Abstract
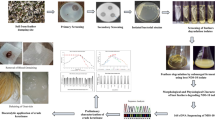
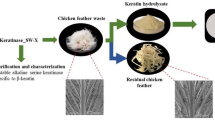
Microbial keratinase dexterity for keratin bioconversion into protein hydrolysates with high economic value is premised on its unique hydrolytic properties. Consequently, a novel keratinolytic Sphingobacterium multivorum HNFx (NCBI: MW165488.1) was grown on chicken feathers as the only source of carbon and nitrogen. Accordingly, extracellular keratinase production by the isolate was enhanced by optimizing various physico-nutritional parameters. The amino acid composition of the feather hydrolysate was analyzed, and the biochemical properties of the produced keratinase were evaluated. The results of the study indicated that HNFx elaborated maximum keratinase (1526.36 ± 8.99 U/mL) 72 h post-incubation. Analysis of the feather hydrolysate showed various amino acids with a relatively high abundance of aspartic acid (3.63%) and glutamic acid (3.56%), with significant concentration of arginine (2.44%), serine (2.08%), glycine (2.06%), and leucine (2.03%). HNFx keratinases showed optimal activity at pH of 8 and temperature of 90 oC. Metal ion chelators; EDTA and 1,10-phenanthroline inhibited the enzyme activity, suggesting a metallokeratinase. The enzyme activity was remarkably enhanced by chemical agents; SDS, triton X-100, DMSO, H2O2, and metal ions; Al3+, Ba2+, Ca2+, Fe2+; but significantly affected by Zn2+ and Co2+. S. multivorum HNFx has shown the propensity to add value to keratinous wastes through bioconversion into quality protein hydrolysate with immense prospects in the livestock sector. The properties of HNFx keratinase highlight its biotechnological and industrial significance for the development of eco-friendly bioprocesses.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets analyzed in the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The nucleotide sequence of the Sphingobacterium multivorum HNFx was deposited in NCBI GenBank and could be accessed through the accession number MW165488.
Abbreviations
- BSM:
-
Basal salt media
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- NCBI:
-
National Centre for Biotechnology Information
- NEAA:
-
Nutritionally nonessential amino acids
- NPN:
-
Nonprotein nitrogen
- PCF:
-
Pulverized chicken feathers
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulphate
References
Abdel-Fattah AM, El-Gamal MS, Ismail SA, Emran MA, Hashem AM (2018) Biodegradation of feather waste by keratinase produced from newly isolated Bacillus licheniformis ALW1. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 16:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2018.05.005
Akhter M, Wal Marzan L, Akter Y, Shimizu K (2020) Microbial bioremediation of feather waste for keratinase production: an outstanding solution for leather dehairing in tanneries. Microbiol Insights 13:1178636120913280. https://doi.org/10.1177%2F1178636120913280
Akram F, ul Haq I, Hayat AK, Ahmed Z, Jabbar Z, Baig IM, Akram R (2021) Keratinolytic enzyme from a thermotolerant isolate Bacillus sp. NDS-10: An efficient green biocatalyst for poultry waste management, laundry and hide-dehairing applications. Waste Biomass Valori 12:5001–5018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01369-2
Bach E, Daroit DJ, Corrêa APF, Brandelli A (2011) Production and properties of keratinolytic proteases from three novel Gram-negative feather-degrading bacteria isolated from Brazilian soils. Biodegradation 22:1191–1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-011-9474-0
Bach E, Sant’Anna V, Daroit DJ, Corrêa APF, Segalin J, Brandelli A (2012) Production, one-step purification, and characterization of a keratinolytic protease from Serratia marcescens P3. Process Biochem 47:2455–2462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.10.007. )
Benkiar A, Nadia ZJ, Badis A, Rebzani F, Soraya BT, Rekik H, Naili B, Ferradji FZ, Beja S, Jaouadi B (2013) Biochemical and molecular characterization of a thermo-and detergent-stable alkaline serine keratinolytic protease from Bacillus circulans strain DZ100 for detergent formulations and feather-biodegradation process. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 83:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.05.014
Bezus B, Ruscasso F, Garmendia G, Vero S, Cavello I, Cavalitto S (2021) Revalorization of chicken feather waste into a high antioxidant activity feather protein hydrolysate using a novel psychrotolerant bacterium. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 32:101925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.101925
Bokveld A, Nnolim NE, Digban TO, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2021) Chryseobacterium aquifrigidense keratinase liberated essential and nonessential amino acids from chicken feather degradation. Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2021.1969597
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Caussette M, Planche H, Delepine S, Monsan P, Gaunand A, Lindet B (1997) The self-catalytic enzyme inactivation induced by solvent stirring: a new example of protein conformational change induction. Protein Eng Des Sel 10:1235–1240. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/10.10.1235
Colombo M, Girard E, Franzetti B (2016) Tuned by metals: the TET peptidase activity is controlled by 3 metal binding sites. Sci Rep 6:20876. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20876
Cope RB (2018) Nonprotein nitrogen (urea) and hyperammonemia. In: Gupta RC (ed) Veterinary Toxicology. Academic Press, pp 1093–1097
Daroit DJ, Brandelli A (2014) A current assessment on the production of bacterial keratinases. Crit Rev Biotechnol 34:372–384. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2013.794768
DeVries JW, Koski CM, Egberg DC, Larson PA (1980) Comparison between a spectrophotometric and a high-pressure liquid chromatography method for determining tryptophan in food products. J Agric Food Chem 28:896–898. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60231a025
Einarsson S, Josefsson B, Lagerkvist S (1983) Determination of amino acids with 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 282:609–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(00)91638-8
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Emran MA, Ismail SA, Abdel-Fattah AM (2020) Valorization of feather via the microbial production of multi-applicable keratinolytic enzyme. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 27:101674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101674
Friedrich AB, Antranikian G (1996) Keratin degradation by Fervidobacterium pennavorans, a novel thermophilic anaerobic species of the order Thermotogales. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2875–2882. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.62.8.2875-2882.1996
Gehrke CW, Wall Sr LL, Absheer JS, Kaiser FE, Zumwalt RW (1985) Sample preparation for chromatography of amino acids: acid hydrolysis of proteins. J AOAC Int 68:811–821. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/68.5.811
Hendrick Q, Nnolim NE, Nwodo UU (2021) Chryseobacterium cucumeris FHN1 keratinolytic enzyme valorized chicken feathers to amino acids with polar, anionic and non-polar imino side chain characteristics. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 35:102109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102109
Jagadeesan Y, Meenakshisundaram S, Saravanan V, Balaiah A (2020) Sustainable production, biochemical and molecular characterization of thermo-and-solvent stable alkaline serine keratinase from novel Bacillus pumilus AR57 for promising poultry solid waste management. Int J Biol Macromol 163:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.219
Jeong JH, Jeon YD, Lee OM, Kim JD, Lee NR, Park GT, Son HJ (2010a) Characterization of a multifunctional feather-degrading Bacillus subtilis isolated from forest soil. Biodegradation 21:1029–1040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9363-y
Jeong JH, Park KH, Oh DJ, Hwang DY, Kim HS, Lee CY, Son HJ (2010b) Keratinolytic enzyme-mediated biodegradation of recalcitrant feather by a newly isolated Xanthomonas sp. P5. Polym Degrad Stab 95:1969–1977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.07.020
Habbeche A, Saoudi B, Jaouadi B, Haberra S, Kerouaz B, Boudelaa M, Badis A, Ladjama A (2014) Purification and biochemical characterization of a detergent-stable keratinase from a newly thermophilic actinomycete Actinomadura keratinilytica strain Cpt29 isolated from poultry compost. J Biosci Bioeng 117:413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.09.006
Kaewsalud T, Yakul K, Jantanasakulwong K, Tapingkae W, Watanabe M, Chaiyaso T (2020) Biochemical characterization and application of thermostable-alkaline keratinase from Bacillus halodurans SW-X to valorize chicken feather wastes. Waste Biomass Valori 12:3951–3964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01287-9
Kowalczyk P, Mahdi-Oraibi S, Misiewicz A, Gabzdyl N, Miskiewicz A, Szparecki G (2018) Feather-degrading bacteria: their biochemical and genetic characteristics. Arab J Sci Eng 43:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2700-2
Kshetri P, Ningthoujam DS (2016) Keratinolytic activities of alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. MBRL 575 from a novel habitat, limestone deposit site in Manipur, India. SpringerPlus 5:595. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2239-9
Kshetri P, Roy SS, Chanu SB, Singh TS, Tamreihao K, Sharma SK, Ansari MA, Prakash N (2020) Valorization of chicken feather waste into bioactive keratin hydrolysate by a newly purified keratinase from Bacillus sp. RCM-SSR-102. J Environ Manage 273:111195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111195
Kshetri P, Roy SS, Sharma SK, Singh TS, Ansari MA, Prakash N, Ngachan SV (2019) Transforming chicken feather waste into feather protein hydrolysate using a newly isolated multifaceted keratinolytic bacterium Chryseobacterium sediminis RCM-SSR-7. Waste Biomass Valori 10:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0037-4
Li Q (2021) Structure, application and biochemistry of Microbial Keratinases. Front Microbiol 12:674345. https://dx.doi.org/10.3389%2Ffmicb.2021.674345
Longo MA, Combes D (1998) Analysis of the thermal deactivation kinetics of α-chymotrypsin modified by chemoenzymatic glycosylation. In: Ballesteros, A., Plou, F.J., Iborra, J.U., Hailing, P.J., (Eds), Progress in Biotechnology, Elsevier pp. 135–140
Nam GW, Lee DW, Lee HS, Lee NJ, Kim BC, Choe EA, Hwang JK, Suhartono MT, Pyun YR (2002) Native-feather degradation by Fervidobacterium islandicum AW-1, a newly isolated keratinase-producing thermophilic anaerobe. Arch Microbiol 178:538–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-002-0489-0
Nnolim NE, Nwodo UU (2020) Bacillus sp. CSK2 produced thermostable alkaline keratinase using agro-wastes: keratinolytic enzyme characterization. BMC Biotechnol 20:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-020-00659-2
Nnolim NE, Nwodo UU (2021) Microbial keratinase and the bio-economy: a three-decade meta-analysis of research exploit. AMB Express 11:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-020-01155-8
Nnolim NE, Mpaka L, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2020b) Biochemical and molecular characterization of a thermostable alkaline metallo-keratinase from Bacillus sp. Nnolim-K1. Microorganisms 8:1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091304
Nnolim NE, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2021) Elucidation of coding gene and characterization of alkaline metallo-keratinase produced by acidophilic Bacillus sp. Okoh-K1 grown on chicken feather. Environ Technol Innov 21:101285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101285
Nnolim NE, Udenigwe CC, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2020a) Microbial keratinase: Next generation green catalyst and prospective applications. Front Microbiol 11:3280. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.580164
Park GT, Son HJ (2009) Keratinolytic activity of Bacillus megaterium F7-1, a feather-degrading mesophilic bacterium. Microbiol Res 164:478–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2007.02.004
Phang JM, Liu W, Hancock C (2013) Bridging epigenetics and metabolism: role of nonessential amino acids. Epigenetics 8:231–236. https://doi.org/10.4161/epi.24042
Prejanò M, Alberto ME, Russo N, Toscano M, Marino T (2020) The effects of the metal ion substitution into the active site of metalloenzymes: A theoretical insight on some selected cases. Catalysts 10:1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091038
Riffel A, Brandelli A, Bellato CDM, Souza GH, Eberlin MN, Tavares FC (2007) Purification and characterization of a keratinolytic metalloprotease from Chryseobacterium sp. kr6. J Biotechnol 128:693–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.11.007
Sharma I, Kango N (2021) Production and characterization of keratinase by Ochrobactrum intermedium for feather keratin utilization. Int J Biol Macromol 166:1046–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.260
Sharma KM, Kumar R, Panwar S, Kumar A (2017) Microbial alkaline proteases: Optimization of production parameters and their properties. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 15:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2017.02.001
Srivastava B, Khatri M, Singh G, Arya SK (2020) Microbial keratinases: an overview of biochemical characterization and its eco-friendly approach for industrial applications. J Clean Prod 252:119847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119847. )
Tallentire CW, Mackenzie SG, Kyriazakis I (2018) Can novel ingredients replace soybeans and reduce the environmental burdens of European livestock systems in the future? J Clean Prod 187:338–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.212
Thankaswamy SR, Sundaramoorthy S, Palanivel S, Ramudu KN (2018) Improved microbial degradation of animal hair waste from leather industry using Brevibacterium luteolum (MTCC 5982). J Clean Prod 189:701–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.095
Thys RCS, Brandelli A (2006) Purification and properties of a keratinolytic metalloprotease from Microbacterium sp. J Appl Microbiol 101:1259–1268. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03050.x
Tian J, Xu Z, Long X, Tian Y, Shi B (2019) High-expression keratinase by Bacillus subtilis SCK6 for enzymatic dehairing of goatskins. Int J Biol Macromol 135:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.131
Tiwary E, Gupta R (2010) Medium optimization for a novel 58 kDa dimeric keratinase from Bacillus licheniformis ER-15: biochemical characterization and application in feather degradation and dehairing of hides. Bioresour Technol 101:6103–6110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.090
Tong X, Lian Z, Miao L, Qi B, Zhang S, Li Y, Wang H, Jiang L (2020) An innovative two-step enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction for the production of reduced bitterness soybean protein hydrolysates with high nutritional value. LWT 134:110151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110151
Tork SE, Shahein YE, El-Hakim AE, Abdel-Aty AM, Aly MM (2013) Production and characterization of thermostable metallo-keratinase from newly isolated Bacillus subtilis NRC 3. Int J Biol Macromol 55:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.01.002
Venkatachalam M, Rathinam A, Rao JR, Krishnan C (2021) Bioconversion of animal hair waste using salt-and sulphide-tolerant Bacillus sp. KLP1 and depilation using keratinase. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03437-5
Wang SL, Hsu WT, Liang TW, Yen YH, Wang CL (2008) Purification and characterization of three novel keratinolytic metalloproteases produced by Chryseobacterium indologenes TKU014 in a shrimp shell powder medium. Bioresour Technol 99:5679–5686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.10.024
Wu G (2014) Dietary requirements of synthesizable amino acids by animals: a paradigm shift in protein nutrition. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 5:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-1891-5-34
Yusuf I, Ahmad SA, Phang LY, Syed MA, Shamaan NA, Khalil KA, Dahalan FA, Shukor MY (2016) Keratinase production and biodegradation of polluted secondary chicken feather wastes by a newly isolated multi heavy metal tolerant bacterium- Alcaligenes sp. AQ05-001. J Environ Manage 183:182–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.059
Zhang RX, Gong JS, Zhang DD, Su C, Hou YS, Li H, Shi JS, Xu ZH (2016) A metallo-keratinase from a newly isolated Acinetobacter sp. R-1 with low collagenase activity and its biotechnological application potential in leather industry. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1503-7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Industrial Biocatalysis Hub, funded by the Department of Science and Innovation and the Technology Innovation Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Uchechukwu Nwodo and Nonso Nnolim; Methodology: Qaphela Hendrick and Nonso Nnolim; Formal analysis and investigation: Nonso Nnolim and Nolonwabo Nontongana; Writing - original draft preparation: Qaphela Hendrick and Nonso Nnolim; Writing - review and editing: Uchechukwu Nwodo; Resources and Supervision: Uchechukwu Nwodo. The authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animal experiments.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hendrick, Q., Nnolim, N.E., Nontongana, N. et al. Sphingobacterium multivorum HNFx produced thermotolerant and chemostable keratinase on chicken feathers. Biologia 77, 2921–2931 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01126-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01126-3