Abstract
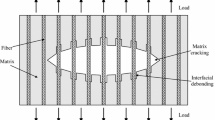
In this paper, the debonding of a single fiber-matrix system of carbon fiber reinforced composite (CFRP) AS4/Epson 828 material is studied using Cohesive Zone Model (CZM). The effect of parameters namely, maximum tangential contact stress, tangential slip distance and artificial damping coefficient on the debonding length at the interface of the fiber-matrix is analyzed. Contact elements used in the CZM are coupled based on a bilinear stress-strain curve. Load is applied on the matrix, tangential to the interface. Hence, debonding is observed primarily in Mode II.Wide range of values are considered to study the inter-dependency of the parameters and its effect on debonding length. Out of the three parameters mentioned, artificial damping coefficient and tangential slip distance significantly affect debonding length. A thorough investigation is recommended for case wise interface debonding analysis, to estimate the optimal parametric values while using CZM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pattabhi Ramaiah B, Rammohan B, Vijay Kumar S, Satish Babu D, Raghuatnhan R. Aero-elastic analysis of stiffened composite wing structure. Advances in Vibration Engineering, 2009, 8(3): 255–264
Sudhir Sastry Y B, Budarapu P R, Madhavi N, Krishna Y. Buckling analysis of thin wall stiffened composite panels. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 96(B): 459–471
Frolov V A. Strength of a composite material for structural applications. Mechanics of Composite Materials, 1987, 23(2): 148–154
Sudhir Sastry Y B, Budarapu P R, Krishna Y, Devaraj S. Studies on ballistic impact of the composite panels. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 72: 2–12
BP O’Rourke. The uses of composite materials in the design and manufacture of formula 1 racing cars. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 1990, 204: 41–48
Parga-Landa B, Hernández-Olivares F. Analytical model to predict behaviour of soft armours. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1995, 16(3): 455–466
Anderson C E Jr, Bodner S R. Ballistic impact: The status of analytical and material modeling. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1988, 7(1): 9–35
Naik N K, Shrirao P. Composite structures under ballistic impact. Composite Structures, 2004, 66(1-4): 579–590
James C. Leslie, The use of composite material increase the availability of oil and gas and reduce the cost of drilling and production operations. Proc. SPIE 6531, Nondestructive Characterization for Composite Materials, Aerospace Engineering, Civil Infrastructure, and Homeland Security, 65310E, 2007
Anderson C E Jr, Bodner S R. Ballistic impact: The status of analytical and material modeling. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1988, 7(1): 9–35
Naik N K, Shrirao P. Composite structures under ballistic impact. Composite Structures, 2004, 66(1–4): 579–590
Katz S, Grossman E, Gouzman I, Murat M, Wiesel E, Wagner H D. Response of composite materials to hypervelocity impact. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(12): 1606–1611
Budarapu P R, Narayana T S S, Rammohan B, Rabczuk T. Directionality of sound radiation from rectangular panels. Applied Acoustics, 2015, 89: 128–140
Scoutis C. Carbon fiber reinforced plastics in aircraft construction. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2005, 412(1–2): 171–176
Paipetis A S. Room vs. temperature studies of model composites: Modes of failure of carbon fibre/epoxy interfaces. Composite Interfaces, 2012, 19(2): 135–158
Xu Z, Li J, Wu X, Huang Y, Chen L, Zhang G. Effect of kidney-type and circular cross sections on carbon fiber surface and composite interface. Composites. Part A, Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2008, 39(2): 301–307
Zhao J, Ho K K C, Shamsuddin S R, Bismarck A, Dutschk V. A comparative study of fibre/matrix interface in glass fibre reinforced polyvinylidene fluoride composites. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem, Eng Asp, 2012, 413: 58–64
Nath R B, Fenner D N, Galiotis C. Progressional approach to interfacial failure in carbon reinforced composites: Elasto-plastic finite element modelling of interface cracks. Composites. Part A, Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2000, 31(9): 929–943
Kim B W, Nairn J A. Observations of fiber fracture and interfacial debonding phenomena using the fragmentation test in single fiber composites. Journal of Composite Materials, 2002, 36(15): 1825–1858
Ho H, Drzal L T. Non-linear numerical study of the single-fiber fragmentation test Part I: Test mechanics. Composites Engineering, 1995, 5(10–11): 1231–1244
Yang S W, Budarapu P R, Roy Mahapatra D, Bordas S, Rabczuk T. A meshless adaptive multiscale method for fracture. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 96(B): 382–395
Budarapu P R, Gracie R, Yang SW, Zhuang X, Rabczuk T. Efficient coarse graining in multiscale modelling of fracture. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 69: 126–143
Budarapu P R, Gracie R, Bordas S P A, Rabczuk T. An adaptive multiscale method for quasi-static crack growth. Computational Mechanics, 2014, 53(6): 1129–1148
Sudhir Sastry Y B, Krishna Y, Budarapu P R. Parametric studies on buckling of thin walled channel beams. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 96(B): 416–424
Budarapu P R, Yb S S, Javvaji B, Mahapatra D R. Vibration analysis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes embedded in elastic medium. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering, 2014, 8(2): 151–159
Xiao S P, Belytschko T. A bridging domain method for coupling continua with molecular dynamics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 193(17–20): 1645–1669
Rabczuk T, Samaniego E. Discontinuous modelling of shear bands using adaptive meshfree methods. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 197(6–8): 641–658
Rabczuk T, Gracie R, Song J H, Belytschko T. Immersed particle method for fluid–structure interaction. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2010, 81(1): 48–71
Robert G, Belytschko T. Concurrently coupled atomistic and XFEM models for dislocations and cracks. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2008, 78: 354–378
Rabczuk T, Rabczuk T, Zi G. A meshfree method based on the local partition of unity for cohesive cracks. Computational Mechanics, 2007, 39(6): 743–760
Rabczuk T, Bordas S P, Zi G. A three-dimensional meshfree method for continuous multiple-crack initiation, propagation and junction in statics and dynamics. Computational Mechanics, 2007, 40(3): 473–495
Bordas S P, Rabczuk T, Zi G. Three-dimensional crack initiation, propagation, branching and junction in non-linear materials by an extended meshfree method without asymptotic enrichment. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2008, 75(5): 943–960
Gracie R, Belytschko T. Adaptive continuum-atomistic simulations of dislocation dynamics. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2011, 86(4–5): 575–597
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T. A three dimensional large deformation meshfree method for arbitrary evolving cracks. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 196(29–30): 2777–2799
Rabczuk T, Areias P M A, Belytschko T. A simplified meshfree method for shear bands with cohesive surfaces. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2007, 69(5): 993–1021
Rabczuk T, Song J H, Belytschko T. Simulations of instability in dynamic fracture by the cracking particles method. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2009, 76(6): 730–741
Rabczuk T, Zi G, Bordas S P, Nguyen-Xuan H. A simple and robust threedimensional cracking-particle method without enrichment. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 199(37–40): 2437–2455
Turon A, Camanho P P, Costa J, Dávila C G. A damage model for the simulation of delamination in advanced composites under variable-mode loading, Mechanics of Materials, 2006, 38(11): 1072–1089
Irwin G R. Fracture. Handbuch der Physik. Flugge S, ed. Berlin: Springer, 1958, VI: 551–590
Rybicki E F, Kanninen M F. A finite element calculation of stress intensity factors by a modified crack closure integral. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1977, 9(4): 931–938
Shivakumar K N. Tan,PW. Newman, JC. A virtual crack-closure technique for calculating stress intensity factors for cracked three dimensional bodies. International Journal of Fracture, 1988, 36: R43–R50
Krueger R. Virtual crack closure technique: History, approach, and applications. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2004, 57(2): 109–143
Raju I S. Calculation of strain-energy release rates with higher order and singular finite elements. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1987, 28(3): 251–274
Rice J R. A path independent integral and the approximate analysis of strain concentration by notches and cracks. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1968, 35(2): 379–386
Hellen T K. On the method of virtual crack extensions. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1975, 9(1): 187–207
Parks D M. A stiffness derivative finite element technique of crack tip stress intensity factors. International Journal of Fracture, 1974, 10(4): 487–502
Griffith A A. The phenomenon of rupture and flow in solids. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1921, 221(582–593): 163–198
Turon A, Costa J, Camanho P P, Davila, C G. Simulation of delamination propagation in composites under high-cycle fatigue by means of cohesive-zone models, NASA/TM 214532 1–28, 2006
Turon A, Camanho P P, Costa J, Dávila C G. Mechanics of Materials, 2006, 38: 1072–1089
Turon A, Costa J, Camanho P P, Dávila C G. Composites. Part A, Applied science and manufacturing, 2008, 38: 2270–2282
Kumar S, Singh I V, Mishra B K. A homogenized XFEM approach to simulate fatigue crack growth problems. Computers & Structures, 2015, 150: 1–22
Kumar S, Singh I V, Mishra B K, Rabczuk T. Modeling and simulation of kinked cracks by virtual node XFEM. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 283: 1425–1466
Kumar S, Singh I V, Mishra B K. A multigrid coupled (FE-EFG) approach to simulate fatigue crack growth in heterogeneous materials. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 72: 121–135
Agarwal A, Singh I V, Mishra B K. Numerical prediction of elastoplastic behaviour of interpenetrating phase composites by EFGM. Composites. Part B, Engineering, 2013, 51: 327–336
Bhardwaj G, Singh I V, Mishra B K, Bui T Q. Numerical simulation of functionally graded cracked plates using NURBS based XIGA under different loads and boundary conditions. Composite Structures, 2015, 126: 347–359
Bhardwaj G, Singh I V, Mishra B K. Stochastic fatigue crack growth simulation of interfacial crack in bi-layered FGMs using XIGA. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 284: 186–229
Dugdale D S. Yielding of steel sheets containing slits. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1960, 8(2): 100–104
Barenblatt G I. The mathematical theory of equilibrium cracks in brittle fracture. Advances in Applied Mechanics, 1962, 7(C): 55–129
Bažant Z P, Jirásek M. Nonlocal integral formulations of plasticity and damage: Survey of progress. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2002, 128(11): 1119–1149
Alfano G, Crisfield M A. Finite element interface models for the delamination analysis of laminated composites: mechanical and computational issues. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2001, 50(7): 1701–1736
Fujimoto T, Kagami J, Kawaguchi T, Hatazawa T. Microdisplacement characteristics under tangential force. Wear, 2000, 241(2): 136–142
Grzemba B, Pohrt R, Teidelt E, Popov V L. Maximum micro-slip in tangential contact of randomly rough self-affine surfaces. Wear, 2014, 309(1–2): 256–258
Design M, Section C S, Technical N, Introduction I. An artificial damping method for the harmonically excited non-linear systems. 1988, 120: 597–608
Kim S. Artificial damping in multigrid methods. Applied Mathematics Letters, 2001, 14(3): 359–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dronamraju, N., Solass, J. & Hildebrand, J. Studies of fiber-matrix debonding. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 9, 448–456 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-015-0316-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-015-0316-8