-l.
WANG Yang-yang, LIU Yi-dan, ZHAN Wen-hao, ZHENG Kai-xuan, LIAN Ming-ming, ZHANG Chao-sheng, RUAN Xin-ling, LI Tao. Long-term stabilization of Cd in agricultural soil using mercapto-functionalized nano-silica (MPTS/nano-silica): A three-year field study [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 197: 110600. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110600.
SINGH P K, WANG W, SHRIVASTAVA A K. Cadmium-mediated morphological, biochemical and physiological tuning in three different Anabaena species [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2018, 202: 36–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.06.011.
CHAI Li-yuan, DING Chun-lian, TANG Chong-jian, YANG Wei-chun, YANG Zhi-hui, WANG Yang-yang, LIAO Qi, LI Jia-wei. Discerning three novel chromate reduce and transport genes of highly efficient Parmonibacter phragmitetus BB: From genome to gene and protein [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 162: 139–146. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.090.
MA Ya-meng, LI Fang-fang, YANG Wei-hua, LV Lv, XUE Hao-tian, WANG Yang-yang. Remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil using the acidified hydrazine hydrate [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2016, 97(3): 392–394. DOI: 10.1007/s00128-016-1862-z.
WANG Yang-yang, PENG Bing, YANG Zhi-hui, CHAI Li-yuan, LIAO Qi, ZHANG Zhi, LI Chuang. Bacterial community dynamics during bioremediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil [J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2015, 85: 50–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.09.002.
MDLALOSE L, BALOGUN M, SETLEGO K, WUKULULA M, CHIMUKA L, CHETTY A. Synthesis, characterization and optimization of poly (p-phenylenediamine)-based organoclay composite for Cr(VI) remediation [J]. Applied Clay Science, 2017, 139: 72–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.01.015.
WANG Yang-yang, CHAI Li-yuan, LIAO Qi, TANG Chong-jian, LIAO Ying-ping, PENG Bing, YANG Zhi-hui. Structural and genetic diversity of hexavalent chromium-resistant bacteria in contaminated soil [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2016, 33(3, 4): 222–229. DOI: 10.1080/01490451.2015.1054006.
OWLAD M, AROUA M K, DAUD W A W, BAROUTIAN S. Removal of hexavalent chromium-contaminated water and wastewater: A review [J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 2009, 200(1–4): 59–77. DOI: 10.1007/s1l270-008-9893-7.
SINGH R, MISRA V, SINGH R P. Removal of Cr(VI) by Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) from soil contaminated with tannery wastes [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2012, 88(88): 2–210. DOI: 10.1007/sOO 128-011-0425-6.
MIN Xiao-bo, WANG Yang-yang, CHAI Li-yuan, YANG Zhi-hui, LIAO Qi. High-resolution analyses reveal structural diversity patterns of microbial communities in chromite ore processing residue (COPR) contaminated soils [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 183: 266–276. DOI: 10.1016/ j.chemosphere.2017.05.105.
LI Yao, CUI Wen-quan, LIU Li, ZONG Rui-long, YAO Wen-qing, LIANG Ying-hua, ZHU Yong-fa. Removal of Cr (VI) by 3D Ti02-graphene hydrogel via adsorption enriched with photocatalytic reduction [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 199: 412–423. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.053.
ZAFAR S, AQIL F, AHMAD I. Metal tolerance and biosorption potential of filamentous fungi isolated from metal contaminated agricultural soil [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2007, 98(98): 13–2557. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.051.
WANG Yang-yang, LIU Yi-dan, ZHAN Wen-hao, ZHENG Kai-xuan, WANG Jun-nan, ZHANG Chao-sheng, CHEN Run-hua. Stabilization of heavy metal-contaminated soils by biochar: challenges and recommendations [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 30: 139060. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139060.
LIU Wei-fang, ZHANG Jian, ZHANG Cheng-lu, WANG Yi-fu, LI Ye. Adsorptive removal of CrCVT) by Fe-modified activated carbon prepared from Trapa natans husk [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 162(162): 2–677. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.06.020.
ZENG Yue-bin, WOO H, LEE G, PARK J. Removal of chromate from water using surfactant modified Pohang clinoptilolite and Haruna chabazite [J]. Desalination, 2010, 257(1–3): 102–109. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.02.039.
KIM Y J, CHOI J, KIM E S. Removal of heavy metal ion in wastewater by dendritic nano-structured complex material [J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2019, 19(19): 2–1010. DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2019.15960.
WANG Yang-yang, ZHAN Wen-hao, ZHENG Kai-xuan, LIU Yi-dan, ZOU Xue-yan, ZHANG Chao-sheng, RUAN Xin-ling. Effect of surface-modified nano-silica on the mobility and fraction of Cd in contaminated agricultural soils [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 2020, 29(29): 1–96. DOI: 10.1080/15320383.2019.1679086.
LIU Xue-ming, SONG Kai-nan, LIU Wei-zhen, XIONG Yue-cheng, XU Yun-yun, SHI Zheng-qing, ZHAO Dong-ye, LIN Zhang. Removal and recovery of Pb from wastewater through a reversible phase transformation process between nano-flower-like Mg(OH)2 and soluble Mg(HCO3)2 [J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2019, 6(6): 2–467. DOI: 10.1039/C8EN01173G.
DINDA D, GUPTA A, SAHA S K. Removal of toxic Cr(VI) by UV-active functionalized graphene oxide for water purification [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(1): 37–11221. DOI: 10.1039/C3TA12504A.
ZHANG Ke-xin, LI Hai-yan, XU Xing-jian, YU Hong-wen. Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/NiO nanocomposites for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous water by adsorption [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 255: 7–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.07.037.
WANG Ting, ZHANG Li-yuan, LI Chao-fang, YANG Wei-chun, SONG Ting-ting, TANG Chong-jian, MENG Yun, DAI Shuo, WANG Hai-ying, CHAI Li-yuan, LUO Jian. Synthesis of core-shell magnetic Fe3O4@ poly (m-phenylenediamine) particles for chromium reduction and adsorption [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(49): 9–5654. DOI: 10.1021/es5061275.
MEHTA D, MAZUMDAR S, SINGH S K. Magnetic adsorbents for the treatment of water/wastewater—A review [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2015, 7: 244–265. DOI: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.07.001.
LI WEI, MU Bing-nan, YANG Yi-qi. Feasibility of industrial-scale treatment of dye wastewater via bio-adsorption technology [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 227: 157–170. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.002.
BAHRAMI H R T, AZIZI A, SAFFARI H. Dropwise condensation heat transfer enhancement on surfaces micro/nano structured by a two-step electrodeposition process [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(26): 5–1065. DOI: 10.1007/s 11771-019-4071-1.
ZHANG Li-yuan, WANG Yang-yang, PENG Bing, YU Wan-ting, WANG Hai-ying, WANG Ting, DENG Bai-wan, CHAI Li-yuan, ZHANG Kai, WANG Jie-xi. Preparation of a macroscopic, robust carbon-fiber monolith from filamentous fungi and its application in Li-S batteries [J]. Green Chemistry, 2014, 16(16): 8–3926. DOI: 10.1039/ c4gc00761a.
LI Qing-zhu, CHAI Li-yuan, YANG Zhi-hui, WANG Qing-wei. Kinetics and thermodynamics of Pb(II) adsorption onto modified spent grain from aqueous solutions [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(255): 7–4298. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.11.024.
KONG Miao-miao, SONG Hui, LI Feng-hua, DAI Dong-mei, GAO Hong-tao. Facile synthesis of Bi2Fe4O9 nanoplate and its application as a novel adsorbent for Cu(II) removal [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2017, 5(5): 1–69. DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.11.020.
DONG Hao-ran, DENG Jun-min, XIE Yan-kai, ZHANG Cong, JIANG Zhao, CHENG Yu-jun, HOU Kun-jie, ZENG Guang-ming. Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 332(332): 15–79. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.03.002.
WANG Lin, SONG Huan, YUAN Li-yong, LI Zi-jie, ZHANG Peng, GIBSON J K, ZHENG Li-rong, WANG Hong-qing, CHAI Zhi-fang, SHI Wei-qun. Effective removal of anionic Re (VII) by surface-modified Ti2CTx MXene nanocomposites: Implications for Tc (VII) sequestration [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(53): 7–3739. DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.8b07083.
SHI Li-na, LIN Yu-man, ZHANG Xin, CHEN Zu-liang. Synthesis, characterization and kinetics of bentonite supported nZVI for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 171(171): 2–612. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.04.038.
WANG Yan, TANG Xiao-wu, WANG Heng. Characteristics and mechanisms of Ni (II) removal from aqueous solution by Chinese loess [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(22): 11–4184. DOI: 10.1007/s1l771-015-2966-z.
HUANG Guan-xing, ZHANG Ying, SUN Ji-chao, JING Ji-hong, LIU Jing-tao, WANG Ying. Effects of different conditions on Pb2+ adsorption from soil by irrigation of sewage in South China [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(19): 1–213. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-012-0994-5.
JIANG Zhu-wu, WANG Xue-jiang, NING Xue. Removal of lead (II) from aqueous solutions by activated carbon developed from surplus sludge [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(21): 9–3568. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-014-2337-1.
HOJATI S, KHADEMI H. Cadmium sorption from aqueous solutions onto Iranian sepiolite: Kinetics and isotherms [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(20): 12–3627. DOI: 10.1007/s1l771-013-1889-9.
RAO M P, MUSTHAFA S, WU J J, ANANDAN S. Facile synthesis of perovskite LaFeO3 ferroelectric nanostructures for heavy metal ion removal applications [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2019, 232(232): 15–200. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.04.086.
LIU Chong, WU Tong, HSU Po-chun, XIE Jin, ZHAO Jie, LIU Kai, SUN Jie, XU Jin-wei, TANG Jing, YE Zi-wen, LIN Ding-chang, CUI Yi. Direct/alternating current electrochemical method for removing and recovering heavy metal from water using graphene oxide electrode [J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(13): 6–6431. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.8b09301.
LIU Jing, LI Ruo-fan, YAO Yi-hao, LIU Ai-rong. Fate and mechanistic insights into the transformation of aged nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVIA) reacted with Cr(VI): Impact of aging time in oxic water [J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2019, 3(3): 7–1288. DOI: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.9b00095.
ZHANG Bao, WANG Yin-hui, WANG Shao-peng, WEI Chao-shuai, WANG Rui, ZHANG Wei. Oxidation of high iron content electroplating sludge in supercritical water: stabilization of zinc and chromium [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(26): 15–15001. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-019-04897-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(18B195) supported by Excellent Youth Project of Hunan Education Department, China; Projects(51804353, 51704093) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(kq1801074) supported by Key Projects of Changsha Science and Technology Plan, China; Project(2018JJ4010) supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Joint Funds of Provincial and Zhuzhou Municipal); Project(2018JJ3885) supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (Science Foundation for Youths)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Rh., Cheng, Yy., Wang, P. et al. High efficient removal and mineralization of Cr(VI) from water by functionalized magnetic fungus nanocomposites. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 1503–1514 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4386-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4386-y