Abstract
One of the major concerns affecting the public health is microbial pathogens. Commercial antibiotics have a wide range of applications, however harmful microorganisms have increased their resistance to antibiotics, making the fight against these pathogens difficult. For many years, scientists have focused on finding natural sources with strong antimicrobial activity. At this point, microalgae cells have attracted great attention due to their biological activities including, antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral effects. In order to discover promising strains with strong antimicrobial activity and to obtain interested components efficiently, a thorough scientific approach is needed by considering all steps of the process. This process mainly consisted of strain selection, cultivation, harvesting of biomass, extraction and purification of compounds and screening their antimicrobial properties. Using microalgal compounds against microbial pathogens is still in its early days. In this context, the present review aims to contribute existing database of antimicrobial potential of microalgae. With this aim, the impact of microalgae species and their components were investigated according to their bioactivities against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The crucial points in this regard were emphasized and important suggestions were presented for further researches.
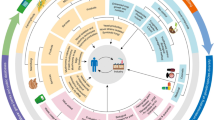
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new datasets were generated or analyzed in the current paper.
References
Abidin AAZ, Othman NA, Yusoff FM, Yusof ZNB (2021) Determination of transgene stability in Nannochloropsis sp. transformed with immunogenic peptide for oral vaccination against vibriosis. Aquac Int 29(2):477–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00634-w
Alsenani F, Tupally KR, Chua ET, Eltanahy E, Alsufyani H, Parekh HS, Schenk PM (2020) Evaluation of microalgae and cyanobacteria as potential sources of antimicrobial compounds. Saudi Pharm J 28(12):1834–1841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2020.11.010
Amaro HM, Catarina Guedes A, Xavier Malcata F (2011) Antimicrobial activities of microalgae: an invited review. In: Mendez Vilaz A (ed) Science against microbial pathogens: Communicating current research and technological advances. Formatex Research Center, Badajoz, Spain, pp 1272–1280
Aslanbay Guler B, Deniz I, Demirel Z, Yesil-Celiktas O, Imamoglu E (2020) A novel subcritical fucoxanthin extraction with a biorefinery approach. Biochem Eng J 153(June 2019):107403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107403
Assunção J, Malcata FX (2020) Enclosed “non-conventional” photobioreactors for microalga production: a review. Algal Res 52(June):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2020.102107
Bergø J, Bourgougnon N, Alban S, Pojer F, Billaudel S, Chermann J, Robert JM, Franz G (1999) Antiviral and Anticoagulant Activities of a Water-Soluble Fraction of the Marine Diatom Haslea ostearia. Planta Med 65:604–609
Bagul VP, Annapure US (2020) Effect of sequential recycling of spent media wastewater on docosahexaenoic acid production by newly isolated strain Aurantiochytrium sp. ICTFD5. Bioresour Technol 306:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123153
Bai VDM, Krishnakumar S (2013) Evaluation of antimicrobial metabolites from microalgae Tetraselmis suecica using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC – MS) analysis. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5(3):17–23
Benedetti M, Vecchi V, Barera S, Dall’Osto L (2018) Biomass from microalgae: the potential of domestication towards sustainable biofactories. Microb Cell Factories 17(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-1019-3
Betterle N, Hidalgo Martinez D, Melis A (2020) Cyanobacterial production of biopharmaceutical and biotherapeutic proteins. Front Plant Sci 11(March):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00237
Bhagavathy S, Sumathi P, Jancy Sherene Bell I (2011) Green algae Chlorococcum humicola- a new source of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial activity. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 1:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(11)60111-1
Bhalamurugan GL, Valerie O, Mark L (2018) Valuable bioproducts obtained from microalgal biomass and their commercial applications: a review. Environ Eng Res 23(3):229–241. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2017.220
Bhattacharjee M (2016) Pharmaceutically valuable bioactive compounds of algae. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 9(6):43–47. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2016.v9i6.14507
Borowitzka MA (2018) Microalgae in medicine and human health: A historical perspective. In: Levine IA, Fleurence J (eds) Microalgae in Health and Disease Prevention. Academic Press, London, pp 195–210
Boyd MR, Gustafson KR, McMahon JB, Shoemaker RH, O’Keefe BR, Mori T, Gulakowski RJ, Wu L, Rivera MI, Laurencot CM, Currens MJ, Cardellina JH, Buckheit RW, Nara PL, Pannell LK, Sowder RC, Henderson LE (1997) Discovery of cyanovirin-N, a novel human immunodeficiency virus- inactivating protein that binds viral surface envelope glycoprotein gp120: potential applications to microbicide development. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41(7):1521–1530. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.41.7.1521
Brunner G, Saure C, Buss D (2009) Phase equilibrium of hydrogen, carbon dioxide, squalene, and squalane. J Chem Eng Data 54(5):1598–1609. https://doi.org/10.1021/je800926z
Bule MH, Ahmed I, Maqbool F, Bilal M, Iqbal HMN (2018) Microalgae as a source of high-value bioactive compounds. Front Biosci- Scholar 10(2):197–216. https://doi.org/10.2741/s509
Chang T, Ohta S, Ikegami N, Miyata H, Kashimoto T, Kondo M (1993) Antibiotic substances produced by a marine green alga, Dunaliella primolecta. Bioresour Technol 44(2):149–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(93)90189-I
Chassaing B, Cascales E (2018) Antibacterial weapons: targeted destruction in the microbiota. Trends Microbiol 26(4):329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2018.01.006
Chen Y, Mu T (2021) Revisiting greenness of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem Eng 2(2):174–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2021.01.004
Chen CL, Chang JS, Lee DJ (2015) Dewatering and drying methods for microalgae. Dry Technol 33(4):443–454. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2014.997881
Correa PS, Morais Junior WG, Martins AA, Caetano NS, Mata TM (2021) Microalgae biomolecules: extraction, separation and purification methods. Processes 9(10):1–43. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010010
Da Silva Ferreira V, ConzFerreira ME, Lima LMTR, Frasés S, de Souza W, Sant’Anna C (2017) Green production of microalgae-based silver chloride nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity against pathogenic bacteria. Enzym Microb Technol 97:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.10.018
Daniel R (2016) Antibacterial activity of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum against selected human pathogens. Int J Curr Pharm Rev Res 7(5):233–236
De Grahl I, Reumann S (2021) Stramenopile microalgae as “green biofactories” for recombinant protein production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37(9):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03126-y
Desbois AP, Mearns-Spragg A, Smith VJ (2009) A fatty acid from the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum is antibacterial against diverse bacteria including multi-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Mar Biotechnol 11(1):45–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-008-9118-5
Elias NA, Abu Hassan MS, Yusoff NAH, Tosin OV, Harun NA, Rahmah S, Hassan M (2023) Potential and limitation of biocontrol methods against vibriosis: a review. Aquac Int 31:2355–2398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-023-01091-x
Falaise C, François C, Travers MA, Morga B, Haure J, Tremblay R, Turcotte F, Pasetto P, Gastineau R, Hardivillier Y, Leignel V, Mouget JL (2016) Antimicrobial compounds from eukaryotic microalgae against human pathogens and diseases in aquaculture. Mar Drugs 14(9):1–27. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14090159
Gallego R, Bueno M, Herrero M (2019) Sub- and supercritical fluid extraction of bioactive compounds from plants, food-by-products, seaweeds and microalgae – an update. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 116:198–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.04.030
Ghasemi Y, Moradian A, Mohagheghzadeh A, Shokravi S, Morowvat MH (2007) Antifungal and antibacterial activity of the MicroAlgae collected from Paddy fields of Iran. J Biol Sci 7(6):904–910
Gong Y, Hu H, Gao Y, Xu X, Gao H (2011) Microalgae as platforms for production of recombinant proteins and valuable compounds: Progress and prospects. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(12):1879–1890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-011-1032-6
Gromov BV, Vepritskiy AA, Titova NN, Mamkayeva KA, Alexandrova OV (1991) Production of the antibiotic cyanobacterin LU-1 by Nostoc linckia CALU 892 (cyanobacterium). J Appl Phycol 3(1):55–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00003919
Hachicha R, Elleuch F, Hlima H, Dubessay P, de Baynast H, Delattre C, Pierre G, Hachicha R, Abdelkafi S, Michaud P, Fendri I (2022) Biomolecules from microalgae and Cyanobacteria: applications and market survey. Appl Sci (Switzerland) 12(4):1–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041924
Hasui M, Matsuda M, Okutani K, Shigeta S (1995) In vitro antiviral activities of sulfated polysaccharides from a marine microalga (Cochlodinium polykrikoides) against human immunodeficiency virus and other enveloped viruses. Int J Biol Macromol 17(5):293–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-8130(95)98157-T
Huheihel M, Ishanu V, Tal J, Arad S (2002) Activity of Porphyridium sp. polysaccharide against herpes simplex viruses in vitro and in vivo. J Biochem Biophys Methods 50(2–3):189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-022X(01)00186-5
Hans N, Malik A, Naik S (2021) Antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae and its application in combating COVID-19: mini review. Bioresour Technol Rep 13(October 2020):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2020.100623
Hassan S, Meenatchi R, Pachillu K, Bansal S, Brindangnanam P, Arockiaraj J, Kiran GS, Selvin J (2022) Identification and characterization of the novel bioactive compounds from microalgae and cyanobacteria for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. J Basic Microbiol 62(9):999–1029. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.202100477
Herrero M, Ibáñez E, Cifuentes A, Reglero G, Santoyo S (2006) Dunaliella salina microalga pressurized liquid extracts as potential antimicrobials. J Food Prot 69(10):2471–2477. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-69.10.2471
Herrero M, del Pilar Sánchez-Camargo A, Cifuentes A, Ibáñez E (2015) Plants, seaweeds, microalgae and food by-products as natural sources of functional ingredients obtained using pressurized liquid extraction and supercritical fluid extraction. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 71:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.01.018
Hussein HA, Syamsumir DF, Radzi SAM, Siong JYF, Zin NAM, Abdullah MA (2020) Phytochemical screening, metabolite profiling and enhanced antimicrobial activities of microalgal crude extracts in co-application with silver nanoparticle. Bioresour Bioprocess 7(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-00322-w
Jaiswal KK, Dutta S, Banerjee I, Pohrmen CB, Kumar V (2021) Photosynthetic microalgae–based carbon sequestration and generation of biomass in biorefinery approach for renewable biofuels for a cleaner environment. Biomass Convers Biorefin :1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01504-y
Jha D, Jain V, Sharma B, Kant A, Garlapati VK (2017) Microalgae-based pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals: an emerging field with immense market potential. ChemBioEng Rev 4(4):257–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201600023
Kalogeropoulos N, Chiou A, Gavala E, Christea M, Andrikopoulos NK (2010) Nutritional evaluation and bioactive microconstituents (carotenoids, tocopherols, sterols and squalene) of raw and roasted chicken fed on DHA-rich microalgae. Food Res Int 43(8):2006–2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010.05.018
Katiyar R, Gurjar BR, Biswas S, Pruthi V, Kumar N, Kumar P (2017) Microalgae: an emerging source of energy based bio-products and a solution for environmental issues. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72(August 2016):1083–1093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.10.028
Khan MI, Shin JH, Kim JD (2018) The promising future of microalgae: current status, challenges, and optimization of a sustainable and renewable industry for biofuels, feed, and other products. Microb Cell Factories 17(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0879-x
Kharkwal H, Joshi DD, Panthari P, Kant Pant M, Kharkwal AC (2012) Algae as future drugs. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 5(4):1–4
Kim SK, Karadeniz F (2012) Biological importance and applications of squalene and Squalane. Adv Food Nutr Res 65:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416003-3.00014-7
Kim DY, Vijayan D, Praveenkumar R, Han JI, Lee K, Park JY, Chang WS, Lee JS, Oh YK (2016) Cell-wall disruption and lipid/astaxanthin extraction from microalgae: Chlorella and Haematococcus. Bioresour Technol 199:300–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.107
Kowthaman CN, Senthil Kumar P, Arul Mozhi Selvan V, Ganesh D (2022) A comprehensive insight from microalgae production process to characterization of biofuel for the sustainable energy. Fuel 310:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122320
Kuppusamy P, Soundharrajan I, Srigopalram S, Yusoff MM, Maniam GP, Govindan N, Choi KC (2017) Potential pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of diatoms microalgae - an overview. Indian J Mar Sci 46(4):663–667
Lafarga T (2020) Cultured microalgae and compounds derived thereof for food applications: strain selection and cultivation, drying, and processing strategies. Food Rev Int 36(6):559–583. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129.2019.1655572
Lam TP, Lee TM, Chen CY, Chang JS (2018) Strategies to control biological contaminants during microalgal cultivation in open ponds. Bioresour Technol 252(November 2017):180–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.088
Lauritano C, Andersen JH, Hansen E, Albrigtsen M, Escalera L, Esposito F, Helland K, Hanssen K, Romano G, Ianora A (2016) Bioactivity screening of microalgae for antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, anti-diabetes, and antibacterial activities. Front Mar Sci 3(MAY):1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2016.00068
Lee JB, Hayashi K, Hirata M, Kuroda E, Suzuki E, Kubo Y, Hayashi T (2006) Antiviral sulfated polysaccharide from Navicula directa, a diatom collected from deep-sea water in Toyama Bay. Biol Pharm Bull 29(10):2135–2139. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.29.2135
Lozano-Grande MA, Gorinstein S, Espitia-Rangel E, Dávila-Ortiz G, Martínez-Ayala AL (2018) Plant sources, extraction methods, and uses of squalene. Int J Agron 2018:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1829160
Maeda Y, Yoshino T, Matsunaga T, Matsumoto M, Tanaka T (2018) Marine microalgae for production of biofuels and chemicals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 50:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.11.018
Malhadas C, Malheiro R, Pereira JA, Guedes de Pinho P, Baptista P (2017) Antimicrobial activity of endophytic fungi from olive tree leaves. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33(3):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2216-7
Mehariya S, Goswami RK, Karthikeysan OP, Verma P (2021) Microalgae for high-value products: a way towards green nutraceutical and pharmaceutical compounds. Chemosphere 280:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130553
Metting FB (1996) Biodiversity and application of microalgae. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 17(5–6):477–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01574779
Miazek K, Kratky L, Sulc R, Jirout T, Aguedo M, Richel A, Goffin D (2017) Effect of organic solvents on microalgae growth, metabolism and industrial bioproduct extraction: a review. Int J Mol Sci 18(7):1–31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071429
Mimouni V, Ulmann L, Pasquet V, Mathieu M, Picot L, Bougaran G, Cadoret J-P, Morant-Manceau A, Schoefs B (2012) The potential of microalgae for the production of bioactive molecules of pharmaceutical interest. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 13(15):2733–2750. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920112804724828
Mudimu O, Rybalka N, Bauersachs T, Born J, Friedl T, Schulz R (2014) Biotechnological screening of microalgal and cyanobacterial strains for biogas production and antibacterial and antifungal effects. Metabolites 4(2):373–393. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4020373
Mutanda T, Naidoo D, Bwapwa JK, Anandraj A (2020) Biotechnological applications of microalgal oleaginous compounds: current trends on microalgal bioprocessing of products. Front Energy Res 8(December):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2020.598803
Najdenski HM, Gigova LG, Iliev II, Pilarski PS, Lukavský J, Tsvetkova IV, Ninova MS, Kussovski VK (2013) Antibacterial and antifungal activities of selected microalgae and cyanobacteria. Int J Food Sci Technol 48(7):1533–1540. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12122
Narala RR, Garg S, Sharma KK, Thomas-Hall SR, Deme M, Li Y, Schenk PM (2016) Comparison of microalgae cultivation in photobioreactor, open raceway pond, and a two-stage hybrid system. Front Energy Res 4(AUG):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2016.00029
Netanel Liberman G, Ochbaum G, Arad SM, Bitton R (2016) The sulfated polysaccharide from a marine red microalga as a platform for the incorporation of zinc ions. Carbohydr Polym 152:658–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.025
Obermeier A, Schneider J, Föhr P, Wehner S, Kühn KD, Stemberger A, Schieker M, Burgkart R (2015) In vitro evaluation of novel antimicrobial coatings for surgical sutures using octenidine. BMC Microbiol 15(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-015-0523-4
Ohta S, Ono F, Shiomi Y, Nakao T, Aozasa O, Nagate T, Kitamura K, Yamaguchi S, Nishi M, Miyata H (1998) Antiherpes simplex virus substances produced by the marine green alga, Dunaliella primolecta. J Appl Phycol 10(4):349–356. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008065226194
Okoro V, Azimov U, Munoz J, Hernandez HH, Phan AN (2019) Microalgae cultivation and harvesting: growth performance and use of flocculants - a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 115:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109364
Olabi AG, Alami AH, Alasad S, Aljaghoub H, Sayed ET, Shehata N, Rezk H, Abdelkareem MA (2022) Emerging technologies for enhancing microalgae biofuel production: recent progress , barriers , and limitations. Fermentation 8(649):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110649
Pane G, Cacciola G, Giacco E, Mariottini GL, Coppo E (2015) Assessment of the antimicrobial activity of algae extracts on bacteria responsible of external otitis. Mar Drugs 13(10):6440–6452. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13106440
Rawat I, Ranjith Kumar R, Mutanda T, Bux F (2013) Biodiesel from microalgae: a critical evaluation from laboratory to large scale production. Appl Energy 103:444–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.10.004
Reichelt JL, Borowitzka MA (1984) Antimicrobial activity from marine algae: results of a large-scale screening programme. Hydrobiologia 116–117(1):158–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00027657
Ruffell SE, Müller KM, McConkey BJ (2016) Comparative assessment of microalgal fatty acids as topical antibiotics. J Appl Phycol 28(3):1695–1704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0692-4
Santoyo S, Jaime L, Plaza M, Herrero M, Rodriguez-Meizoso I, Ibañez E, Reglero G (2012) Antiviral compounds obtained from microalgae commonly used as carotenoid sources. J Appl Phycol 24(4):731–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9692-1
Seraspe EB, Tıcar BF, Formacion MJ, Pahila IG, de la Pena MR, Amar EC (2012) Antibacterial properties of the microalgae Chaetoceros calcitrans. Asian Fish Sci 25:343–356
Sibi G (2015) Inhibition of lipase and inflammatory mediators by Chlorella lipid extracts for antiacne treatment. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 6(1):7–12. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-4040.150364
Singh G, Patidar SK (2018) Microalgae harvesting techniques: a review. J Environ Manag 217:499–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.010
Skjånes K, Rebours C, Lindblad P (2013) Potential for green microalgae to produce hydrogen, pharmaceuticals and other high value products in a combined process. Crit Rev Biotechnol 33(2):172–215. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2012.681625
Smee DF, Bailey KW, Wong M, Keefe BRO, Kirk R, Mishin VP, Gubareva LV (2008) Treatment of influenza A (H1N1) virus infections in mice and ferrets with Cyanovirin-N. Antivir Res 80(3):266–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.06.003.Treatment
Suparmaniam U, Lam MK, Uemura Y, Lim JW, Lee KT, Shuit SH (2019) Insights into the microalgae cultivation technology and harvesting process for biofuel production: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 115(January):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109361
Tan JS, Lee SY, Chew KW, Lam MK, Lim JW, Ho SH, Show PL (2020) A review on microalgae cultivation and harvesting, and their biomass extraction processing using ionic liquids. Bioengineered 11(1):116–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2020.1711626
Tsianta A (2019) Pharmaceutical applications of eukaryotic microalgae. International Hellenic University
Wali AF, Dhaheri YA, Pillai JR, Mushtaq A, PGM R, Rabbani SA, Firdous A, Elshikh MS, Al Farraj DA (2020) Lc-ms phytochemical screening, in vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticancer activity of microalgae nannochloropsis oculata extract. Separations 7(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7040054
Wen X, Wang Z, Ding Y, Geng Y, Li Y (2020) Enhancing the production of astaxanthin by mixotrophic cultivation of Haematococcus pluvialis in open raceway ponds. Aquac Int 28(2):625–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00483-2
Wong JF, Hong HJ, Foo SC, Yap MKK, Tan JW (2022) A review on current and future advancements for commercialized microalgae species. Food Sci Hum Wellness 11(5):1156–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2022.04.007
Xia D, Qiu W, Wang X, Liu J (2021) Recent advancements and future perspectives of microalgae-derived pharmaceuticals. Mar Drugs 19(12):1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120703
Xu L, Meng W, Cao C, Wang J, Shan W, Wang Q (2015) Antibacterial and antifungal compounds from marine fungi. Mar Drugs 13(6):3479–3513. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063479
Yan N, Fan C, Chen Y, Hu Z (2016) The potential for microalgae as bioreactors to produce pharmaceuticals. Int J Mol Sci 17(6):1–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060962
Yarkent Ç, Oncel SS (2022) Recent Progress in microalgal squalene production and its cosmetic application. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 11:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0355-z
Yarkent Ç, Gürlek C, Oncel SS (2020) Potential of microalgal compounds in trending natural cosmetics: a review. Sustain Chem Pharm 17(February). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100304
Zhang R, Parniakov O, Grimi N, Lebovka N, Marchal L, Vorobiev E (2019) Emerging techniques for cell disruption and extraction of valuable bio-molecules of microalgae Nannochloropsis sp. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42(2):173–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-2038-5
Acknowledgments
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Çağla Yarkent: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Bahar Aslanbay Güler: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Esra İmamoğlu: Conceptualization, Writing - review & editing, Supervision, Suphi Ş. Öncel: Conceptualization, Writing - review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yarkent, Ç., Aslanbay Güler, B., Imamoglu, E. et al. Microalgae-factories as potential antimicrobial agents: a comprehensive review. Biologia 79, 1237–1250 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-024-01616-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-024-01616-6