Abstract
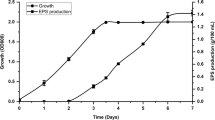
This study investigates the antibacterial activity of exopolysaccharides (EPS) produced by the marine bacterium Bacillus halotolerans against clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens. EPS production was optimized by exploring different carbon sources with glucose, peptone, and calcium chloride identified as significant factors for enhanced production. The optimized medium achieved a production rate of 0.612 g/L, surpassing the unoptimized medium’s production of 0.556 g/L. The EPS exhibited noteworthy hydroxyl scavenging activity and demonstrated hydrogen-donating ability by scavenging DPPH radicals. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy analysis revealed characteristic peaks representing hydroxyl and carboxyl groups, glycosidic linkages, and sulfate groups within the EPS structure. Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis confirmed the complex and heterogeneous nature of the EPS, with glucose and galactose residues and the presence of polysaccharides identified. Monomer units of the EPS structure were identified as glucose and galactose, and a prominent peak at 7.942 min indicated the presence of beta-1,5-O-Dibenzoyl-ribofuranose. This study provides valuable insights into optimizing EPS production, characterizing its properties, and evaluating its antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas sp. strains. Further investigations are necessary to explore the potential applications and underlying mechanisms of these antibacterial EPS, contributing to advancements in microbiology and biotechnology.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EPS:
-
Exopolysaccharides
- g/L:
-
Grams per litre
- μg/mL:
-
Micrograms per milliliter
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- DPPH:
-
2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
- min:
-
minutes
- g/mL:
-
grams per millilitre
- RBC:
-
Red blood cells
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffer saline
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- GCMS:
-
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- MHz:
-
megahertz
- 2θ:
-
2 theta
- CRA:
-
Congo Red Agar
- ZMB:
-
Zobel Marine Agar
- RPM:
-
Revolutions Per Minute
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- AST:
-
Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
- RSM:
-
Response Surface Methodology
- CCRD:
-
Central Composite Rotatable Design
- BLAST:
-
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
References
Chandki R, Banthia P, Banthia R (2011) Biofilms: a microbial home. J Indian Soc Periodontol 15:111–114. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-124X.84377
Chen Q, Xie S, Lou X, Cheng S, Liu X, Zheng W, Zheng Z, Wang H (2020) Biofilm formation and prevalence of adhesion genes among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from different food sources. Microbiologyopen 9:e00946. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.946
Cui JD, Zhang B (2011) Comparison of culture methods on exopolysaccharide production in the submerged culture of Cordyceps militaris and process optimization. Lett Appl Microbiol 52:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02987.x
Cui F, Liu Z, Li Y, Ping L, Ping L, Zhang Z, Huang D (2010) Production of mycelial biomass and exo-polymer by Hericium erinaceus CZ-2: optimization of nutrients levels using response surface methodology. Biotechnol Bioproc E 15:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-0117-9
das Chagas Faustino Alves MG, Dore CMPG, Castro AJG, do Nascimento MS, Cruz AKM, Soriano EM, Benevides NMB, Leite EL (2012) Antioxidant, cytotoxic and hemolytic effects of sulfated galactan from edible red alga Hypnea musciformis. J Appl Phycol 24:1217–1227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9763-3
De Carvalho CC (2018) Marine biofilms: a successful microbial strategy with economic implications. Front Mar Sci 5:126. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00126
Felz S, Vermeulen P, van Loosdrecht MC, Lin YM (2019) Chemical characterization methods for the analysis of structural extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Water Res 157:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.068
Fong JNC, Yildiz FH (2015) Biofilm matrix proteins. Microbiol Spectr 3:2. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.mb-0004-2014
Ha DG, O’Toole GA (2015) C-di-GMP and its effects on biofilm formation and dispersion: a Pseudomonas aeruginosa review. Microbiol Spectr 3:301–317. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.mb-0003-2014
Halder U, Mazumde K, Kumar KJ, Bandopadhyay R (2022) Structural insight into a glucomannan-type extracellular polysaccharide produced by a marine Bacillus altitudinis SORB11 from Southern Ocean. Sci Rep 12:16322. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20822-3
Hobley L, Harkins C, MacPhee CE, Stanley-Wall NR (2015) Giving structure to the biofilm matrix: an overview of individual strategies and emerging common themes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39:649–669. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuv015
Kavita K, Mishra A, Jha B (2011) Isolation and physicochemical characterisation of extracellular polymeric substances produced by the marine bacterium Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biofouling 27:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2011.562605
Klock JH, Wieland A, Seifert R, Michaelis W (2007) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from cyanobacterial mats: characterisation and isolation method optimisation. Mar Biol 152:1077–1085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0754-5
Krasowska A, Sigler K (2014) How do microorganisms use hydrophobicity, and what does this mean for human needs? Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:112. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2014.00112
Lung MY, Huang PC (2010) Optimization of exopolysaccharide production from Armillaria mellea in submerged cultures. Lett Appl Microbiol 50:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2009.02777.x
Paulo EM, Boffo EF, Branco A, Valente ÂM, Melo IS, Ferreira AG, Roque MR, Assis SAD (2012) Production, extraction and characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by the native Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides R2 strain. An Acad Bras Ciênc 84:495–508. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0001-37652012000200018
Priester JH, Horst AM, Van De Werfhorst LC, Saleta JL, Mertes LA, Holden PA (2007) Enhanced visualization of microbial biofilms by staining and environmental scanning electron microscopy. J Microbiol Methods 68:577–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2006.10.018
Rajoka MSR, Mehwish HM, Hayat HF, Hussain N, Sarwar S, Aslam H, Nadeem A, Shi J (2019) Characterization, the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of exopolysaccharide isolated from poultry origin Lactobacilli. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 11:1132–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9494-8
Ramamoorthy S, Ramachandran K, Sekar J, Natesan S, Gopal S, Rajaram S (2021) Production and characterization of EPS from the sponge-associated Bacillus subtilis MKU SERB2 and its in-vitro biological properties. Int J Biol Macromol 166:1471–1479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.026
Shyam KP, Rajkumar P, Ramya V, Sivabalan S, Kings AJ, Miriam LM (2021) Exopolysaccharide production by optimized medium using novel marine Enterobacter cloacae MBB8 isolate and its antioxidant potential. Carbohydr Polym Technol Appl 2:100070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2021.100070
Siddharth T, Sridhar P, Vinila V, Tyagi RD (2021) Environmental applications of microbial extracellular polymeric substance (EPS): a review. J Environ Manag 287:112307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112307
Sushmitha TJ, Rajeev M, Toleti SR, Pandian SK (2022) Complete genome sequence of Halomonas boliviensis strain kknpp38, a chlorine-resistant bacterium isolated from the early-stage marine biofilm. Mar Genom 62:100890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2021.100890
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tiwari ON, Sasmal S, Kataria AK, Devi I (2020) Application of microbial extracellular carbohydrate polymeric substances in food and allied industries. 3 Biotech 10:221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02200-w
Travis SM, Anderson NN, Forsyth WR, Espiritu C, Conway BD, Greenberg EP, McCray PB Jr, Lehrer RI, Welsh MJ, Tack BF (2000) Bactericidal activity of mammalian cathelicidin-derived peptides. Infect Immun 68:2748–2755. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.68.5.2748-2755.2000
Vadakkan K, Vijayanand S, Hemapriya J, Gunasekaran R (2019) Quorum sensing inimical activity of Tribulus terrestris against gram negative bacterial pathogens by signalling interference. 3 Biotech 9:163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1695-7
Waheed H, Mehmood CT, Yang Y, Tan W, Fu S, Xiao Y (2022) Dynamics of biofilms on different polymeric membranes – a comparative study using five physiologically and genetically distinct bacteria. J Membr Sci 642:120000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.120000
Yang YP, Peng Q, Guo YY, Han Y, Xiao HZ, Zhou ZJ (2015) Isolation and characterization of dextran produced by Leuconostoc citreum NM105 from manchurian sauerkraut. Carbohydr Polym 133:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.07.061
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to RUSA 2.0, Alagappa University. The project was funded by Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R231), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ravindran, A., Manivannan, A.C., Bharathi, G.S.J. et al. Production and characterization of exopolysaccharide (EPS) from marine Bacillus halotolerans and its antibacterial activity against clinical pathogens. Biologia 79, 605–619 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01580-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01580-7