Abstract
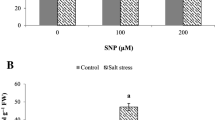
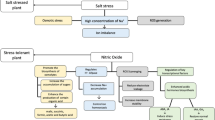
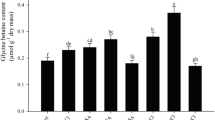
Sodium nitroprusside (SNP), as a nitric oxide (NO) donor, has well-documented properties for increasing plant tolerance to environmental stresses such as salinity. Here, we evaluated the effect of SNP (0, 50 and 100 µM) on growth, metabolism of chlorophyll, proline and glutathione (GSH), ionic homeostasis, nitrate reductase, the antioxidant defense system and the glyoxalase system in pot marigold (Calendula officinalis) under NaCl (0, 50, 100 and 150 mM) treatments. The results showed that 100 and 150 mM NaCl reduced photosynthetic pigments and plant growth by diminishing nutrient uptake (K, Ca, P and N) and disrupting ionic homeostasis as well as increasing the levels of toxic compounds (hydrogen peroxide, methylglyoxal and superoxide anion) and inducing oxidative stress. SNP application improved the performance of photosynthetic apparatus and increased the plant growth and biomass under salinity by modulating chlorophyll metabolism. SNP also increased proline and GSH and improved plant salinity tolerance by inducing proline and GSH metabolisms. SNP increased the K/Na ratio and maintained ion homeostasis under salinity by decreasing the uptake of Na and Cl and increasing the uptake of K, P, N and Ca. By inducing the activity of enzymes involved in the antioxidant defense system and the glyoxalase system, SNP diminished the level of toxic compounds and mitigated oxidative stress under salinity. Our results revealed that concentrations of more than 100 mM NaCl can induce salt stress in pot marigolds; however, the exogenous application of SNP as a stress alleviator can improve pot marigold tolerance under salinity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraf M, Foolad MA (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.12.006
Baniasadi F, Saffari VR, Maghsoudi Moud AA (2018) Physiological and growth responses of Calendula officinalis L. plants to the interaction effects of polyamines and salt stress. Sci Hortic 234:312–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.02.069
Bates LS, Walden RT, Tearse ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Botella MA, Martínez V, Nieves M, Cerdá A (1997) Effect of salinity on the growth and nitrogen uptake by wheat seedlings. J Plant Nutr 20(6):793–804. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169709365295
Campbell HW (1999) Nitrate reductase structure, function and regulation: bridging the gap between biochemistry and physiology. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:277–303. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.277
Costa ML, Civello PM, Chaves AR, Martínez GA (2005) Effect of ethephon and 6–benzylaminopurine on chlorophyll degrading enzymes and a peroxidase–linked chlorophyll bleaching during post–harvest senescence of broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.) at 20 C. Postharvest Biol Technol 35(2):191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2004.07.007
Dagmar P, Sairam RK, Srivastava GC, Singh DV (2001) Oxidative stress and antioxidant activity as the basis of senescence in maize leaves. Plant Sci 161:765–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00462-9
Del Rio LA, Corpas FJ, Barroso JB (2004) Nitric oxide and nitric oxide synthase activity in plants. Phytochemistry 65:783–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.02.001
Diao Q, Cao Y, Fan H, Zhang Y (2020) Transcriptome analysis deciphers the mechanisms of exogenous nitric oxide action on the response of melon leaves to chilling stress. Biol Plant 64:465–472. https://doi.org/10.32615/bp.2020.021
Dole JM, Wilkins HF (2005) Floriculture: Principles and Species, 2nd edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, pp 347
El-Shabrawi H, Kumar B, Kaul T, Reddy MK, Singla-Pareek SL, Sopory SK (2010) Redox homeostasis, antioxidant defense, and methylglyoxal detoxification as markers for salt tolerance in Pokkali rice. Protoplasma 245:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-010-0144-6
Farnese FS, Oliveira JA, Gusman GS, Leão GA, Silveira NM, Silva PM, Ribeiro C, Cambraia J (2014) Effects of adding nitroprusside on arsenic stressed response of Pistia stratiotes L. under hydroponic conditions. Int J Phytoremediation 16(2):123–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2012.759532
Gaitonde MK (1967) A spectrophotometric method for the direct determination of cysteine in the presence of other naturally occurring amino acids. Biochem J 104:627–633. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1040627
Garcia-Rios M, Fujita T, LaRosa PC, Locy RD, Clithero JM, Bressan RA, Csonka LN (1997) Cloning of a polycistronic cDNA from tomato encoding -glutamyl kinase and -glutamyl phosphate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8249–8254. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.15.8249
Ghadakchiasl A, Mozafari AA, Ghaderi N (2017) Mitigation by sodium nitroprusside of the effects of salinity on the morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics of Rubus idaeus under in vitro conditions. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23(1):73–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-016-0396-5
Ghasemi-Omran VO, Ghorbani A, Sajjadi-Otaghsara SA (2021) Melatonin alleviates NaCl-induced damage by regulating ionic homeostasis, antioxidant system, redox homeostasis, and expression of steviol glycosides-related biosynthetic genes in in vitro cultured Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 57:319–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-021-10161-9
Ghorbani A, Razavi SM, Ghasemi Omran VO, Pirdashti H (2018a) Piriformospora indica alleviates salinity by boosting redox poise and antioxidative potential of tomato. Russ J Plant Physiol 65:898–907. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443718060079
Ghorbani A, Razavi SM, Ghasemi Omran VO, Pirdashti H (2018b) Piriformospora indica inoculation alleviates the adverse effect of NaCl stress on growth, gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Biol 20:729–736. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12717
Ghorbani A, Ghasemi Omran VO, Razavi SM, Pirdashti H, Ranjbar M (2019) Piriformospora indica confers salinity tolerance on tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) through amelioration of nutrient accumulation, K+/Na+ homeostasis and water status. Plant Cell Rep 38:1151–1163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02434-w
Ghorbani A, Pishkar L, Roodbari N, Pehlivan N, Wu C (2021) Nitric oxide could allay arsenic phytotoxicity in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by modulating photosynthetic pigments, phytochelatin metabolism, molecular redox status and arsenic sequestration. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:337–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.08.019
Ghorbani A, Pishkar L, Roodbari N, Tavakoli SA, Moein Jahromi E, Wu C (2022) Nitrate reductase is needed for methyl jasmonate-mediated arsenic toxicity tolerance of rice by modulating the antioxidant defense system, glyoxalase system and arsenic sequestration mechanism. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10616-2
Ghorbani A, Tafteh M, Roudbari N, Pishkar L, Zhang W, Wu C (2020) Piriformospora indica augments arsenic tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) by immobilizing arsenic in roots and improving iron translocation to shoots. Ecotoxicol Environmen Saf 209:111793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111793
Gill RA, Ali B, Islam F, Farooq MA, Gill MB, Mwamba TM, ZhouW (2015) Physiological and molecular analyses of black and yellow seeded Brassica napus regulated by 5-aminolivulinic acid under chromium stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 94:130–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.06.001
Hameed A, Farooq T, Hameed A, Sheikh MA (2021) Sodium nitroprusside mediated priming memory invokes water-deficit stress acclimation in wheat plants through physio-biochemical alterations. Plant Physiol Biochem 160:329–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.01.037
Hasanuzzaman M, Hossain MA, Fujita M (2012) Exogenous selenium pretreatment protects rapeseed from cadmium-induced oxidative stress by upregulating antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification systems. Biol Trace Elem Res 149:248–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9419-4
Hayat S, Yadav S, Wani AS, Irfan M, Alyemini MN, Ahmad A (2012) Impact of sodium nitroprusside on nitrate reductase, proline content, and antioxidant system in tomato under salinity stress. Hort Environ Biotechnol 53(5):362–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-012-0481-9
Hopkins WJ (1995) Introduction to plant physiology. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York
Jabeen Z, Fayyaz HA, Irshad F, Hussain N, Hassan MN, Li J, Hassan MN, Li J, Rehman S, Haider W, Yasmin H, Mumtaz S, Bukhari SAH, Khalofah A, Al- Qthanin RN, Alsubeie MS (2021) Sodium nitroprusside application improves morphological and physiological attributes of soybean (Glycine max L.) under salinity stress. PLoS ONE 16(4):e0248207. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248207
Jackson ML (1967) Soil chemical analysis, 1st edn. Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, pp 144–197
Jain A, Srivastava HS (1981) Effect of salicylic acid on nitrate reductase activity in maize seedlings. Physiol Plant 51:339–342. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1981.tb05565.x
Jain M, Gadre R (2004) Inhibition of 5-amino levulinic acid dehydratase activity by arsenic in excised etiolated maize leaf segments during greening. J Plant Physiol 161:251–255. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00879
Jez JM, Cahoon RE, Chen S (2004) Arabidopsis thaliana glutamate-cysteine ligase. J Biol Chem 279(32):33463–33470. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M405127200
Ji T, Li S, Huang M, Di Q, Wang X, Wei M, Shi Q, Li Y, Gong B, Yang F (2017) Overexpression of Cucumber Phospholipase D alpha Gene (CsPLDα) in tobacco enhanced salinity stress tolerance by regulating Na+/K+ balance and lipid peroxidation. Front Plant Sci 8:499. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00499
Kay CJ, Barber MJ (1986) Assimilatory nitrate reductase from Chlorella: Effect of ionic strength and pH on catalytic activity. J Biol Chem 261:14125–14129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)66991-1
Kaya C (2021) Nitrate reductase is required for salicylic acid-induced water stress tolerance of pepper by upraising the AsA-GSH pathway and glyoxalase system. Physiol Plant 172:351–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13153
Kaya C, Ashraf M, Sonmez O (2015) Exogenously applied nitric oxide confers tolerance to salinity-induced oxidative stress in two maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars differing in salinity tolerance. Turk J Agric For 39:909–919. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1411-26
Ke DS, Wang AG, Sun GC, Dong LF (2002) The effect of active oxygen on the activity of ACC synthase induced by exogenous IAA. Acta Bot Sin 44:551–556
Kitson R, Mellon M (1944) Colorimetric determination of phosphorus as molybdivanado phosphonic acid. Ind Eng Chem Res 16:379–383. https://doi.org/10.1021/i560130a017
Kram NA, Hafeez N, Farid-ul-Haq M, Ahmad A, Sadiq M, Ashraf M (2020) Foliage application and seed priming with nitric oxide causes mitigation of salinity-induced metabolic adversaries in broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.) plants. Acta Physiol Plant 42:155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03140-x
Lee HJ, Lee JH, Lee SG, An S, Lee HS, Choi CK, Kim SK (2019) Foliar application of biostimulants affects physiological responses and improves heat stress tolerance in Kimchi cabbage. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 60:841–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00193-x
Lei Y, Yin C, Ren J, Li C (2007) Effect of osmotic stress and sodium nitroprusside pretreatment on proline metabolism of wheat seedlings. Biol Plant 51:386–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0082-0
Lichtenthaler HK, Buschmann C (2001) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: measurement and characterization by UV–VIS spectroscopy. Curr Protoc Food Anal Chem 1:F4–F13. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142913.faf0403s01
Mohsenzadeh S, Zohrabi M (2018) Auxin and sodium nitroprusside effects on wheat antioxidants in salinity. Russ J Plant Physiol 65:651–657. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443718050138
Monsur MB, Ivy NA, Haque MM, Hasanuzzaman M, EL-Sabagh A, Rohman MM (2020) Oxidative stress tolerance mechanism in rice under salinity. Phyton Int J Exp Bot 89:497–517. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2020.09144
Muley BP, Khadabadi SS, Banarase Muley NB (2009) Phytochemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Calendula officinalis Linn (Asteraceae): A Review. Trop J Pharm Res 8:455–465. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v8i5.48090
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a076232
Principato GB, Rosi G, Talesa V, Govannini E, Uolila L (1987) Purification and characterization of two forms of glyoxalase II from rat liver and brain of Wistar rats. Biochem Biophys Acta 911:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4838(87)90076-8
Ramadan AA, Abd Elhamid EM, Sadak MS (2019) Comparative study for the effect of arginine and sodium nitroprusside on sunflower plants grown under salinity stress conditions. Bull Natl Res Cent 43:118. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0156-0
Ramezani M, Enayati M, Ramezani M, Ghorbani A (2021) A study of different strategical views into heavy metal (oid) removal in the environment. Arab J Geosci 14:2225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08572-4
Rena AB, Splittstoesser WE (1975) Proline dehydrogenase and pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase from pumpkin cotyledons. Phytochemistry 14:657–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(75)83010-X
Sun C, Lu L, Liu L, Liu W, Yu Y, Liu X, Lin X (2014) Nitrate reductase-mediated early nitric oxide burst alleviates oxidative damage induced by aluminum through enhancement of antioxidant defenses in roots of wheat (Triticum aestivum). New Phytol 201(4):1240–1250. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12597
Wang L, Liu X, Liang M, Tan F, Liang W, Chen Y, Lin Y, Huang L, Xing J, Chen W (2014) Proteomic analysis of salt-responsive proteins in the leaves of mangrove Kandelia candel during short-term stress. PLoS ONE 9(1):e83141. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083141
Wendehenne D, Pugin A, Klessig DF, Durner J (2001) Nitric oxide: comparative synthesis and signaling in animal and plant cells. Trends Plant Sci 6:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(01)01893-3
Wild R, Ooi L, Srikanth V, Münch G (2012) A quick, convenient and economical method for the reliable determination of methylglyoxal in millimolar concentrations: The N-acetyl-L-cysteine assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:2577–2581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6086-4
Xu Z, Pehlivan N, Ghorbani A, Wu C (2022) Effects of Azorhizobium caulinodans and Piriformospora indica co-inoculation on growth and fruit quality of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) under salt stress. Horticulturae 8(4):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8040302
Yang Y, Guo Y (2018) Unravelling salt signaling in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 60:796–804. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12689
Yu X, Sukumaran S, Marton L (2001) Differential expression of the Arabidopsis Nia1 and Nia2 genes cytokinin-induced nitrate reductase. Plant Physiol 116:1091–1096. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.116.3.1091
Zhangyuan D, Bramlage WJ (1992) Modified thiobarbituric acid assay for measuring lipid oxidation in sugar-rich plant tissue extracts. J Agric Food Chem 40:1566–1570. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00021a018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzin, G., Kazemi, M.M. & Entezari, M. The interaction effects of NaCl stress and sodium nitroprusside on growth, physiological and biochemical responses of Calendula officinalis L. Biologia 77, 2081–2091 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01068-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01068-w