Abstract
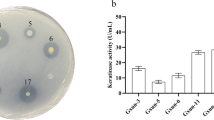
In this study, we isolated and characterized a novel feather-degrading bacterium that shows keratinolytic, antifungal and plant growth-promoting activities. A bacterium S8 was isolated from forest soil and confirmed to belong to Bacillus subtilis by BIOLOG system and 16S rRNA gene analysis. The improved culture conditions for the production of keratinolytic protease were 0.1% (w/v) sorbitol, 0.3% (w/v) KNO3, 0.1% (w/v) K2HPO4, 0.06% (w/v) KH2PO4 and 0.04% (w/v) MgCl2·6H2O (pH 8.0 and 30°C), respectively. In the improved medium containing 0.1% (w/v) feather, keratinolytic protease production was around 53.3 ± 0.3 U/ml at 4 day; this value was 10-fold higher than the yield in the basal feather medium (5.3 ± 0.1 U/ml). After cultivation for 5 days in the improved medium, intact feather was completely degraded. Feather degradation resulted in free –SH group, soluble protein and amino acids production. The concentration of free –SH group in the culture medium was 15.5 ± 0.2 μM at 4 days. Nineteen amino acids including all essential amino acids were produced in the culture medium; the concentration of total amino acid produced was 3360.4 μM. Proline (2809.9 μM), histidine (371.3 μM) and phenylalanine (172.0 μM) were the major amino acids released in the culture medium. B. subtilis S8 showed the properties related to plant growth promotion: hydrolytic enzymes, ammonification, indoleacetic acid (IAA), phosphate solubilization, and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Interestingly, the strain S8 grown in the improved medium produced IAA and antifungal activity, indicating simultaneous production of keratinolytic and antifungal activities and IAA by B. subtilis S8. These results suggest that B. subtilis S8 could be not only used to improve the nutritional value of feather wastes but also is useful in situ biodegradation of feather wastes. Furthermore, it could also be a potential biofertilizer or biocontrol agent applicable to crop plant soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FA, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Smith J, Seidman JG, Struhl K (1988) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York
Böckle B, Müller R (1997) Reduction of disulfide bonds by Streptomyces pactum during growth on chicken feathers. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:790–792
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chernin L, Ismailov Z, Haran S, Chet I (1995) Chitinolytic Enterobacter agglomerans antagonistic to fungal plant pathogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1720–1726
Clesscerl LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA-AWWA-WEF, Washington, DC
Daroit DJ, Correa APF, Brandelli A (2009) Keratinolytic potential of a novel Bacillus sp. P45 isolated from the Amazon basin fish Piaractus mesopotamicus. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:358–363
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Fisher SH, Sonenshein AL (1991) Control of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Microbiol 45:107–135
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Wester EW (1981) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, New York
Ghosh A, Chakrabarti K, Chattopadhyay D (2008) Degradation of raw feather by a novel high molecular weight extracellular protease from newly isolated Bacillus cereus DCUW. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:825–834
Gioppo NM da R, Moreira-Gasparin FG, Costa AM, Alexandrino AM, de Souza CGM, Peralta RM (2009) Influence of the carbon and nitrogen sources on keratinase production by Myrothecium verrucaria in submerged and solid state cultures. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:705–711
Gupta R, Singal R, Shankar A, Kuhad RC, Saxena RK (1994) A modified plate assay for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. J Gen Appl Microbiol 40:255–260
Hadas A, Kautsky L (1994) Feather meal, a semi-slow-release nitrogen fertilizer for organic farming. Fertilizer Res 38:165–170
Haddar HO, Zaghloul TI, Saeed HM (2009) Biodegradation of native feather keratin by Bacillus subtilis recombinant strains. Biodegradation 20:687–694
Harrap BS, Woods EF (1964) Soluble derivatives of feather keratin. Biochem J 92:8–18
Ignatova Z, Gousterova A, Spassov G, Nedkov P (1999) Isolation and partial characterization of extracellular keratinase from a wool degrading thermophilic actinomycetes strain Thermoactinomyces. Can J Microbiol 45:217–222
Langeveld JPM, Wang JJ, Van de Wiel DFM, Shih GC, Garssen GJ, Bossers A, Shih JCH (2003) Enzymatic degradation of prion protein in brain stem from infected cattle and sheep. J Infect Dis 188:1782–1789
Lee YJ, Kim JH, Kim HK, Lee JS (2004) Production and characterization of keratinase from Paracoccus sp. WJ-98. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 9:17–22
Lin X, Lee C, Casale ES, Shih JCH (1992) Purification and characterization of a keratinase from a feather degrading Bacillus licheniformis strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3271–3275
Lucy M, Reed E, Glick BR (2004) Applications of free living plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 86:1–25
Matsui T, Yamada Y, Mitsuya H, Shigeri Y, Yoshida Y, Saito Y, Matsui H, Watanabe K (2009) Sustainable and practical degradation of intact chicken feathers by cultivating a newly isolated thermophilic Meiothermus rubber H328. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:941–950
Mazzoto AM, Cedrola SML, Lins U, Rosado AS, Silva KT, Chaves JQ, Rabinovitch L, Zingali RB, Vermelho AB (2010) Keratinolytic activity of Bacillus subtilis AMR using human hair. Lett Appl Microbiol 50:89–96
Nautiyal CS (1999) An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 170:265–270
Onifade AA, Al-Sane NA, Al-Musallam AA, Al-Zarban S (1998) Potentials for biotechnological applications of keratin-degrading microorganisms and their enzymes for nutritional improvement of feathers and other keratins as livestock feed resources. Bioresour Technol 66:1–11
Papadoulos MC, Ketelaars EH (1986) Effects of processing time and moisture content on amino acid composition and nitrogen characteristics of feather meal. Anim Feed Sci Technol 14:279–290
Park KH, Lee OM, Jung HI, Jeong JH, Jeon YD, Hwang DY, Lee CY, Son HJ (2010) Rapid solubilization of insoluble phosphate by a novel environmental stress-tolerant Burkholderia vietnamiensis M6 isolated from ginseng rhizospheric soil. Appl Micobiol Biotechnol 86:947–955
Pavlica DA, Hora TI, Bradshaw JJ, Skogerboe RK, Baker R (1978) Volatiles from soil influencing activities of soil fungi. Phytopathology 14:758–765
Rai SK, Mukherjee AK (2010) Statistical optimization of production, purification and industrial application of a laundry detergent and organic solvent-stable subtilisin-like serine protease (Alzwiprase) from Bacillus subtilis DM-04. Biochem Eng J 48:173–180
Rao MB, Tanksale AM, Ghatge MS, Deshpande VV (1998) Molecular and biotechnological aspects of microbial proteases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:597–635
Riffel A, Lucas F, Heeb P, Brandelli A (2003) Characterization of a new keratinolytic bacterium that completely degrades native feather keratin. Arch Microbiol 179:258–265
Rodriguez H, Reynaldo F (1999) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol Adv 17:319–339
Rozs M, Manczinger L, Vagvolgyi Cs, Kevei F, Hochkoeppler A, Rodriguez AGV (2001) Fermentation characteristics and secretion of proteases of a new keratinolytic strain of Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol Lett 23:1925–1929
Sangali S, Brandelli A (2000) Feather keratin hydrolysis by a Vibrio sp. strain kr2. J Appl Microbiol 89:735–743
Shama G, Berwick PG (1991) Production of keratinolytic enzymes in a rotating frame bioreactor. Biotechnol Tech 5:359–362
Shoebitz M, Ribaudo CM, Pardo MA, Cantore ML, Ciampi L, Cura JA (2009) Plant growth promoting properties of a strain of Enterobacter ludwigii isolated from Lolium perenne rhizosphere. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1768–1774
Smit E, Leeflang P, Gommans S, van den Broek J, van Mil S, Wernars K (2001) Diversity and seasonal fluctuations of the dominant members of the bacterial soil community in a wheat field as determined by cultivation and molecular methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2284–2291
Sommer P, Bormann C, Gotz F (1997) Genetic and biochemical characterization of a new extracellular lipase from Streptomyces cinnamomeus. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3553–3560
Tang YW, Bonner J (1947) The enzymatic inactivation of indoleacetic acid I. Some characteristics of the enzyme contained in pea seedlings. Arch Biochem 13:17–25
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Trivedi P, Pandy A, Palni LM (2008) In vitro evaluation of antagonistic properties of Pseudomonas corrugata. Microbiol Res 163:329–336
Wawrzkiewicz K, Lobarzewski J, Wolski T (1987) Intracellular keratinase of Trichophton gallinae. J Med Vet Mycol 25:261–268
Williams CM, Richter CS, Mackenzie JM, Shih JCH (1990) Isolation, identification and characterization of a feather-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1509–1515
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, JH., Jeon, YD., Lee, OM. et al. Characterization of a multifunctional feather-degrading Bacillus subtilis isolated from forest soil. Biodegradation 21, 1029–1040 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9363-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9363-y