Abstract
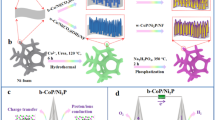
The use of two-dimensional (2D) layered metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as self-sacrificial templates has been proven to be a successful method to create high-efficiency Selenium (Se)-containing electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Herein, two strategies are then utilized to introduce Se element into the Co–Fe MOF, one being the etching of as-prepared MOF by SeO2 solution, and the other, the replacing of SCN− with SeCN− as the construction unit. The electrochemical activity of the pristine 2D MOF and their calcinated derivatives for catalyzing the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is evaluated and further discussed. It is found that the effect of introducing Se on improving electrochemical catalytic activity is significant for the HER process. Specifically, the calcinated derivative in the replacing method exhibits an overpotential of 235 mV for HER and 270 mV for OER at a current density of 10 mA/cm2. For comparing the two methods of introducing Se element into MOF, similar electrocatalytic activity can be achieved on the their calcinated derivatives. The high electrochemical performance of 2D CoFe-MOF derivatives may be resulted from the unique 2D hierarchical porous structure and strong synergistic effect between different components in the material.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan S, Zhang J, Wu Q Y, et al. Morphological and electronic dual regulation of cobalt–nickel bimetal phosphide heterostructures inducing high water-splitting performance. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2020, 11(10): 3911–3919
Feng X, Bo X, Guo L. CoM (M = Fe, Cu, Ni)-embedded nitrogen-enriched porous carbon framework for efficient oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 389: 249–259
Gao H, Yang M, Du Z J, et al. Metal-organic framework derived bimetal oxide CuCoO2 as efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(15): 5997–6006
Han L, Xu J, Huang Y, et al. High-performance electrocatalyst of vanadium-iron bimetal organic framework arrays on nickel foam for overall water splitting. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2021, 32(7): 2263–2268
He L H, Huang S J, Liu Y K, et al. Multicomponent Co9S8@MoS2 nanohybrids as a novel trifunctional electrocatalyst for efficient methanol electrooxidation and overall water splitting. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 586: 538–550
Hou J, Zhang B, Li Z, et al. Vertically aligned oxygenated-CoS2-MoS2 heteronanosheet architecture from polyoxometalate for efficient and stable overall water splitting. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(5): 4612–4621
Huang Z, Yang Z X, Hussain M Z, et al. Bimetallic Fe–Mo sulfide/carbon nanocomposites derived from phosphomolybdic acid encapsulated MOF for efficient hydrogen generation. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2021, 84: 76–85
Hu Q, Gao K, Wang X, et al. Subnanometric Ru clusters with upshifted D band center improve performance for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3958
Feng C, Lv M, Shao J, et al. Lattice strain engineering of Ni2P enables efficient catalytic hydrazine oxidation-assisted hydrogen production. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(42): 2305598
Li G, Zheng K, Li W, et al. Ultralow Ru-induced bimetal electrocatalysts with a Ru-enriched and mixed-valence surface anchored on a hollow carbon matrix for oxygen reduction and water splitting. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(46): 51437–51447
Li Y, Zhang W, Wu T, et al. Segregation induced self-assembly of highly active perovskite for rapid oxygen reduction reaction. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(29): 1801893
Xiao M, Wu C, Zhu J, et al. In situ generated layered NiFe-LDH/MOF heterostructure nanosheet arrays with abundant defects for efficient alkaline and seawater oxidation. Nano Research, 2023, 16(7): 8945–8952
Zheng Y, Li Y, Wu T, et al. Controlling crystal orientation in multilayered heterostructures toward high electro-catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy, 2019, 62: 521–529
Li F, Li Y, Chen H, et al. Impact of strain-induced changes in defect chemistry on catalytic activity of Nd2NiO4+δ electrodes. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(43): 36926–36932
Li X, Deng C, Kong Y, et al. Unlocking the transition of electrochemical water oxidation mechanism induced by heteroatom doping. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(40): e202309732
Zheng Y, Zhao C, Li Y, et al. Directly visualizing and exploring local heterointerface with high electro-catalytic activity. Nano Energy, 2020, 78: 105236
Ma Y D, Dai X P, Liu M Z, et al. Strongly coupled FeNi alloys/NiFe2O4@carbonitride layers-assembled microboxes for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(50): 34396–34404
Palani R, Anitha V, Karuppiah C, et al. Imidazolatic-framework bimetal electrocatalysts with a mixed-valence surface anchored on an rGO matrix for oxygen reduction, water splitting, and dye degradation. ACS Omega, 2021, 6(24): 16029–16042
Qiu B C, Cai L J, Wang Y, et al. Fabrication of nickel–cobalt bimetal phosphide nanocages for enhanced oxygen evolution catalysis. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(17): 1706008
Shah S S A, Jery A E, Najam T, et al. Surface engineering of MOF-derived FeCo/NC core-shell nanostructures to enhance alkaline water-splitting. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(8): 5036–5043
Luo J, Feng M, Dai Z, et al. MoS2 wrapped MOF-derived N-doped carbon nanocomposite with wideband electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Research, 2022, 15(7): 5781–5789
Wang F, Xiao Z, Liu X, et al. Strategic design of cellulose nanofibers@zeolitic imidazolate frameworks derived mesoporous carbon-supported nanoscale CoFe2O4/CoFe hybrid composition as trifunctional electrocatalyst for Zn-air battery and self-powered overall water-splitting. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 521: 230925
Wang J, Jiang Y, Liu C B, et al. In situ growth of hierarchical bimetal-organic frameworks on nickel-iron foam as robust electrodes for the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 614: 532–537
Wang Y L, Tang W J, Li X, et al. Improving the electrocatalytic activity of NiFe bimetal-organic framework toward oxygen evolution reaction by Zr doping. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 381: 138292
Wang Y, Ma J, Wang J, et al. Interfacial scaffolding preparation of hierarchical PBA-based derivative electrocatalysts for efficient water splitting. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(5): 1802939
Wei D, Tang W, Ma N, et al. NiCo bimetal organic frames derived well-matched electrocatalyst pair for highly efficient overall urea solution electrolysis. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 874: 159945
Ying M, Tang R, Yang W, et al. Tailoring electronegativity of bimetallic Ni/Fe metal-organic framework nanosheets for electrocatalytic water oxidation. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(2): 1967–1975
Yu H, Qi L, Hu Y, et al. Nanowire-structured FeP-CoP arrays as highly active and stable bifunctional electrocatalyst synergistically promoting high-current overall water splitting. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 600: 811–819
Cheng P, Wang X, Markus J, et al. Carbon nanotube-decorated hierarchical porous nickel/carbon hybrid derived from nickel-based metal-organic framework for enhanced methyl blue adsorption. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 638: 220–230
Yu J, Tian Y M, Zhou F, et al. Metallic and superhydrophilic nickel cobalt diselenide nanosheets electrodeposited on carbon cloth as a bifunctional electrocatalyst. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2018, 6(36): 17353–17360
Zhang L, Wang W, Xu G, et al. Facile synthesis of CoxFe1−xP microcubes derived from metal-organic frameworks for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 554: 202–209
Zhang L, Wang X, Li A, et al. Rational construction of macroporous CoFeP triangular plate arrays from bimetal-organic frameworks as high-performance overall water-splitting catalysts. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2019, 7(29): 17529–17535
Zhang P, Liu Y, Liang T, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon wrapped Co-Mo2C dual Mott-Schottky nanosheets with large porosity for efficient water electrolysis. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 284: 119738
Zhang T, Du J, Xi P, et al. Hybrids of cobalt/iron phosphides derived from bimetal-organic frameworks as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(1): 362–370
Wang C H, Zhang D W, Liu S, et al. Ultrathin nanosheet-assembled nickel-based metal-organic framework microflowers for supercapacitor applications. Chemical Communications, 2022, 58(7): 1009–1012
Wang J S, Yi X H, Xu X, et al. Eliminating tetracycline antibiotics matrix via photoactivated sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation process over the immobilized MIL-88A: Batch and continuous experiments. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 133213
Jadhav H S, Bandal H A, Ramakrishna S, et al. Critical review, recent updates on zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67) and its derivatives for electrochemical water splitting. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(11): 2107072
Qin R, Wang P, Li Z, et al. Ru-incorporated nickel diselenide nanosheet arrays with accelerated adsorption kinetics toward overall water splitting. Small, 2022, 18(6): 2105305
Liu Y, Zhou D, Deng T, et al. Research progress of oxygen evolution reaction catalysts for electrochemical water splitting. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(24): 5359–5383
Noor T, Yaqoob L, Iqbal N. Recent advances in electrocatalysis of oxygen evolution reaction using noble-metal, transition-metal, and carbon-based materials. ChemElectroChem, 2021, 8(3): 447–483
Li X, Zhang H, Hu Q, et al. Amorphous NiFe oxide-based nanoreactors for efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(15): e202300478
Zhao J, Zhang J J, Li Z Y, et al. Recent progress on NiFe-based electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Small, 2020, 16(51): 2003916
Zheng F, Zhang Z, Xiang D, et al. Fe/Ni bimetal organic framework as efficient oxygen evolution catalyst with low overpotential. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 555: 541–547
Zhou J, Dou Y B, He T, et al. Encapsulation of bimetallic phosphides into graphitized carbon for pH-universal hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 63: 253–261
Zhou S, Chen K, Huang J, et al. Preparation of heterometallic CoNi-MOFs-modified BiVO4: A steady photoanode for improved performance in photoelectrochemical water splitting. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 266: 118513
Zhu W, Zhu G, Yao C, et al. Porous amorphous FeCo alloys as pre-catalysts for promoting the oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 828: 154465
Li W, Zhang H, Zhang K, et al. Altered electronic structure of trimetallic FeNiCo-MOF nanosheets for efficient oxygen evolution. Chemical Communications, 2023, 59(32): 4750–4753
Mu X, Yuan H, Jing H, et al. Superior electrochemical water oxidation in vacancy defect-rich 1.5 nm ultrathin trimetal-organic framework nanosheets. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 296: 120095
Zhang L, Lu C, Ye F, et al. Selenic acid etching assisted vacancy engineering for designing highly active electrocatalysts toward the oxygen evolution reaction. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(14): 2007523
Wang Z H, Wang X F, Tan Z, et al. Polyoxometalate/metal-organic framework hybrids and their derivatives for hydrogen and oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. Materials Today. Energy, 2021, 19: 100618
Zhang Y, Wu Y, Zhong W, et al. Highly efficient sodium-ion storage enabled by an rGO-wrapped FeSe2 composite. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(5): 1336–1343
Zhou Y N, Zhu Y R, Chen X Y, et al. Carbon-based transition metal sulfides/selenides nanostructures for electrocatalytic water splitting. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 852: 156810
Ding H, Xu G, Zhang L, et al. A highly effective bifunctional catalyst of cobalt selenide nanoparticles embedded nitrogen-doped bamboo-like carbon nanotubes toward hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions based on metal-organic framework. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 566: 296–303
Fan Z S, Valentino Kaneti Y, Chowdhury S, et al. Weak base-modulated synthesis of bundle-like carbon superstructures from metal-organic framework for high-performance supercapacitors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 462: 142094
Chowdhury S, Torad N L, Ashok A, et al. Template- and etching-free fabrication of two-dimensional hollow bimetallic metal-organic framework hexagonal nanoplates for ammonia sensing. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138065
Li T M, Hu B Q, Han J H, et al. Highly effective OER electrocatalysts generated from a two-dimensional metal-organic framework including a sulfur-containing linker without doping. Inorganic Chemistry, 2022, 61(18): 7051–7059
Wang K, Wang X, Li Z, et al. Designing 3d dual transition metal electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline electrolyte: Beyond oxides. Nano Energy, 2020, 77: 105162
Jia J, Zhao X, Hu W, et al. Role of cobalt phthalocyanine on the formation of high-valent cobalt species revealed by in situ Raman spectroscopy. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2023, 11(15): 8141–8149
Liu Y, Dong S, Wang L, et al. Bimetal cobalt-zinc MOF and its derivatives as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2022, 26(10): 2301–2313
Yaqoob L, Noor T, Iqbal N, et al. Electrochemical synergies of Fe–Ni bimetallic MOF CNTs catalyst for OER in water splitting. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 850: 156583
Liu S, Xu J, Dai E, et al. Synthesis and properties of ferrocene confined within UiO-67 MOFs. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 264: 133–138
Zhao H, Li Y, Wang D, et al. Synthesis of N-doped core-shell-structured porous CoSe@C composites and their efficient catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2018, 2018(9): 1145–1151
Zhang C, Tao H, Dai Y, et al. Effect of solvent on Se-modified ruthenium/carbon catalyst for oxygen reduction. Progress in Natural Science, 2014, 24(6): 671–675
Mi Q, Zhang D, Zhang X, et al. Highly sensitive ammonia gas sensor based on metal-organic frameworks-derived CoSe2@nitrogen-doped amorphous carbon decorated with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 860: 158252
Liu S, Dong F, Tang Z, et al. The formation of wrapping type Pt-Ni alloy on three-dimensional carbon nanosheet for electrocatalytic oxidation of methanol. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(29): 15431–15441
Kang Z, Lin E, Qin N, et al. Effect of oxygen vacancies and crystal symmetry on piezocatalytic properties of Bi2WO6 ferroelectric nanosheets for wastewater decontamination. Environmental Science. Nano, 2021, 8(5): 1376–1388
Shwetharani R, Nagaraju D H, Balakrishna R G, et al. Hydrogenase enzyme like nanocatalysts FeS2 and FeSe2 for molecular hydrogen evolution reaction. Materials Letters, 2019, 248: 39–42
Tripathy R K, Samantara A K, Mane P, et al. Cobalt metal organic framework (Co-MOF) derived CoSe2/C hybrid nanostructures for the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction supported by DFT studies. New Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 46(6): 2730–2738
Theerthagiri J, Sudha R, Premnath K, et al. Growth of iron diselenide nanorods on graphene oxide nanosheets as advanced electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(18): 13020–13030
Liu X B, Liu Y C, Fan L Z. MOF-derived CoSe2 microspheres with hollow interiors as high-performance electrocatalysts for the enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2017, 5(29): 15310–15314
Li Z, Jiang Z, Zhu W, et al. Facile preparation of CoSe2 nano-vesicle derived from ZIF-67 and their application for efficient water oxidation. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 504: 144368
Li G, Yin F, Lei Z, et al. Se-doped cobalt oxide nanoparticle as highly-efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(1): 216–227
Pandit M A, Hemanth Kumar D S, Ramadoss M, et al. Template free-synthesis of cobalt-iron chalcogenides [Co0.8Fe0.2L2, L = S, Se] and their robust bifunctional electrocatalysis for the water splitting reaction and Cr(vi) reduction. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(13): 7762–7772
Wei G, Du K, Zhao X, et al. Cable-like carbon nanotubes decorated metal-organic framework derived ultrathin CoSe2/CNTs nanosheets for electrocatalytic overall water splitting. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2020, 31(10): 2641–2644
Park C E, Senthil R A, Jeong G H, et al. Architecting the high-entropy oxides on 2D MXene nanosheets by rapid microwave-heating strategy with robust photoelectrochemical oxygen evolution performance. Small, 2023, 19(27): 2207820
Gao Y, Wu Y, He H, et al. Potentiostatic electrodeposition of Ni–Se–Cu on nickel foam as an electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 578: 555–564
Shabik M F, Hasan M M, Alamry K A, et al. Electrocatalytic oxidation of ammonia in the neutral medium using Cu2O. CuO film immobilized on glassy carbon surface. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2021, 897: 115592
Schumacher S, Madauß L, Liebsch Y, et al. Revealing the heterogeneity of large-area MoS2 layers in the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9(17): e202200586
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22250710676), the Excellent Discipline Cultivation Project of Jianghan University, China (No. 2023XKZ039), the Fundamental Research Funds for State Key Laboratory of Precision Blasting of Jianghan University, China (No. PBSKL2022202), and the Minjiang Scholar Program of Fujian Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic Supplementary Material
11708_2024_924_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supporting Information: Two-Dimensional Bimetallic Selenium-Containing Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Calcinated Derivatives as Electrocatalysts for Overall Water Splitting
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, Zt., Li, Tm., Hu, Bq. et al. Two-dimensional bimetallic selenium-containing metal-organic frameworks and their calcinated derivatives as electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Front. Energy (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-024-0924-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-024-0924-x