Abstract
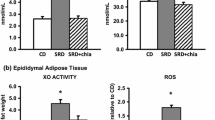
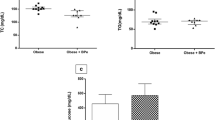
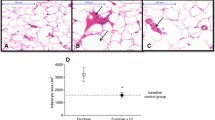
The objective of this study was to evaluate the status of the markers related to inflammation in db/db mice fed black raspberry seed (BRS) oil, which is rich in α-linolenic acid. Mice were divided into four groups: (1) C57BL/6 mice fed 16 % calories from soybean oil (normal CON); (2) C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice fed 16 % calories from soybean oil (CON); (3) C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice fed 8 % calories from soybean and 8 % calories from BRS oil (BRS 50 %); and (4) C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice fed 16 % calories from BRS oil (BRS 100 %). After 10 weeks, n-6/n-3 fatty acid ratios were significantly (P < 0.05) lower in the livers and epididymal adipose tissues of the BRS 50 % and BRS 100 % mice than in the CON. Serum TNFα and IL-6 were significantly (P < 0.05) lower in the BRS 50 % and BRS 100 % than in the CON. Serum IL-10 was significantly (P < 0.05) higher in the BRS 100 % than the CON. In the liver and epididymal adipose tissue, mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory markers in the BRS 50 % and BRS 100 % were lower than in the CON. Anti-inflammatory markers were higher in the epididymal adipose tissues of the BRS 50 % and BRS 100 % than in the CON. In the epididymal adipose tissue, macrophage infiltration markers (F4/80 and CD68) and leptin mRNA were significantly (P < 0.05) lower in the BRS 50 % and BRS 100 % than in the CON. Results of this study suggest that BRS oil may have anti-inflammatory effects in obese diabetic mice by ameliorating inflammatory responses.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALA:
-
Alpha linolenic acid
- ARA:
-
Arachidonic acid
- CCR2:
-
C–C motif chemokine receptor 2
- CD:
-
Cluster of differentiation
- Chi3l3:
-
Chitinase 3-like 3
- COX2:
-
Cyclooxygenase 2
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- MCP1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- Mgl1:
-
Macrophage galactose N-acetyl-galactosamine-specific lectin-1
- MUFA:
-
Monounsaturated fatty acid
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
References
Oh HH, Hwang KT, Shin MK, Lee HK, Kim SZ (2007) Oils in the seeds of caneberries produced in Korea. J Amer Oil Chem Soc 84:549–555
Adhikari P, Hwang KT, Shin MK, Lee BK, Kim SK, Kim SY, Lee K, Lim SZ (2008) Tocols in caneberry seed oils. Food Chem 111:687–690
González-Périz A, Horrillo R, Ferré N, Gronert K, Dong B, Morán-Salvador E, Titos E, Martínez-Clemente M, López-Parra M, Arroyo V, Clària J (2009) Obesity-induced insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis are alleviated by ω-3 fatty acids: a role for resolvins and protectins. FASEB J 23:1946–1957
Liu H, Qiu Y, Mu Y, Zhang X, Liu L, Hou X, Zhang L, Xu X, Ji A, Cao R, Yang R, Wang F (2012) A high ratio of dietary n-3/n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids improves obesity-linked inflammation and insulin resistance through suppressing activation of TLR4 in SD rats. Nutr Res 33:849–858
Yang LG, Song ZX, Yin H, Wang YY, Shu GF, Lu HX, Wang SK, Sun GJ (2016) Low n-6/n-3 PUFA ratio improves lipid metabolism, inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial function in rats using plant oils as n-3 fatty acid source. Lipids 51:49–59
Jangale NM, Devarshi PP, Dubal AA, Ghule AE, Koppikar SJ, Bodhankar SL, Chougale AD, Kulkarni MJ, Harsulkar AM (2013) Dietary flaxseed oil and fish oil modulates expression of antioxidant and inflammatory genes with alleviation of protein glycation status and inflammation in liver of streptozotocin–nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Food Chem 141:187–195
Chang HH, Chen CS, Lin JY (2008) Dietary perilla oil inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of ovalbumin-challenged mice. Lipids 43:499–506
Kalupahana NS, Claycombe K, Newman SJ, Stewart T, Siriwardhana N, Matthan N, Lichtenstein AH, Moustaid-Moussa N (2010) Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents and reverses insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice via modulation of adipose tissue inflammation. J Nutr 140:1915–1922
Clària J, González-Périz A, López-Vicario C, Rius B, Titos E (2011) New insights into the role of macrophages in adipose tissue inflammation and fatty liver disease: modulation by endogenous omega-3 fatty acid-derived lipid mediator. Front Immunol 49:1–8
Chan KC, Pen PJ, Yin M (2012) Anticoagulatory and antiinflammatory effects of astaxanthin in diabetic rats. J Food Sci 77:H76–H80
Nilsson E, Jansson PA, Perfilyev A, Volkov P, Pedersen M, Svensson MK, Poulsen P, Ribel-Madsen R, Pedersen NL, Almgren P, Fadista J, Rönn T, Pedersen BK, Scheele C, Vagag A, Ling C (2014) Altered DNA methylation and differential expression of genes influencing metabolism and inflammation in adipose tissue from subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 63:2962–2976
Kwon H, Pessin JE (2013) Adipokines mediate inflammation and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol 4:1–13
Lee HJ, Jung H, Cho HN, Hwang KT (2015) Anti-inflammatory effect of black raspberry seed oil in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J Food Biochem 39:612–621
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:912–917
Lee HJ, Jung H, Lee SR, Jeong JH, Lee MW, Hwang KT, Hwang I (2010) Fatty acid composition and oxidation of the lipids in sweetfish cultured in Korea. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 39:853–858
Simopoulos AP (2002) The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed Pharmacother 56:365–379
Perini JAL, Stevanato FB, Visentainer JEL, Sargi SC, Oliveira MM, Souza NE, Matsushita M, Visentainer JV (2011) Incorporation of n-3 fatty acids by the liver of mice fed linseed oil as a function of feeding duration. Braz Arch Biol Technol 54:307–313
Puppel K, Kuczyńska B, Nałęcz-Tarwacka T, Gołębiewski M, Sakowski T, Kapusta A, Budziński A, Balcerak M (2015) Effect of supplementation of cows diet with linseed and fish oil and different variants of β-lactoglobulin on fatty acid composition and antioxidant capacity of milk. J Sci Food Agric. doi:10.1002/jsfa.7341
Rustichelli C, Avallone R, Campioli E, Braghiroli D, Baraldi M (2012) Polyunsaturated fatty acid levels in rat tissues after chronic treatment with dietetic oils. J Sci Food Agric 92:239–245
Shi H, Kokoeva MV, Inouye K, Tzameli I, Yin H, Flier JS (2006) TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid–induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116:3015–3025
Siriwardhana N, Kalupahana NS, Fletcher S, Xin W, Claycombe KJ, Quignard-Boulange A, Zhao L, Saxton AM, Moustaid-Moussa N (2012) n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids differentially regulate adipose angiotensinogen and other inflammatory adipokines in part via NF-kB dependent mechanisms. J Nutr Biochem 23:1661–1667
Todoric J, Löffler M, Huber J, Bilban M, Reimers M, Kadl A, Zeyda M, Waldhäusl W, Stulnig TM (2006) Adipose tissue inflammation induced by high-fat diet in obese diabetic mice is prevented by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Diabetologia 49:2109–2119
Titos E, Bibiana R, González-Périz A, López-Vicario C, Morán-Salvador E, Martínez-Clemente M, Arroyo V, Clària J (2011) Resolvin D1 and its precursor docosahexaenoic acid promote resolution of adipose tissue inflammation by eliciting macrophage polarization toward an M2-like phenotype. J Immunol 187:5408–5418
Yoshihira T, Shimada K, Fukao K, Sai E, Sato-Okabayashi Y, Matsumori R, Shiozawa T, Alshahi H, Miyazaki T, Tada N, Daida H (2015) Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids suppress the development of aortic aneurysm through the inhibition of macrophage-mediated inflammation. Jpn Circulation J 79:1470–1478
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR (2007) Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest 117:175–184
Khazen W, M’Bika J, Tomkiewicz C, Benelli C, Chany C, Achour A, Forest C (2005) Expression of macrophage-selective markers in human and rodent adipocytes. FEBS Lett 579:5631–5634
Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K, Hiasa K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Miyachi H, Maeda S, Egashira K, Kasuga M (2006) MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J Clin Invest 116:1494–1505
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ, Walsh K (2011) Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:85–97
Ryo M, Nakamura T, Kihara S, Kumada M, Shibazaki S, Takahashi M, Nagai M, Matsuzawa Y, Funahash T (2004) Adiponectin as a biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. Circ J 68:975–981
Tapia G, Valenzuela R, Espinosa A, Romanque P, Dossi C, Gonzalez-Manán D, Videla LA, D’Espessailles A (2014) N-3 long-chain PUFA supplementation prevents high fat diet induced mouse liver steatosis and inflammation in relation to PPAR-α upregulation and NF-κB DNA binding abrogation. Mol Nutr Food Res 58:1333–1341
Yuan F, Wang H, Tian Y, He L, Liu Z (2016) Fish oil alleviated high-fat diet–induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via regulating hepatic lipid metabolism and metaflammation: a transcriptomic study. Lipids Health Dis 15:20
Han H, Ma H, Rong S, Chen L, Shan Z, Xu J, Zhang Y, Liu L (2015) Flaxseed oil containing flaxseed oil ester of plant sterol attenuates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in apolipoprotein-E knockout mice. J Funct Foods 13:169–182
Bushman BS, Phillips BP, Isbell T, Ou B, Crane JM, Knapp SJ (2004) Chemical composition of caneberry (Rubus spp.) seeds and oils and their antioxidant potential. J Agri Food Chem 52:7982–7987
Pieszka M, Tombarkiewicz B, Roman A, Migdal W, Niedziółka J (2013) Effect of bioactive substances found in rapeseed, raspberry and strawberry seed oils on blood lipid profile and selected parameters of oxidative status in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:1055–1062
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Mid-career Researcher Program through a National Research Foundation (Grant No. 20110010846) by Korean Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H.J., Jung, H., Cho, H. et al. Dietary Black Raspberry Seed Oil Ameliorates Inflammatory Activities in db/db Mice. Lipids 51, 715–727 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4159-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4159-4