Abstract
Aim
The objective of this study is to compare 3-year follow-up results of one anastomosis gastric bypass (MGB-OAGB) and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) in terms of weight loss, complications, resolution of comorbidities and quality of life.
Materials and Methods
A prospective randomised study of results between 100 LSG patients and 101 MGB-OAGB patients was done from 2012 to 2015. The results were compared regarding operative outcomes, percentage of excess weight loss (%EWL), complications, resolution of comorbidities and quality of life (BAROS score) at 3 years follow-up.
Results
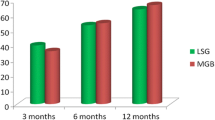
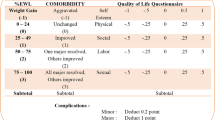
Follow-up was achieved in 93 MGB-OAGB vs 92 LSG patients for 3-year period. The average %EWL for MGB-OAGB vs LSG was 66.48 vs 61.15% at the end of 3 years respectively, which was statistically insignificant. Diabetes remission was seen in 89.13% of MGB-OAGB patients and 81.82% of LSG patients. Remission of hypertension was seen in 74% of MGB-OAGB patients and 72.22% of LSG patients. Bariatric analysis reporting and outcome system (BAROS) with comorbidity in LSG patients and MGB-OAGB patients was 6.03 and 6.96 respectively, whereas in patients without comorbidity, BAROS score was 3.86 in LSG group and 4.34 in MGB-OAGB group.
Conclusions
In our study, at 36 months follow up, there was no significant difference between LSG and MGB-OAGB in %EWL and remission of HTN. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remission rates were higher after MGB-OAGB as compared to LSG but the difference was statistically insignificant. MGB-OAGB patients with comorbidities have a better quality of life and BAROS score compared to LSG patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA: J Am Med Assoc. 2004;292(14):1724–37.
LeeWJ, Huang MT, Wang W et al. Effects of obesity surgery on the metabolic syndrome. Arch Surg 2004;139(10):1088–1092.
Sjostrom L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M, et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(26):2683–93.
Kular KS, Manchanda N, Cheema GK. Seven years of mini-gastric bypass in type II diabetes patients with a body mass index <35 kg/m2. Obes Surg. 2016;26(7):1457–62.
Mahawar KK, Jennings N, Rown J, et al. Mini gastric bypass: systematic review of a controversial procedure. Obesity Surg. 2013;23(11):1890–8.
Kular KS, Manchanda N, Rutledge R. Analysis of the five-year outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy and mini gastric bypass: a report from the Indian sub-continent. Obes Surg. 2014;24:1724–8.
Baltasar A, Serra C, Perez N, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: a multi-purpose bariatric operation. Obes Surg. 2005;15(8):1124–8.
Eid GM, Brethauer S, Mattar SG, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for super obese patients: forty-eight percent excess weight loss after 6 to 8 years with 93%follow-up. Ann Surg. 2012;256(2):262–5.
Sanchez-Santos R, Masdevall C, Baltasar A, et al. Short- and midterm outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy for morbid obesity: the experience of the Spanish National Registry. Obes Surg. 2009;19(9):1203–10.
Kueper MA, Kramer KM, Kirschniak A, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: standardized technique of a potential standalone bariatric procedure in morbidly obese patients. World J Surg. 2008;32(7):1462–5.
Angrisani L, Santonicola A, Iovino P et al. Bariatric surgery worldwide 2013. Obes Surg 25(10):1822–1832.
Stroh C, Weiner R, Horbach T, et al. Kompetenznetz Adipositas, Arbeitsgruppe Adipositaschirurgie. New data on quality assurance in bariatric surgery in Germany. Zentralbl Chir. 138:180–8.
Magouliotis DE, S V, et al. One-anastomosis gastric bypass versus sleeve gastrectomy for morbid obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2017; https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-017-2807-2.
Boza C, Gamboa C, Salinas J, et al. Laparoscopic roux–en–Y gastric bypass vs laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and: a case control study and 3 years of follow up. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2012;8:243–9.
Rutledge R. The mini-gastric bypass: experience with the 1,274 cases. Obes Surg. 2001;11:276–80.
Noun R, Zeidan S. Laparoscopic mini-gastric bypass: an effective option for the treatment ofmorbid obesity. J Chir (Paris). 2007;144:301–4.
Wang W, Wei PL, Lee YC, et al. Short-term results of laparoscopic mini-gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2005;15:648–54.
Jammu GS, Sharma R. A 7-year clinical audit of 1107 cases comparing sleeve gastrectomy, roux-En-Y gastric bypass, and mini-gastric bypass, to determine an effective and safe bariatric and metabolic procedure. Obes Surg. 2016;26:926–32.
Quan Y, Huang A, Ye M, et al. Efficacy of laparoscopic mini gastric bypass for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;152852
Shivakumar S, Tantia O, et al. LSG vs MGB-OAGB—1 year follow-up data—a randomized control trial 2016. Obes Surg. 2017;27:948–54.
Oria HE, Moorehead MK. Bariatric analysis and reporting outcome system (BAROS). Obes Surg. 1998;8:487–99.
Buse JB, Caprio S, Cefalu WT, et al. How do we define cure of diabetes? Diabetes Care. 2009;32(11):2133–5.
Benaiges D, Sagué M, Roux JAF-L, et al. Predictors of hypertension remission and recurrence after bariatric surgery. Am J Hypertens. May 2016;29(5):653–9.
Kothari A, Kanojiya R, et al. Comparison between laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) and mini gastric bypass (MGB-OAGB) for remission of type II diabetes mellitus in morbidly obese patients. IJSR Vol 6 Issue. Apr 2017:4.
Moszkowicz D, Arienzo R, Khettab I, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy severe complications: is it always a reasonable surgical option? Obes Surg. 2013;23(5):676–86.
Chevallier JM, Chakhtoura G, Zinzindohoué F. Laparoscopic minigastric bypass. J Chir (Paris). 2009;146(1):60–4.
Tacchino RM, Greco F, Matera D, et al. Single-incision laparoscopic gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2010;20(8):1154–60.
LeeWJ YPJ, Wang W, et al. Laparoscopic roux-en-Y versus minigastric bypass for the treatment of morbid obesity. Ann Surg. 2005;242:20–8.
Noun R, Skaff J, Riachi E, et al. One thousand consecutive minigastric bypass: short and long-term outcome. Obes Surg. 2012;22(5):697–703.
Rutledge R, Walsh W. Continued excellent results with the minigastric bypass: six-year study in 2,410 patients. Obes Surg. 2005;15(9):1304–8.
Madhok B, Mahawar KK, Boyle M, et al. Management of super-super obese patients: comparison between mini (one anastomosis) gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2016;26:1646–9.
Plamper A, Lingohr P, Nadal J, et al. Comparison of mini-gastric bypass with sleeve gastrectomy in a mainly super-obese patient group: first results. Surg Endosc. 2017;31:1156–62.
Magouliotis DE, Tasiopoulou VS, Sioka E, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for morbid obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2017;27:245–53.
Piazza L, Ferrara F, Leanza S, et al. A laparoscopic mini-gastric bypass: short-term single-institute experience. Updat Surg. 2011;63(4):239–42.
Carbajo M, García-Caballero M, Toledano M, et al. One-anastomosis gastric bypass by laparoscopy: results of the first 209 patients. Obes Surg. 2005;15(3):398–404.
Felsenreich DM, Langer FB, Kefurt R, et al. Weight loss, weight regain and conversions to roux-en-Y gastric bypass—10-year results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Obes Relat Disease. 2016;12(9):1655–62.
Liou TH, Chen HH, Wang W, et al. ESR1, FTO, and UCP2 genes interact with bariatric surgery affecting weight loss and glycemic control in severely obese patients. Obes Surg. 2011;21(11):1758–65.
Wang W, Liou TH, Lee WJ, et al. ESR1 gene and insulin resistance remission are associated with serum uric acid decline for severely obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014;10(1):14–22.
Himpens J, Dobbeleir J, Peeters G. Long-term results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity. Ann Surg. 2010;252:319–24.
Bruzzi M, Rau C, Voron T, et al. Single anastomosis or mini-gastric bypass: long-term results and quality of life after a 5-year follow-up. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015;11:321–6.
Pok E-H, Lee WJ, Ser KH, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in Asia: long term outcome and revisional surgery. Asian Journal of Surgery. 2016;39(1):21–8.
Lee WJ, Ser KH, Lee YC, et al. Laparoscopic roux-en-Y vs. minigastric bypass for the treatment of morbid obesity: a 10-year experience. Obes Surg. 2012;22(12):1827–34.
Cummings DE, Overduin J, Shannon MH, et al. Hormonal mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution after bariatric surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2005;1(3):358–68.
Bohdjalian A, Langer FB, Shakeri-Leidenmuhler S, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy as sole and definitive bariatric procedure: 5-year results for weight loss and ghrelin. Obes Surg. 2010;20:535–40.
Acknowledgements
We extend our heartfelt gratitude to Dr. Aruna Tantia, Dr. Pramod Sureka, Dr. Ramanuj Mukherjee, Dr. Abhijit Hazra, Dr. Bimalendu Sen, Dr. Debjit Ghosh, Ram Sundar Bhandari, OT staffs, Shampa Ghosh, Jhuma Chowdhury, Sonam Gupta and Hanie Gupta who have worked hard to make this project a success. The staffs of ILS Hospital deserve a special mention for their dedicated support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shivakumar, S., Tantia, O., Goyal, G. et al. LSG vs MGB-OAGB—3 Year Follow-up Data: a Randomised Control Trial. OBES SURG 28, 2820–2828 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3255-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3255-3
Keywords
- One anastomosis gastric bypass (MGB-OAGB)
- Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG)
- Bariatric analysis reporting and outcome system (BAROS)
- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Percentage excess weight loss (%EWL)
- Percentage actual weight loss (%AWL)
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM)
- Hypertension (HTN)
- Randomised control trial (RCT)
- Roux-En-Y gastric bypass (RYGB)
- Quality of life (QOL)