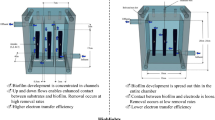
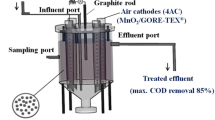
Abstract
To examine the impact of wastewater volume on the ionic strength of an electron acceptor, the performance of a 1000 mL multi (4)-anode shared single cathode MFC (MFC 1) was investigated and its performance was compared to two 250 mL standard single anode/cathode MFCs, the first (MFC 2) with the same cathode surface area as MFC 1: 84cm2 and the second (MFC 3) with 42cm2. The performance of the MFCs was evaluated under high and low external resistances to elucidate the differences in MFCs’ performance. MFC 2 (4.36 mW/cm2 at 0.0102 mA/cm2) produced 2.8-times and 1.02-times higher in power density than that of MFC 1 and MFC 3, respectively. The multi (4)-anode shared cathode MFC (MFC 1) produced the lowest internal resistance (100 Ω), which was more than 3-times lower than MFC 2 and MFC 3. At the lower external resistance of 100 Ω, a more distinct difference between the multi-anode shared cathode MFC and the single anode/cathode MFCs was revealed in continuous current and power generation (1.2 mA and 153.76 mW), which were 1.7-times and 2.7-times than that of MFC 2 and MFC 3, respectively. MFC 1 also attained a 1.1-times higher COD removal efficiency and treated 1000 mL of wastewater without any significant difference in anolyte/catholyte conductivity and pH, compared to MFC 2 and MFC 3 which only treated 250 mL of wastewater over the same time. To deplete the cationic conductivity of the shared single cathode in MFC 1, an estimated 7.945 mL of wastewater is required.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials will be made available on request.
Abbreviations
- MFC:
-
Microbial fuel cell
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- MFC 1:
-
4-anode/1-shared cathode (84cm2) MFC
- MFC 2:
-
1-anode/1-cathode (84cm2) MFC
- MFC 3:
-
1-anode/1-cathode (42cm2) MFC
- EC:
-
Electrical conductivity
- OECD:
-
Organization for economic cooperation and development
- A:
-
Anode
- An:
-
n th number of the anode electrode
- MFC 1-A1:
-
Anode 1 of MFC 1
References
Aelterman P, Versichele M, Marzorati M et al (2008) Loading rate and external resistance control the electricity generation of microbial fuel cells with different three-dimensional anodes. Bioresour Technol 99:8895–8902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.04.061
AGENCY E (2007) The determination of chemical oxygen demand in waters and effluents. Harper et al.-Environ Agency
Arkatkar A, Mungray AK, Sharma P (2021) Biological modification in air-cathode microbial fuel cell: Effect on oxygen diffusion, current generation and wastewater degradation. Chemosphere 284:131243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131243
Behera M, Ghangrekar MM (2009) Performance of microbial fuel cell in response to change in sludge loading rate at different anodic feed pH. Bioresour Technol 100:5114–5121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.05.020
Beliaev AS, Klingeman DM, Klappenbach JA et al (2005) Global transcriptome analysis of shewanella oneidensis MR-1 exposed to different terminal electron acceptors. J Bacteriol 187:7138–7145. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.20.7138-7145.2005
Bennetto HP, Stirling JL, Tanaka K, Vega CA (1983) Anodic reactions in microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 25:559–568. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260250219
Cai J, Zheng P, Mahmood Q (2016) Effect of cathode electron acceptors on simultaneous anaerobic sulfide and nitrate removal in microbial fuel cell. Water Sci Technol 73:947–954. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.570
Chaudhuri SK, Lovley DR (2003) Electricity generation by direct oxidation of glucose in mediatorless microbial fuel cells. Nat Biotechnol 21:1229–1232. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt867
Clauwaert P, Aelterman P, Pham TH et al (2008) Minimizing losses in bio-electrochemical systems: the road to applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:901–913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1522-2
Dykstra CM, Pavlostathis SG (2017) Methanogenic biocathode microbial community development and the role of bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 51:5306–5316. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04112
Erable B, Féron D, Bergel A (2012) Microbial catalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction for microbial fuel cells: a review. ChemSusChem 5:975–987. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201100836
Feng Y, He W, Liu J et al (2014) A horizontal plug flow and stackable pilot microbial fuel cell for municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 156:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.104
González Del Campo A, Cañizares P, Rodrigo MA et al (2013) Microbial fuel cell with an algae-assisted cathode: a preliminary assessment. J Power Sources 242:638–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.05.110
Guo F, Fu G, Zhang Z (2015) Performance of mixed-species biocathode microbial fuel cells using saline mustard tuber wastewater as self-buffered catholyte. Bioresour Technol 180:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.113
Hl Ã, Parameswaran P, Kato-marcus A et al (2008) Evaluation of energy-conversion efficiencies in microbial fuel cells ( MFCs ) utilizing fermentable and non-fermentable substrates. Water Res 42:1501–1510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.036
Hoang AT, Nižetić S, Ng KH et al (2022) Microbial fuel cells for bioelectricity production from waste as sustainable prospect of future energy sector. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132285
Huang S, Zhu G, Gu X (2020) The relationship between energy production and simultaneous nitrification and denitrification via bioelectric derivation of microbial fuel cells at different anode numbers. Environ Res 184:109247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109247
Huang J, Opoku PA, Guang L et al (2021) A multi-emission analysis of organic and inorganic pollutants during the combustion of sludge with high and low calorific value coals. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:65399–65409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15301-7
Jadhav GS, Ghangrekar MM (2009) Performance of microbial fuel cell subjected to variation in pH, temperature, external load and substrate concentration. Bioresour Technol 100:717–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.041
Jang JK, Pham TH, Chang IS et al (2004) Construction and operation of a novel mediator- and membrane-less microbial fuel cell. Process Biochem 39:1007–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00203-6
Jiang D, Li X, Raymond D et al (2010) Power recovery with multi-anode/cathode microbial fuel cells suitable for future large-scale applications. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:8683–8689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.04.136
Jiang Y, Liang P, Liu P et al (2017) A cathode-shared microbial fuel cell sensor array for water alert system. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42:4342–4348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.12.050
Jingyu H, Ewusi-Mensah D, Norgbey E (2017) Microbial desalination cells technology: a review of the factors affecting the process, performance and efficiency. Desalin Water Treat 87:140–159. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.21302
Jung S, Regan JM (2007) Comparison of anode bacterial communities and performance in microbial fuel cells with different electron donors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:393–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1162-y
Jung S, Regan JM (2011) Influence of external resistance on electrogenesis, methanogenesis, and anode prokaryotic communities in microbial fuel cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01392-10
Katuri KP, Scott K, Head IM et al (2011) Microbial fuel cells meet with external resistance. Bioresour Technol 102:2758–2766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.147
Kim JR, Premier GC, Hawkes FR et al (2010) Modular tubular microbial fuel cells for energy recovery during sucrose wastewater treatment at low organic loading rate. Bioresour Technol 101:1190–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.023
Koók L, Rózsenberszki T, Nemestóthy N et al (2016) Bioelectrochemical treatment of municipal waste liquor in microbial fuel cells for energy valorization. J Clean Prod 112:4406–4412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.116
Kumar SS, Basu S, Bishnoi NR (2017) Effect of cathode environment on bioelectricity generation using a novel consortium in anode side of a microbial fuel cell. Biochem Eng J 121:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2017.01.014
Lawson K, Rossi R, Regan JM, Logan BE (2020) Impact of cathodic electron acceptor on microbial fuel cell internal resistance. Bioresour Technol 316:123919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123919
Li Z, Yao L, Kong L, Liu H (2008) Electricity generation using a baffled microbial fuel cell convenient for stacking. Bioresour Technol 99:1650–1655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.003
Liu H, Logan B (2004) Electricity generation using an air-cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell (MFC) in the presence and absence of a proton exchange membrane. ACS Natl Meet B Abstr 228:4040–4046
Logan BE (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:375–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2113
Logan BE, Rabaey K (2012) Conversion of wastes into bioelectricity and chemicals by using microbial electrochemical technologies. Science 337(6095):686–690. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1217412
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R et al (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40:5181–5192. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0605016
Logan BE, Rossi R, Ragab A, Saikaly PE (2019) Electroactive microorganisms in bioelectrochemical systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 17:307–319. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0173-x
Mateo S, Cañizares P, Fernandez-Morales FJ, Rodrigo MA (2018) A critical view of microbial fuel cells: what is the next stage? ChemSusChem 11:4183–4192. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201802187
Mathuriya AS (2016) Novel microbial fuel cell design to operate with different wastewaters simultaneously. J Environ Sci (China) 42:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.06.014
Mathuriya AS, Jadhav DA, Ghangrekar MM (2018) Architectural adaptations of microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:9419–9432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9339-0
Mclean JS, Wanger G, Gorby YA et al (2010) Quantification of electron transfer rates to a solid phase electron acceptor through the stages of biofilm formation from single cells to multicellular communities. Environ Sci Technol 44:2721–2727. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903043p
Menicucci J, Beyenal H, Marsili E et al (2006) Procedure for determining maximum sustainable power generated by microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40:1062–1068. https://doi.org/10.1021/es051180l
Nielsen ME, Reimers CE, Stecher HA (2007) Enhanced power from chambered benthic microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 41:7895–7900. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071740b
Norgbey E, Li Y, Ya Z et al (2020) High resolution evidence of iron-phosphorus-sulfur mobility at hypoxic sediment water interface: an insight to phosphorus remobilization using DGT-induced fluxes in sediments model [J]. Sci Total Environ 724:138204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138204
Oh S, Min B, Logan BE (2004) Cathode performance as a factor in electricity generation in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 38:4900–4904. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049422p
Opoku PA, Jingyu H, Yi L et al (2022) Scaled-up multi-anode shared cathode microbial fuel cell for simultaneous treatment of multiple real wastewaters and power generation. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134401
Pham TH, Rabaey K, Aelterman P et al (2006) Microbial fuel cells in relation to conventional anaerobic digestion technology. Eng Life Sci 6:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200620121
Picioreanu C, Head IM, Katuri KP et al (2007) A computational model for biofilm-based microbial fuel cells. Water Res 41:2921–2940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.04.009
Pinto RP, Srinivasan B, Uiot SR, Tartakovsky B (2011) The effect of real-time external resistance optimization on microbial fuel cell performance. Water Res 45:1571–1578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.11.033
Potrykus S, León-Fernández LF, Nieznański J et al (2021) The influence of external load on the performance of microbial fuel cells. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14030612
Rabaey K, Clauwaert P, Aelterman P, Verstraete W (2005) Tubular microbial fuel cells for efficient electricity generation. Environ Sci Technol 39:8077–8082. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050986i
Ren Z, Yan H, Wang W et al (2011) Characterization of microbial fuel cells at microbially and electrochemically meaningful time scales. Environ Sci Technol 45:2435–2441. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103115a
Rismani-Yazdi H, Carver SM, Christy AD, Tuovinen OH (2008) Cathodic limitations in microbial fuel cells: an overview. J Power Sources 180:683–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.02.074
Rismani-Yazdi H, Christy AD, Carver SM et al (2011) Effect of external resistance on bacterial diversity and metabolism in cellulose-fed microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102:278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.012
Rozendal RA, Hamelers HVM, Buisman CJN (2006) Effects of membrane cation transport on pH and microbial fuel cell performance. Environ Sci Technol 40:5206–5211. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060387r
Samsudeen N, Sharma A, Radhakrishnan TK, Matheswaran M (2015) Performance investigation of multi-chamber microbial fuel cell: an alternative approach for scale up system. J Renew Sustain Energy. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4923393
Shah KJ (2021) Advances in wastewater treatment I. Introduction to conventional wastewater treatment technologies : limitations and recent advances, 91st edn. Materials Research Forum LLC, Millersville, USA
Sharma T, Mohana Reddy AL, Chandra TS, Ramaprabhu S (2008) Development of carbon nanotubes and nanofluids based microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 33:6749–6754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.05.112
Sonawane JM, Gupta A, Ghosh PC (2013) Multi-electrode microbial fuel cell (MEMFC): a close analysis towards large scale system architecture. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38:5106–5114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.02.030
Song TS, Yan ZS, Zhao ZW, Jiang HL (2010) Removal of organic matter in freshwater sediment by microbial fuel cells at various external resistances. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:1489–1493. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2454
Torres CI, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Parameswaran P et al (2009) Selecting anode-respiring bacteria based on anode potential: phylogenetic, electrochemical, and microscopic characterization. Environ Sci Technol 43:9519–9524. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902165y
Torres CI, Marcus AK, Lee HS et al (2010) A kinetic perspective on extracellular electron transfer by anode-respiring bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00191.x
Vologni V, Kakarla R, Angelidaki I, Min B (2013) Increased power generation from primary sludge by a submersible microbial fuel cell and optimum operational conditions. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0918-2
Water U (2015) A UN-Water Analytical Brief
Wei J, Liang P, Huang X (2011) Recent progress in electrodes for microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102:9335–9344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.019
Wei L, Han H, Shen J (2012) Effects of cathodic electron acceptors and potassium ferricyanide concentrations on the performance of microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:12980–12986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.05.068
Yazdi H, Alzate-Gaviria L, Ren ZJ (2015) Pluggable microbial fuel cell stacks for septic wastewater treatment and electricity production. Bioresour Technol 180:258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.12.100
You S, Zhao Q, Zhang J et al (2006) A microbial fuel cell using permanganate as the cathodic electron acceptor. J Power Sources 162:1409–1415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.07.063
Zhang L, Zhu X, Li J et al (2011) Biofilm formation and electricity generation of a microbial fuel cell started up under different external resistances. J Power Sources 196:6029–6035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.04.013
Zhang X, Shi J, Liang P et al (2013) Power generation by packed-bed air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 142:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.05.014
Zhang J, Li Z, Cui X et al (2020) Effect of external resistance on denitrification and electricity generation performance of double-cathode microbial fuel cell. Chinese J Environ Eng 14:1762–1770. https://doi.org/10.12030/j.cjee.201909114
Zhu G, Huang S, Lu Y, Gu X (2019) Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in the bio-cathode of a multi-anode microbial fuel cell. Environ Technol (UK) 0:1–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1663938
Acknowledgment
We thank Assoc. Prof. Huang Jingyu and Dr. Li Guang for the provision of a laboratory space and materials during the COVID pandemic for the successful completion of these experiments.
Funding
This research was supported by Haijian Environmental Engineering & Design Co. Ltd., Changchun.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PAO and LG were involved in data curation. PAO was involved in writing—original draft. LG, JH, HJ and EN were involved in writing—review & editing. JH performed methodology and software. HJ was involved in formal analysis, visualization and supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript for publication.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Opoku, P.A., Guang, L., Huang, J. et al. Impact of wastewater volume on cathode environment of the multi-anode shared cathode and standard single anode/cathode microbial fuel cells. Chem. Pap. 76, 6309–6321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02316-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02316-8