Abstract
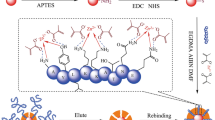
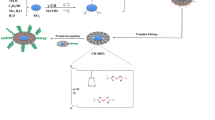
A kind of surface imprinted particles was synthesized to recognize cytochrome c (Cyt c) by a novel strategy combining reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) radical polymerization and epitope surface imprinting. N-terminal epitope nonapeptide of Cyt c was chosen as the template. The selectivity of these particles for protein recognition was obviously improved due to the selection of epitopes rather than the whole protein as templates and the controllable length of polymer shell chain. After epitope had been modified on the surface of silica, the surface imprinted polymer with controlled imprinted layer was synthesized with monomers and cross-linkers by RAFT radical polymerization strategy. The epitope surface imprinted particles were obtained after the peptide removed and trithioester group destruction by hexylamine. The binding capacity of N-terminal peptide reached 1.88 mg peptide per gram with imprinting factor (IF) as 2.42 while the binding capacity of Cyt c reached 8.89 mg protein per gram with IF as 1.71, which were obviously higher than the IF of the material without RAFT strategy. Moreover, Cyt c could be selectively recognized by the epitope surface imprinted particles even in presence of the competitive proteins with different molecular weight and isoelectric point. The performance of protein recognition remained 90% after five cycles of adsorption and desorption. All these results demonstrated that the epitope surface imprinted particles prepared by RAFT strategy are promising to achieve the protein recognition with higher recognition ability, selectivity and reusability.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartold K, Pietrzyk-Le A, Golebiewska K, Lisowski W, Cauteruccio S, Licandro E, D’Souza F, Kutner W (2018) Oligonucleotide determination via peptide nucleic acid macromolecular imprinting in an electropolymerized CG-rich artificial oligomer analogue. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(33):27562–27569. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b09296
Capriotti A, Piovesana S, Zenezini Chiozzi R, Montone CM, Bossi AM, Lagana A (2020) Does the protein corona take over the selectivity of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles? The biological challenges to recognition. J Proteomics 219:103736–103747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103736
Chen L, Wang X, Lu W, Wu X, Li J (2016) Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem Soc Rev 45(8):2137–2211. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00061d
Farooq S, Nie J, Cheng Y, Yan Z, Li J, Bacha SAS, Mushtaq A, Zhang H (2018) Molecularly imprinted polymers’ application in pesticide residue detection. Analyst 143(17):3971–3989. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an00907d
Gao R, Mu X, Hao Y, Zhang L, Zhang J, Tang Y (2014) Combination of surface imprinting and immobilized template techniques for preparation of core-shell molecularly imprinted polymers based on directly amino-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. J Mater Chem B 2(12):1733–1741. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb21684e
Gonzato C, Courty M, Pasetto P, Haupt K (2011) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposites via surface-initiated RAFT polymerization. Adv Func Mater 21(20):3947–3953. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201100466
Haupt K, Linares AV, Bompart M, Bui BT (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymers. Top Curr Chem 325:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/128_2011_307
Li Y, Li X, Chu J, Dong CK, Qi JK, Yuan YX (2010) Synthesis of core-shell magnetic molecular imprinted polymer by the surface RAFT polymerization for the fast and selective removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals from aqueous solutions. Environ Pollut 158(6):2317–2323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.02.007
Li Q, Yang K, Liang Y, Jiang B, Liu J, Zhang L, Liang Z, Zhang Y (2014) Surface protein imprinted core-shell particles for high selective lysozyme recognition prepared by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer strategy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(24):21954–21960. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5072783
Li S, Yang K, Liu J, Jiang B, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2015) Surface-imprinted nanoparticles prepared with a His-tag-anchored epitope as the template. Anal Chem 87(9):4617–4620. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5047246
Liu H, Yang F, Zheng Y, Kang J, Qu J, Chen J (2011) Improvement of metal adsorption onto chitosan/Sargassum sp. composite sorbent by an innovative ion-imprint technology. Water Res 45(1):145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.017
Liu J, Yang K, Qu Y, Li S, Wu Q, Liang Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2015) An efficient approach to prepare boronate core-shell polymer nanoparticles for glycoprotein recognition via combined distillation precipitation polymerization and RAFT media precipitation polymerization. Chem Commun 51(18):3896–3898. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc10004b
Lu X, Zheng C, Zhang H (2019) Improvement of surface hydrophilicity and biological sample-compatibility of molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres by facile surface modification with alpha-cyclodextrin. Eur Polymer J 115:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.02.044
Min Y, Jiang B, Wu C, Xia S, Zhang X, Liang Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2014) 1.9 mum superficially porous packing material with radially oriented pores and tailored pore size for ultra-fast separation of small molecules and biomolecules. J Chromatogr A 1356:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.06.049
Nematollahzadeh A, Sun W, Aureliano CS, Lutkemeyer D, Stute J, Abdekhodaie MJ, Shojaei A, Sellergren B (2011) High-capacity hierarchically imprinted polymer beads for protein recognition and capture. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50(2):495–498. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201004774
Nicolas J, Guillaneuf Y, Lefay C, Bertin D, Gigmes D, Charleux B (2013) Nitroxide-mediated polymerization. Prog Polym Sci 38(1):63–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2012.06.002
Pan G, Shinde S, Yeung S, Jakstaite M, Li Q, Wingren AG, Sellergren B (2017) An epitope-imprinted biointerface with dynamic bioactivity for modulating cell-biomaterial interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56(50):15959–15963. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201708635
Qu Y, Qin L, Liu X, Yang Y (2020) Reasonable design and sifting of microporous carbon nanosphere-based surface molecularly imprinted polymer for selective removal of phenol from waste water. Chemosphere 251:126376–126385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126376
Rachkov A, Minoura N (2001) Towards molecularly imprinted polymers selective to peptides and proteins. The epitope approach. Biochem Biophys Acta 1544(1–2):255–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-4838(00)00226-0
Semsarilar M, Perrier S (2010) “Green” reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) polymerization. Nat Chem 2(10):811–820. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.853
Shiomi T, Matsui M, Mizukami F, Sakaguchi K (2005) A method for the molecular imprinting of hemoglobin on silica surfaces using silanes. Biomaterials 26(27):5564–5571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.02.007
Shipp DA (2005) Living radical polymerization: controlling molecular size and chemical functionality in vinyl polymers. J Macromol Sci Part C 45(2):171–194. https://doi.org/10.1081/mc-200055484
Soylemes MA, Guven O, Barsbay M (2018) Method for preparing a well-defined molecularly imprinted polymeric system via radiation-induced RAFT polymerization. Eur Polymer J 103:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.03.037
Tang A, Duan L, Liu M, Dong X (2016) An epitope imprinted polymer with affinity for kininogen fragments prepared by metal coordination interaction for cancer biomarker analysis. J Mater Chem B 4(46):7464–7471. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tb02215d
Whitcombe MJ, Kirsch N, Nicholls IA (2014) Molecular imprinting science and technology: a survey of the literature for the years 2004–2011. J Mol Recognit 27(6):297–401. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2347
Yang K, Zhang L, Liang Z, Zhang Y (2012) Protein-imprinted materials: rational design, application and challenges. Anal Bioanal Chem 403(8):2173–2183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5840-y
Yang K, Li S, Liu L, Chen Y, Zhou W, Pei J, Liang Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2019a) Epitope imprinting technology: progress, applications, and perspectives toward artificial antibodies. Adv Mater 31(50):e1902048. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201902048
Yang K, Li S, Liu L, Chen Y, Zhou W, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2019b) Recent advances and application of epitope imprinted materials. Chin Sci Bull 64(13):1368–1379. https://doi.org/10.1360/n972018-01033
Yang X, Sun Y, Xiang Y, Qiu F, Fu G (2019c) Controlled synthesis of PEGylated surface protein-imprinted nanoparticles. Analyst 144(18):5439–5448. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an01221d
Zahedi P, Ziaee M, Abdouss M, Farazin A, Mizaikoff B (2016) Biomacromolecule template-based molecularly imprinted polymers with an emphasis on their synthesis strategies: a review. Polym Adv Technol 27(9):1124–1142. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.3754
Zang H, Zhang Y, Wang H, Wen H, Yan Z, Huang A, Bie Z, Chen Y (2020) Preparing molecularly imprinted nanoparticles of saponins via cooperative imprinting strategy. J Sep Sci 43(11):2162–2171. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202000019
Zhang Y, Deng C, Liu S, Wu J, Chen Z, Li C, Lu W (2015) Active targeting of tumors through conformational epitope imprinting. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54(17):5157–5160. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201412114
Zhang M, He J, Shen Y, He W, Li Y, Zhao D, Zhang S (2018) Application of pseudo-template molecularly imprinted polymers by atom transfer radical polymerization to the solid-phase extraction of pyrethroids. Talanta 178:1011–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.100
Zhang N, Zhang N, Xu Y, Li Z, Yan C, Mei K, Ding M, Ding S, Guan P, Qian L, Du C, Hu X (2019) Molecularly imprinted materials for selective biological recognition. Macromol Rapid Commun 40(17):e1900096. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.201900096
Zhao X, Li D, He X, Li W, Zhang Y (2014) An epitope imprinting method on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles for specific recognition of bovine serum album. J Mater Chem B 2(43):7575–7582. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tb01381f
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21804099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Lin, M., Zhang, H. et al. N-terminal epitope surface imprinted particles for high selective cytochrome c recognition prepared by reversible addition- fragmentation chain transfer strategy. Chem. Pap. 76, 3937–3947 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02134-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02134-y