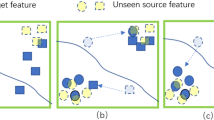
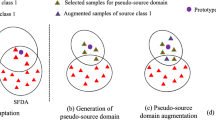
Abstract
Source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) mainly aims to the problem of not being able to access the source domain data during the model migration process. Although significant breakthroughs have been achieved, the current works meet performance ceiling. The key problem is that the source bias of the adapted model is difficult to be eliminated. In this work, we propose a novel SFDA method named rectiFication Upon SEmantic information (FUSE). The key idea is to reduce source bias of the adapted model with the help of pre-trained vision–language model (e.g., CLIP). Two strategies are adapted. The first is named source bias reduction, which is to restrict the impact of the samples with inconsistent predictions between the source and pre-trained models. The samples with high confidence classification based on pre-trained model automatically assume the task of supervision. Another one adjusts the pre-trained model to fit the distribution of the target domain. The features that better represent class centers are extracted. Except these two strategies, we also adapt pseudo-labeling method to further improve the performance of the adapted model. Experiments on three benchmark datasets show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art results.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datesets Office-31, Office-Home and VisDA-C could be downloaded from https://github.com/tim-learn/SHOT [7]
References
Ganin, Y., Lempitsky, V.: Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation, In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1180–1189. PMLR (2015)
Saito, K., Watanabe, K., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T.: Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3723–3732 (2018)
Long, M., Cao, Z., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Conditional adversarial domain adaptation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 31 (2018)
He, J., Wu, L., Tao, C., Lv, F.: Source-free domain adaptation with unrestricted source hypothesis. Pattern Recognit. 149, 110246 (2024)
Yang, S., Wang, Y., Van De Weijer, J., Herranz, L., Jui, S.: Unsupervised domain adaptation without source data by casting a bait, 1(2), 5 (2020). arXiv:2010.12427
Qiu, Z., Zhang, Y., Lin, H., Niu, S., Liu, Y., Du, Q., Tan, M.: Source-free domain adaptation via avatar prototype generation and adaptation. arXiv:2106.15326 (2021)
Liang, J., Hu, D., Feng, J.: Do we really need to access the source data? source hypothesis transfer for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 6028–6039. PMLR (2020)
Yang, S., Wang, Y., Van De Weijer, J., Herranz, L., Jui, S.: Generalized source-free domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8978–8987 (2021)
Tian, L., Zhou, L., Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Ye, M.: Robust self-supervised learning for source-free domain adaptation. Signal Image Video Process. 17(5), 2405–2413 (2023)
Radford, A., Kim, J.W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., Sastry, G., Askell, A., Mishkin, P., Clark, J., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 8748–8763. PMLR (2021)
Ge, C., Huang, R., Xie, M., Lai, Z., Song, S., Li, S., Huang, G.: Domain adaptation via prompt learning. arXiv:2202.06687 (2022)
Lai, Z., Vesdapunt, N., Zhou, N., Wu, J., Huynh, C. P., Li, X., Fu, K.K., Chuah, C.-N.: PADCLIP: Pseudo-labeling with adaptive debiasing in clip for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 16155–16165 (2023)
Zellinger, W., Grubinger, T., Lughofer, E., Natschläger, T., Saminger-Platz, S.: Central moment discrepancy (CMD) for domain-invariant representation learning. arXiv:1702.08811 (2017)
Kang, G., Jiang, L., Yang, Y., Hauptmann, A.G.: Contrastive adaptation network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4893–4902 (2019)
Li, M., Zhai, Y.-M., Luo, Y.-W., Ge, P.-F., Ren, C.-X.: Enhanced transport distance for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition, pp. 13936–13944 (2020)
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, E., Ajakan, H., Germain, P., Larochelle, H., Laviolette, F., Marchand, M., Lempitsky, V.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 2096–2030 (2016)
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7167–7176 (2017)
Liu, M.-Y., Tuzel, O.: Coupled generative adversarial networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 29 (2016)
Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 2223–2232 (2017)
Wang, M., Liu, Y., Yuan, J., Wang, S., Wang, Z., Wang, W.: Inter-class and inter-domain semantic augmentation for domain generalization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2024.3354420
Ghifary, M., Kleijn, W. B., Zhang, M., Balduzzi, D.: Domain generalization for object recognition with multi-task autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2551–2559 (2015)
Sun, Y., Tzeng, E., Darrell, T., Efros, A. A.: Unsupervised domain adaptation through self-supervision. arXiv:1909.11825 (2019)
Tian, J., Zhang, J., Li, W., Xu, D.: VDM-DA: virtual domain modeling for source data-free domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(6), 3749–3760 (2021)
Quattoni, A., Collins, M., Darrell, T.: Learning visual representations using images with captions. In: 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2007)
Srivastava, N., Salakhutdinov, R.R.: Multimodal learning with deep Boltzmann machines. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 25 (2012)
Jia, C., Yang, Y., Xia, Y., Chen, Y.-T., Parekh, Z., Pham, H., Le, Q., Sung, Y.-H., Li, Z., Duerig, T.: Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 4904–4916. PMLR (2021)
Gal, R., Patashnik, O., Maron, H., Bermano, A.H., Chechik, G., Cohen-Or, D.: StyGAN-NADA: CLIP-guided domain adaptation of image generators. ACM Trans. Actions Gr. (TOG) 41(4), 1–13 (2022)
Vidit, V., Engilberge, M., Salzmann, M.: Clip the gap: a single domain generalization approach for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3219–3229 (2023)
Fahes, M., Vu, T.-H., Bursuc, A., Pérez, P., de Charette, R.: PODA: prompt-driven zero-shot domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 18623–18633 (2023)
Khattak, M.U., Wasim, S.T., Naseer, M., Khan, S., Yang, M.-H., Khan, F.S.: Self-regulating prompts: foundational model adaptation without forgetting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 15190–15200 (2023)
Zara, G., Roy, S., Rota, P., Ricci, E.: AutoLabel: CLIP-based framework for open-set video domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11504–11513 (2023)
Kim, Y., Cho, D., Han, K., Panda, P., Hong, S.: Domain adaptation without source data. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2(6), 508–518 (2021)
Kullback, S., Leibler, R.A.: On information and sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat. 22(1), 79–86 (1951)
Saenko, K., Kulis, B., Fritz, M., Darrell, T.: Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 213–226. Springer (2010)
Venkateswara, H., Eusebio, J., Chakraborty, S., Panchanathan, S.: Deep hashing network for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5018–5027 (2017)
Peng, X., Usman, B., Kaushik, N., Hoffman, J., Wang, D., Saenko, K.: VisDA: the visual domain adaptation challenge. arXiv:1710.06924 (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Wu, Y., Inkpen, D., El-Roby, A.: Dual mixup regularized learning for adversarial domain adaptation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 540–555. Springer (2020)
Chen, X., Wang, S., Long, M., Wang, J.: Transferability versus discriminability: batch spectral penalization for adversarial domain adaptation. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, pp. 1081–1090 (2019)
Xu, R., Li, G., Yang, J., Lin, L.: Larger norm more transferable: an adaptive feature norm approach for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1426–1435 (2019)
Cui, S., Wang, S., Zhuo, J., Li, L., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Towards discriminability and diversity: batch nuclear-norm maximization under label insufficient situations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3941–3950 (2020)
Yang, G., Xia, H., Ding, M., Ding, Z.: Bi-directional generation for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 6615–6622 (2020)
Jin, Y., Wang, X., Long, M., Wang, J.: Minimum class confusion for versatile domain adaptation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 464–480. Springer (2020)
Tang, H., Chen, K., Jia, K.: Unsupervised domain adaptation via structurally regularized deep clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8725–8735, (2020)
Liang, J., Hu, D., Feng, J.: Domain adaptation with auxiliary target domain-oriented classifier. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16632–16642 (2021)
Wang, M., Wang, S., Yang, X., Yuan, J., Zhang, W.: Equity in unsupervised domain adaptation by nuclear norm maximization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3346444
Li, R., Jiao, Q., Cao, W., Wong, H.-S., Wu, S.: Model adaptation: unsupervised domain adaptation without source data, In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9641–9650 (2020)
Yang, S., van de Weijer, J., Herranz, L., Jui, S., et al.: Exploiting the intrinsic neighborhood structure for source-free domain adaptation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 29393–29405 (2021)
Tang, S., Zou, Y., Song, Z., Lyu, J., Chen, L., Ye, M., Zhong, S., Zhang, J.: Semantic consistency learning on manifold for source data-free unsupervised domain adaptation. Neural Netw. 152, 467–478 (2022)
Ding, Y., Sheng, L., Liang, J., Zheng, A., He, R.: Proxymix: Proxy-based mixup training with label refinery for source-free domain adaptation, arXiv:2205.14566 (2022)
Tang, S., Su, W., Yang, Y., Chen, L., Ye, M.: Model adaptation via credible local context representation. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1049/cit2.12228
Van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(11), 2579–2605 (2008)
Funding
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (62276048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Liang Tiang contributed to the conception of the study, performed the experiment; Mao Ye contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; Lihua Zhou helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions; Zhenbin Wang helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions;
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This declaration is not applicable.
Ethical approval
This declaration is not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, L., Ye, M., Zhou, L. et al. Source bias reduction for source-free domain adaptation. SIViP (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03200-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03200-6